
Getty Images/iStockphoto
Avoid overprovisioning in cloud computing with tracking
A lack of visibility means organizations can easily lose unused resources which rack up costs. However, there are tools and best practices that can help set up a tracking system.
Overprovisioning is a common mistake in cloud. The more you overprovision and the more unused resources that sit in the background, the more your cloud bill grows.
A key aspect to manage overprovisioning, as well as deprovisioning, is tracking historical cloud usage. If historical usage data is not on hand, it may take three or more months to gather this data. This data is crucial for a successful cost optimization strategy.
Top best practices to tracking overprovisioned cloud resources include the following:
- Regularly monitor. Monitor for resource utilization, including CPU, memory, disk space and network bandwidth, for patterns of overprovisioning.
- Implement automation tools. These tools can monitor and manage resources to use autoscaling to adjust resources based on workload demands.
- Institute regular capacity planning exercises. Understand your future workload demands, and ensure that your cloud teams are provisioning resources accordingly through these exercises.
- Implement a cloud cost optimization tool. Enable organizations to identify areas for cost savings.
Once these practices and tools to track overprovisioning are set in place, consider instituting a chargeback model to track resource usage. This way, you can allocate cloud costs to business units, departments or even projects that can help encourage more efficient use of cloud resources across your organization.
Steps to deprovision cloud resources
Documenting the workflow for deprovisioning resources and publishing it to a central repository is essential. It'll come in handy for onboarding new staff and during compliance audits. Once you determine resources for decommissioning, notify application owners, developers and users, as well as anyone else the change impacts.
Follow these steps to deprovision cloud resources:
- Remove access permissions, including user permissions, and disable API keys from the resources you plan to deprovision. Hence, no users access the resources during the deprovisioning resources.
- Use infrastructure-as-code tools or a manual process to terminate the instance(s) you're deprovisioning.
- Once you terminate the instance of the resource you're deprovisioning, securely delete any data associated with the resource you're deprovisioning. Standard data deletion tools include Google Cloud Storage Object Lifecycle Management and Microsoft Azure Storage.
The reprovisioning process isn't complete until you verify the proper removal of resources by reviewing logs and running tests to ensure the resources and services are no longer present.
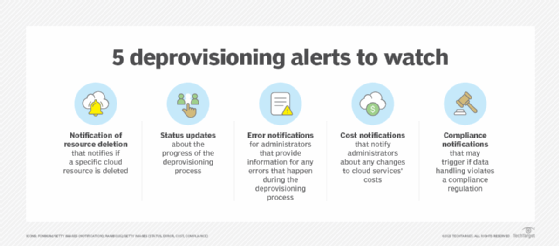
Cost monitoring tools to consider
A cloud management platform provides features for managing the full lifecycle of cloud resources from provisioning onward, including the capability to configure with role-based access control, purchase approval processes and related capabilities, to ensure only authorized staff can manage cloud resources. Additionally, it can record usage patterns, which can help identify which resources should be deprovisioned.
For those that prefer to use native cloud provider tools, consider cost management and audit tools to identify resources that your organization no longer needs. The following are the most popular options from the major cloud providers:
- AWS Cost Explorer. This tool helps visualize, understand and manage AWS costs and usage. AWS Cost Explorer provides detailed reports and recommendations to help reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Microsoft Cost Management. This tool helps optimize cloud spending and manage costs across different Azure services. Microsoft Cost Management provides recommendations and cost analysis tools to help reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Google Cloud Billing. This set of tools manages cloud costs and usage and offers recommendations to help reduce cloud costs and optimize resource usage.







