
Murrstock - stock.adobe.com
4 AWS Backup best practices for reliable data protection
Unlock the power of AWS Backup. Discover how this centralized service enhances data reliability, fortifies disaster recovery and safeguards resources.
With the prevalence of outages, businesses need a backup strategy. High reliability requires a solid disaster recovery plan that identifies failure scenarios and their recovery procedures, as well as requirements for each scenario. To add to the complexity, applications within one organization can have significantly different disaster recovery requirements and fixes based on their business background and technical implementations.
Many AWS services offer data backup and recovery features. For example, services such as Relational Database Service (RDS), DynamoDB, ElastiCache, Elastic File System (EFS) and Redshift offer the option to schedule periodic data backups. They also provide the option to restore resources based on specific data backups. Even though all these individual service features are useful, businesses need a centralized platform, such as AWS Backup, to configure backups and disaster recovery functionality. This is particularly true when a business uses multiple AWS services as part of its cloud infrastructure.
Get a better understanding of AWS Backup, how it plays into a backup strategy and best practices to follow before disaster strikes.
What is AWS Backup?
AWS Backup is a fully managed service that centralizes and automates data backups across various AWS services and on-premises environments. With AWS Backup users can create automated backup plans with policy-based management to enable scheduled backups and retention settings. It also supports cross-account and cross-region replication to meet various compliance requirements.
In addition to Amazon EBS, EC2, EFS, EDS and S3, it supports the following services:
- Amazon Aurora.
- Amazon DocumentDB.
- Amazon DynamoDB.
- Amazon FSx.
- Amazon Neptune.
- Amazon Redshift.
- Amazon Timestream.
- AWS CloudFormation.
- AWS Storage Gateway.
- SAP HANA on Amazon EC2.
- VMware virtual machines.
In the case of CloudFormation, supported services receive backups; however, these are overseen within CloudFormation stacks.
Note that users must enable any required services in the settings section of the AWS Backup console. The service also offers the ability to trigger manual backups, which is recommended before applying potentially disruptive updates to critical components.
Security and data protection
Security and data protection are a critical part of AWS Backup, given that the service stores and manages potentially sensitive data. Using an encryption key is a mandatory requirement when creating a vault, which is used to securely store and manage sensitive information like passwords. AWS Key Management Service manages the key, and users must allow permissions for that key. This enables the backup and copy jobs, as well as restore operations, to execute successfully. It is essential to test the restore jobs and to ensure their completion, particularly when doing cross-account or cross-region replication backups.
Compliance
AWS Backup also offers the Audit Manager, which sets up controls, creates reports and ensures resources are backed up appropriately to meet compliance requirements. For example, this feature can find critical resources that are not being backed up or identify unsuccessful jobs in an AWS account or organization. It can evaluate the frequency of existing rules and ensure they comply with organizational needs. It also creates daily and on-demand reports, which is a very useful way to ensure that the required reliability standards are met.
Together with a consistent tagging pattern, these reports are particularly useful to large enterprises. Amazon CloudWatch alarms can notify teams when jobs fail in a vault, resource type or in the whole account. Amazon EventBridge can execute automated tasks triggered by specific events, such as a job success or failure.
Pricing
AWS Backup pricing follows a pay-per-use model in which users only pay for the backup storage they use. Storage pricing depends on the resource type, if it is placed in warm or cold storage and if that storage has a logically air-gapped vault.
Organizations also need to consider data transfer fees for moving between AWS Regions, data restoration and testing, backup search and AWS Backup Audit Manager pricing.
Essential AWS Backup best practices
Basic configurations can deliver recovery capabilities for many outage root causes, such as accidental data deletion, resource misconfigurations or application-induced data disruptions. However, to truly be disaster-proof, you still need to establish best practices.

Balance retention periods and storage costs
Organizations must determine how long it is appropriate to retain backups and what the cost of backup retention is. There are cases where retention periods are unnecessarily long, resulting in non-optimal costs. For any services that manage their own data backups -- such as RDS, DynamoDB and EBS -- the AWS Backup storage cost is the same as those managed in those services.
Cold storage could be a lower-cost option for backups that need to be kept for longer than 90 days. Cost is an important area to calculate in advance and to monitor regularly.
Optimize backup management with tagging
Tags can help users organize and track their backup plan. Backup vaults group and tag backups by application or any other relevant patterns according to an organization's needs.
Resource assignment configuration uses specific resource IDs or more generic patterns, such as resource types or tags, to determine which resources to back up -- such as RDS databases or S3 buckets. Tags are a useful way to group resources by areas, such as application names, component types, deployment stages, tenants or organizations. Tags can group and assign any backup rules and resource assignments to a backup strategy.
Copy backups and implement cross-region replication
Another useful feature of AWS Backup is the ability to copy backups to a different AWS account. This protects resources and data against security breaches and attacks that could compromise the primary AWS account. Copying backups to a different AWS Region offers protection against region-wide failure events.
It is highly recommended to consider cross-account and cross-region replication configurations to protect application components against extremely disruptive events. A prerequisite for cross-account backups is that accounts must belong to the same organization in the AWS Organizations service and to ensure both the source and destination accounts are members of it.
Set RPO and RTO goals
Before configuring AWS Backup components, it is a best practice to have clear recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO) goals for each application. These objectives are part of the disaster recovery strategy that determine the maximum tolerance for the time it would take to recover from an application disruption and the maximum age of the data points responsible for application restoration.
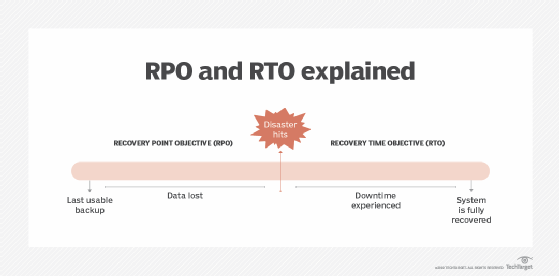
Test and document the different restoration procedures a team would need to execute during disruption. Test these procedures regularly to ensure RPO and RTO goals can be met as the application and teams evolve.
Ernesto Marquez is owner and project director at Concurrency Labs, where he helps startups launch and grow their applications on AWS. He enjoys building serverless architectures, building data analytics solutions, implementing automation and helping customers cut their AWS costs.





