
everythingpossible - Fotolia
Get the lowdown on these 4 Google Cloud management services
Google Cloud Platform offers numerous tools to manage and deploy resources -- each with its own specific focus. Learn about these four services before you get started on Google Cloud.
IT teams need to get cloud management right to ensure good performance, proper security and overall success in the cloud.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) has a variety of management tools and services, including those for hybrid cloud, workflow orchestration and resource management. However, it can be overwhelming to pore over the reams of documentation to find the best fit and learn how to get started.
That's why we've compiled a recap of some of our top tips on notable Google Cloud management services: Anthos, Cloud Deployment Manager, Cloud Composer and Cloud Run. Follow the links below to read the full articles from our cloud experts.
Anthos
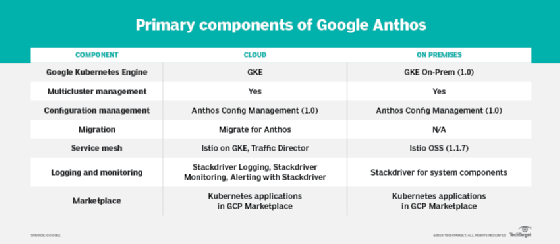
Hybrid cloud remains a popular model that enables enterprises to take advantage of cloud and on-premises systems together. Google Anthos is a cloud-agnostic container environment that delivers a consistent hybrid cloud experience.
Anthos is purely a software product that runs on existing hardware, and its foundation is a container cluster managed by Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The seven main components that make up the tool are: Anthos Config Management, Istio on GKE, Traffic Director, Stackdriver, Migrate for Anthos, Cloud Run and GCP Marketplace.
Unlike Google, other major providers depend on virtualization to sustain consistency between environments instead of containers. Anthos' main competition so far is AWS Outposts and Azure Stack, though Microsoft's planned Azure Arc service pushes Microsoft closer to the approach Google has taken with Anthos. To learn more about Anthos, read the rest of the tip here.
Google Cloud Deployment Manager
Google Cloud Deployment Manager is an infrastructure-as-code tool that enables users to create and manage GCP resources via templates. Like similar tools, it uses a declarative format and supports external references, metadata and environment variables.
The three file types Google Cloud Deployment Manager uses to define a GCP deployment are: configuration, template and schema. The configuration file type is used for simple jobs, while the others are reserved for more complicated tasks, such as automation.
Configuration files have two sections: imports and resources. They can also include outputs, which exposes configurations to other templates or users. In simple terms, infrastructure-as-code templates are configuration files that are split into reusable parts.
To learn more about the tool, similar services and how to deploy Google Cloud infrastructure as code, follow this link.
Google Cloud Composer
Google Cloud Composer is a workflow orchestration service, built on Apache Airflow, that helps enterprises manage data pipelines. Airflow is comprised of a web server, scheduler, executor and metadata database to ensure a task is initiated and executed at the right time and in the right order.
Some main features include support for Stackdriver Logging and Monitoring, full integration with numerous GCP data and analytics services, compatibility with open source Airflow and support for other community-developed integrations. Since it is fully managed, enterprises can focus on workflow management rather than provisioning GCP resources.
For a closer look at the Google Cloud management tool and pricing information, read on here.
Google Cloud Run
Serverless computing has the potential to become a go-to technology for resource management, but the initial services in this space, like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions, only supported a limited number of languages. As an alternative, Google Cloud Run, a managed compute platform, supports any programming language or OS libraries.
Cloud Run combines serverless concepts with containers, which provides portability and scalability. There is no infrastructure management needed so staff can focus on their applications.
Cloud Run is built on the Knative open source project. It includes two deployment options: pay-per-use, which is a managed version for stateless containers on GCP, or Cloud Run for Anthos, which runs in the cloud or on premises on VMware.
There are a few basic rules when deploying workloads. The workloads must:
- be stateless;
- listen for requests on the port defined by the PORT environment variable; and
- not perform background activities outside the scope of request handling.
Since it is natively serverless, enterprises only pay for the GCP resources they consume. Read more for step-by-step instructions on how to deploy a service with Google Cloud Run.








