
Minerva Studio - Fotolia
Don't miss these multi-cloud management tools and tips
Multi-cloud adoption is growing throughout the IT industry. Boost your multi-cloud strategy with third-party tools for management, container orchestration, infrastructure automation and more.
With a multi-cloud model, organizations can utilize a variety of cloud platforms without the risk of vendor lock-in. Several other advantages have driven multi-cloud adoption too, such as increased redundancy, minimal latency and geographic flexibility.
While these benefits are certainly attractive, workload management can be a challenge, as an organization with multiple clouds must manage resources in environments made up of different architectures and requirements. Public cloud providers offer services to deploy and manage resources, but these often only support single cloud architectures. Organizations can fill the gaps with third-party tools and platforms specifically built to support multi-cloud architectures.
Third-party offerings can help with almost any stage of a multi-cloud deployment, from automatically deploying containers and VMs to monitoring workloads and improving security across environments. Here are five tips that highlight multi-cloud management tools, platforms and best practices to maintain functionality across environments and boost your overall cloud performance.
Nine multi-cloud management platforms to know
Cloud management processes get complicated when organizations host data in more than one cloud environment. It's important to have a multi-cloud management strategy in place to simplify these complexities.
IT vendors typically build cloud management tools with five components in mind:
- automation and orchestration
- security
- governance and compliance
- monitoring
- cost management
Multi-cloud management products fulfil these capabilities in different ways. For example, CloudBolt operates via agentless technology and deploys resources to an IT team's multiple cloud environments. CloudBolt offers automatic imports and redeployments of legacy installations to the cloud. But the service has limitations, including being available only as user-installed software and a lack of built-in support.
Another multi-cloud management offering to consider is Embotics, which works with public and private cloud resources. Embotics provides automation templates, expense reporting, compliance auditing and other benefits, but falls short in terms of integrated monitoring features.
Other multi-cloud management platforms include Flexera, CloudSimple and Nutanix. Check out the full list of multi-cloud management platforms and learn the strengths and limitations of each option.
Multi-cloud management tools focus on automation
In a crowded field of multi-cloud management products, vendors and enterprises have moved their focus higher up the stack, with an emphasis on automation, abstraction and orchestration.
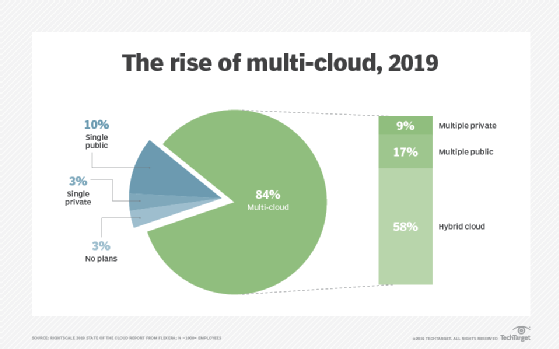
Automation is a central piece of any multi-cloud management strategy. Automation across environments enables IT teams to track usage at a more detailed level. Multi-cloud management tools that have automated updates on service usage, change management and configurations increase visibility into an organization's cloud environments.
Abstraction is another key element for multi-cloud management tools. Tools that incorporate this approach layer service deployments on top of one another, which creates a singular, unified view of resources such as storage, compute and security across different cloud services and platforms that make up a multi-cloud architecture.
The final focus here is container orchestration. With Kubernetes and other container management technologies, developers and operations teams can cluster and maintain resources as containers and provide portability between clouds.
Take a closer look at the main approaches to multi-cloud management with this tip.
Compare infrastructure-as-code tools for multi-cloud deployments
Developers and IT teams use infrastructure as code to automatically provision resources and create consistent infrastructure for applications. Infrastructure-as-code tools provide templates that repeatedly deploy resources and handle version control on configurations.
Public cloud providers offer native infrastructure-as-code services, such as AWS CloudFormation and Microsoft Azure Resource Manager. These tools are useful for organizations that run on a single provider, but do not always suit multi-cloud environments.
Third-party tools support more complex multi-cloud workloads that require functionality across platforms. HashiCorp Terraform is the most popular third-party infrastructure-as-code tool and works with various cloud platforms. Terraform offers reusable templates, which standardize infrastructure configurations throughout multi-cloud environments.
Evaluate native and third-party tools to determine if one, or a combination, is the right fit for your multi-cloud workloads.
Weigh your options for multi-cloud Kubernetes
All the major public cloud providers have their own managed Kubernetes services, but just like cloud-native infrastructure-as-code services, these tools aren't built to support multi-cloud environments. For this capability, users turn to third-party Kubernetes management tools.
There are several prominent third-party offerings that support Kubernetes clusters in multiple environments, including NetApp Kubernetes Service, Cloudify, Rancher and Red Hat OpenShift. Each one has its strengths and weaknesses. For example, NetApp provides a mature service and administrative console, but it doesn't currently support on-premises Kubernetes deployments. Cloudify is built on open source technology that treats Kubernetes environments and services as classes of resources, but some users might be turned off by the additional layer of abstraction.
Compare these multi-cloud Kubernetes management tools and others with a breakdown on features, support and more.
Secure multi-cloud deployments with CASB tools
Cloud access security broker (CASB) tools create an additional layer of security between an organization's on-premises infrastructure and its cloud provider's infrastructure. CASB tools make up for any security features that are not included by the cloud provider, such as authentication and encryption, that are necessary to meet an organization's security and compliance standards.
When selecting a CASB tool for multi-cloud environments, IT teams must choose between two CASB deployment models -- via a proxy or via API integration. The API integration approach is suitable for multi-cloud deployment models that consist of a small subset of different products. For multi-cloud models that involve more complex and niche services, the proxy approach is a better choice, because it's more flexible.
To choose the right multi-cloud CASB tool, organizations must determine their usage and the security requirements of each environment. Follow along with this tip to learn about CASB models for multi-cloud environments.








