What is cloud transformation and how do you get started?
Cloud transformation is a migration process in which a business's IT infrastructure, data, applications and software are moved to cloud-based environments.
But cloud transformation isn't just about relocating data or applications to the cloud; it represents a complete overhaul of an organization's technology, processes and work culture. It enables businesses to embrace innovation and quickly adapt to threats and challenges by adopting the latest digital technologies.
Why is cloud transformation important?
Gartner predicted back in 2023 that cloud computing will become a necessity for businesses by 2028. In today's rapidly changing digital landscape, it can be challenging for organizations to stay adaptable. Cloud transformation plays an important role in keeping businesses flexible, as it fosters a sense of innovation and agility. By migrating to the cloud and rethinking their operational strategies, businesses acquire greater visibility, scalability and cost-efficiency. They move beyond the constraints of traditional on-premises infrastructures and gain more flexibility to scale IT resources instantly.
Cloud transformation also simplifies operations, lowers costs and strengthens organizations' security, backup and disaster recovery capabilities. Businesses tend to take advantage of the economies of scale provided by cloud vendors, such as decentralized data centers, which isn't an option with traditional setups.
Cloud transformation vs. cloud migration
In the context of cloud adoption, cloud transformation and cloud migration are closely related terms, but they differ in their scope and objectives.
Cloud transformation
Cloud transformation is a broader strategy that includes migrating assets and rethinking and redesigning business processes and models to fully take advantage of cloud capabilities. It often involves adopting new cloud-native applications, executing advanced analytics and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
The main aim behind cloud transformation is to enhance agility, innovation and customer engagement by integrating cloud technologies into core business operations.
Cloud migration
Cloud migration is the process of moving an organization's digital assets -- such as data, applications and workloads -- from on-premises infrastructure to cloud environments. This process can involve various strategies, including lift and shift -- also known as rehosting -- replatforming or refactoring applications to better use cloud capabilities.
The primary goal of cloud migration is to achieve operational efficiency and cost optimization by using cloud resources.
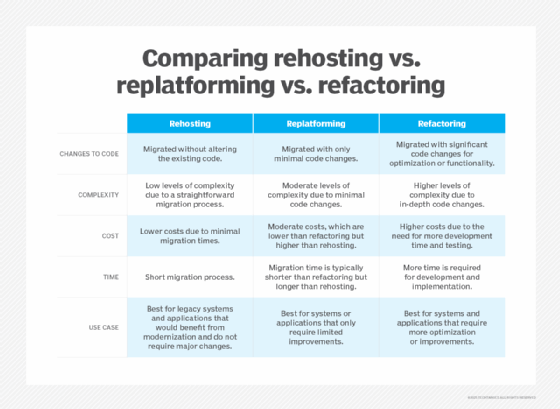
Cloud transformation vs. digital transformation
Digital transformation and cloud transformation are deeply interconnected concepts where both rely on each other to be fully realized.
As mentioned above, cloud transformation is the transitioning of an organization's infrastructure, resources and apps to a cloud-based environment along with the reengineering of its business processes.
Digital transformation is an expansive concept that offers various benefits and entails integrating digital technology into all aspects of a business. It involves rethinking processes, culture and customer experiences while also shifting mindsets and improving engagement and collaboration through innovation. For example, this can include businesses adopting technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, the internet of things, blockchain and cloud computing to drive innovation and optimize operations.
Advantages of cloud transformation
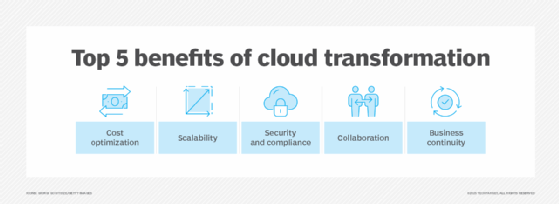
Cloud transformation offers businesses the following long-term benefits:
- Cost optimization. By migrating to the cloud, organizations can reduce upfront hardware investments and lower ongoing maintenance costs. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go (PAYG) model offered by cloud service providers enables businesses to pay for only the resources they consume.
- Improved flexibility and scalability. The PAYG model gives businesses the flexibility to scale resources on demand, letting them quickly respond to market changes and customer needs. Additionally, the cloud model enables businesses to reach a global audience and launch products rapidly, helping them stay ahead of the competition.
- Enhanced security and compliance. According to a RapidScale report, 94% of businesses reported enhanced security after migrating to the cloud and 91% think the cloud made it easier for them to meet government compliance requirements. Most public cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud offer different types of cybersecurity controls, including encryption, built-in threat detection, regular updates and compliance certifications to help organizations protect their sensitive data and mitigate security risks.
- Increased collaboration and teamwork. Cloud computing significantly boosts collaboration by enabling teams to access shared resources and tools from anywhere. For example, real-time access to editing platforms such as Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 lets multiple users collaborate on documents simultaneously, eliminating version control issues and ensuring everyone works with the most up-to-date information.
- Business continuity and disaster recovery. Cloud computing supports business continuity and disaster recovery by providing automated, off-site backups and disaster recovery options. For example, in the event of an outage or disaster, businesses can quickly restore critical data and applications and minimize downtime. Also, the fact that cloud providers typically host data across multiple locations ensures redundancy and reduces the risk of data loss.
Challenges of cloud transformation
While cloud transformation offers numerous benefits, it also presents the following challenges organizations must navigate to succeed:
- Cultural shift and adoption. Cloud transformation involves both a technological shift and a substantial change in the organizational culture. Employees might resist adopting new processes and automation tools, causing issues during the transition. Organizations must nurture a culture that welcomes change and promotes collaboration to avoid this adoption challenge. Keeping employees informed about the transition phases and educating them on the changes can foster a more positive attitude toward cloud adoption.
- Integration challenges. Most legacy systems are built on complex architectures and dependencies that can complicate integration with cloud environments. Organizations can tackle this by assessing their legacy systems, identifying key dependencies and using automated migration tools. Refactoring applications and adopting hybrid cloud architectures can also help gradually transition critical workloads to the cloud.
- Security and compliance issues. Transitioning to the cloud often introduces new security challenges and compliance requirements. Ensuring data security and meeting regulatory standards can be complex for businesses, especially when handling sensitive information. To counter this challenge, organizations must enforce security strategies to safeguard their data in the cloud.
- Vendor lock-in. Sometimes cloud transformation can lead to heavy reliance on a single cloud provider. This can result in vendor lock-in and restrict an organization's ability to switch providers or adopt a multi-cloud approach later. Organizations can follow several best practices to avoid vendor lock-in, such as prioritizing a multi-cloud strategy, designing applications to be portable across different providers and carefully evaluating each vendor's services based on their specific needs.
- Cost management issues. While cloud transformation can result in cost savings, managing cloud expenses can also be challenging for businesses. Without a well-defined financial strategy in place, organizations face unexpected costs for data transfer, storage and other additional services.
- Skills shortage. As organizations transition to the cloud, they often face a shortage of skills and talent because cloud technologies require expertise in niche areas such as cloud architecture, security, data management and DevOps practices. To address this challenge, organizations should invest in training their employees as well as recruiting new talent. They can also partner with specialized consultants for employee training.
How to build your cloud transformation strategy
Building a cloud transformation strategy involves several strategic steps that help organizations effectively transition to cloud-based environments. Key steps involved in creating a cloud transformation strategy include the following.
Step 1. Perform an assessment and define the objectives
The cloud transformation journey must begin with a thorough assessment of the current infrastructure, applications, workloads and the organization's core business goals and objectives.
This assessment should start by analyzing existing systems, evaluating their performance and dependencies, and determining their compatibility with cloud platforms. It should also consider the organization's business requirements, regulatory obligations and security needs to ensure a successful transition.
Step 2. Select the cloud model
The next step is to choose the most suitable cloud deployment model such as public, private or hybrid. Organizations should also select the appropriate cloud service model such as infrastructure as a service, platform as a service or software as a service based on the required level of control and flexibility.
The selection of cloud business models should be based on a thorough assessment of the organization's business needs, regulatory concerns and budget constraints.
Step 3. Plan the migration
Once a clear strategy and vision are established, organizations should develop a detailed migration plan. This plan should outline the steps for transitioning applications and data to the cloud, including decisions on whether to rehost, replatform or refactor existing systems. Organizations should take an agile approach, executing the migration in phases to minimize risks and adjust as needed.
It's also important to prioritize applications based on their business value, risk factors and complexity at this stage.
Step 4. Provide training and skills development
Once the migration strategy is in place, organizations should set aside ample time to train and upskill employees and stakeholders on cloud technologies. This can include investing in in-house training programs or hiring and partnering with experts to fill knowledge gaps.
Fostering a culture of collaboration and adaptability around cloud tools and processes will ease the transition and help mitigate any adoption challenges.
Step 5. Conduct the migration
This is the stage where workloads, applications and data are migrated to the cloud. It requires carefully considering the previously developed migration strategy to ensure a smooth transition of on-premises resources to the cloud infrastructure.
Organizations must remember that if data becomes inaccessible during migration, it can disrupt business operations. To mitigate this risk, each workload should be tested and confirmed to function properly in the new environment before migrating additional components into the cloud. Any changes made to the source data during the migration process should also be synchronized.
Step 6. Monitor and optimize
After migrating to the cloud, organizations must continuously monitor their performance against established key performance indicators. This can be achieved by using performance metrics and security controls and optimizing the apps for cloud-native capabilities.
Regular reviews and adjustments are essential to identify areas for further optimization and to ensure the cloud strategy stays aligned with current and future business objectives.
Step 7. Establish security and governance controls
Establishing governance and cloud security is critical in the cloud transformation journey. As organizations move data and applications to the cloud, new vulnerabilities can arise, making security a top priority.
To protect sensitive data, manage access, prevent security breaches and comply with industry regulations, organizations must establish solid security measures. These measures typically include strong encryption policies, identity and access management, regular security audits and continuous monitoring of systems and applications to ensure ongoing protection.
Step 8. Expand the cloud capabilities
As organizations become more confident in their cloud capabilities, they should broaden their use of cloud services. This can include scaling existing workloads, migrating additional applications or data to the cloud and exploring new opportunities.
Businesses should also try expanding to new regions, adopting multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies and integrating with other cloud-based services. The objective at this stage should be to harness the full potential of cloud computing to fuel innovation and drive business growth.
The costs of cloud repatriation extend beyond migration. Discover the key factors in cloud repatriation cost calculation, including new hardware, backup requirements and the need for skilled personnel.








