What is cloud sprawl?
Cloud sprawl is the uncontrolled proliferation of an organization's cloud instances, services or providers. It typically occurs when an organization lacks visibility into or control over its cloud computing resources.
Cloud sprawl affects all types of cloud services but is especially common in software-as-a-service (SaaS) and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) models.
In SaaS, easy access to deployment enables teams to adopt various applications without oversight, creating an unmanaged patchwork of tools. In IaaS, rapid provisioning of virtual resources enables teams to quickly deploy them, often leading to unused or mismanaged infrastructure.
Causes of cloud sprawl
There are many reasons that cloud sprawl can happen, including the following:
Lack of centralized management
Cloud sprawl can happen due to the uncontrolled proliferation of cloud service providers. This occurs when teams or employees across various departments independently adopt different cloud services or providers. For example, software developers might use Amazon Web Services (AWS) for compute and storage instances, while the research and development group uses Google Cloud resources for big data projects.
This article is part of
What is cloud management? Definition, benefits and guide
Cloud providers aren't fully interoperable yet, so a business that uses different cloud providers could face incompatible application programming interfaces and data quality and consistency challenges.
Insufficient monitoring
Similar to server sprawl or virtual machine sprawl, cloud sprawl usually occurs when an organization fails to adequately monitor and manage its individual cloud instances. For example, a software developer might launch a new workload in AWS or deploy a private cloud to test a new software version or database, but then neglect to power down or delete the workload when it's no longer needed.
Because businesses pay for public cloud computing resources monthly, the proliferation of unneeded cloud instances is costly for most enterprises. Not having real-time insights into cloud metrics makes it hard to detect underutilized or abandoned resources, resulting in unnecessary costs and cloud security risks.
Proliferation of unused instances
Cloud sprawl can also result from the proliferation of SaaS instances, such as Salesforce, Microsoft 365 or any other online service for which an organization creates and pays for new user accounts, but doesn't actually use them.
In some cases, different departments within the same organization might use similar services from different SaaS providers to accomplish the same tasks. This can result in inconsistent or noninteroperable data, which can cause communication issues between business departments. It also can cost a company more because it eliminates the potential for bulk SaaS discounts, which providers often offer to organizations with a large number of user accounts.
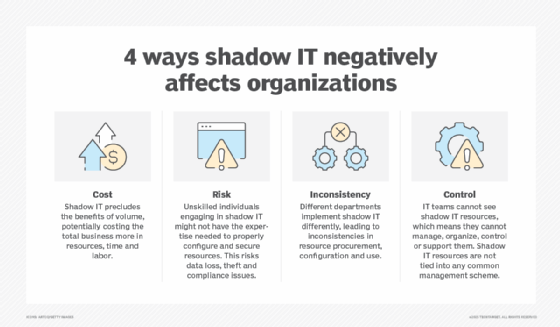
Shadow IT
Shadow IT occurs when employees sign up for cloud and other services without the approval of the IT department. This can create compliance issues and contribute to cloud sprawl as more and more unmonitored services are used. For example, when employees or departments use personal cloud storage accounts, such as Google Drive or Dropbox, to store and share work files without the approval of IT, it can lead to a fragmented cloud environment with multiple unmanaged accounts throughout the organization.
Also, when it comes to compliance audits, organizations could struggle to account for all apps and data sources due to shadow IT.
Inconsistent tagging and naming conventions
Inconsistent tagging and naming conventions can cause cloud sprawl. When resources lack uniform tags or names, it can be difficult to manage, track and identify them, resulting in confusion, resource duplication and inefficient allocation of resources. All of this can eventually lead to an unmanageable cloud environment.
Adopting consistent tagging optimizes cloud costs and reduces the risk of sprawl, as it helps maintain visibility and control over cloud resources.
Insufficient visibility
Organizations often struggle with a lack of visibility into their cloud environments. When there's insufficient tracking of cloud resources, it can become easy to lose control over what services are being used and how much they cost.
Inadequate monitoring also diminishes an organization's ability to promptly detect and address misconfigurations and other noncompliant resources.
Types of cloud sprawl
Cloud sprawl can manifest in various forms and present organizations with unique challenges. The three main types of cloud sprawl include the following:
Platform sprawl
Platform sprawl occurs when an organization uses multiple cloud platforms and services without a decentralized cloud adoption strategy. For example, when multiple cloud management platforms, such as AWS, Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure, are used across an organization without a solid plan, it can cause resource management issues.
A big drawback of the cloud environment is that it can easily add roles, computing power and features without any oversight. This can lead to abandoned or unnecessary workloads and identities and can create security risks when rogue resources go unmonitored for extended periods. For example, developers frequently push code changes for bug fixes or experimental features, especially during migrations, but without proper monitoring and governance policies, these changes can compromise data security and disrupt operations.
Data sprawl
Data sprawl refers to the uncontrolled and widespread distribution of data across various storage options and platforms within an organization. This phenomenon often occurs in cloud environments where data can be easily created, stored and shared.
Data sprawl can also result in redundant and obsolete data, increasing cloud resource usage and exposing organizations to security vulnerabilities. Poorly organized data can hinder decision-making, as it becomes difficult to determine its quality and relevance, potentially leading to misguided strategies and financial losses. For example, relying solely on traditional sales metrics without considering demographic and strategic insights can result in weak product performance.
Identity sprawl
Identity sprawl is the unregulated explosion of human and nonhuman identities such as user accounts, roles and service principles across an organization's cloud systems. As individuals and organizations adopt more digital tools and platforms, the number of accounts associated with a single user can grow significantly, leading to a fragmented identity landscape.
To address and avoid identity sprawl, organizations should prioritize centralized identity and access control options, create clear governance policies and conduct regular reviews and audits of identities and permissions.
Cloud sprawl risks
Cloud sprawl can lead to several risks that can greatly affect an organization. These include the following:
- Increased cost. Cloud sprawl can lead to unnecessary costs as companies pay for idle or forgotten workloads. A sprawling cloud infrastructure demands additional staff time and effort, which can strain a company's budget and cost optimization capabilities.
- Weakened security. Forgotten or unmonitored workloads can weaken systems, which provides hackers with easier access. These instances are also prime targets for credential-based attacks and data breaches. For example, an instance running outdated software can carry security flaws that can be easily exploited by cybercriminals to gain access to the systems.
- Inefficiency. Inefficient cloud management can greatly affect organizations in terms of resources, environmental effects, team understanding and redundancy.
- Compliance issues. Keeping up with different industry standards and regulatory requirements -- including Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, General Data Protection Regulation and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard -- can become challenging with cloud sprawl. Because there's a lack of central visibility and resources are spread out across multiple environments, organizations can find it difficult to keep track of everything.
How to prevent cloud sprawl
Preventing cloud sprawl requires a proactive approach that combines effective management practices, clear policies and ongoing monitoring.
Ways to prevent and manage cloud sprawl include the following:
- Manage and review cloud usage. The best way to mitigate cloud sprawl is to manage cloud use. Organizations should establish clear user policies and ensure ongoing communication among business departments. In addition, organizations should monitor usage and enforce their cloud computing policies with cloud management tools.
- Create a centralized cloud strategy. Companies should establish a clear and centralized cloud management strategy that includes all stakeholders throughout the lifecycle of the cloud projects. This approach ensures consistent monitoring and management of cloud resources across the organization and also minimizes the risk of adopting unapproved services.
- Establish strong policies and controls. Organizations should develop and enforce strong cloud policies. For example, employees should be provided with controls for automatic workload shutdown, guidelines for BYOD usage and protocols for remote access through virtual private networks. These policies should be flexible and provide enough scalability to accommodate evolving needs, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Limit administrative access. Administrative access to cloud resources should be restricted to a select group of IT teams and personnel. This helps prevent unauthorized changes and the creation of shadow IT systems.
- Allocate a set number of virtual resources. Allocating a designated number of virtual resources for each department through resource pools can effectively reduce cloud sprawl. This strategy establishes clear boundaries for resource usage, ensuring that departments stay within their allocated limits. Additionally, it improves visibility and control over cloud resources, decreasing the chances of unauthorized or unmonitored resource adoption.
Cloud cost management tools are designed to optimize and improve an organization's cloud spending and financial oversight. Explore cloud cost management tools that can improve visibility and help with the efficient management of resources.






