
What is IBM Cloud?
IBM Cloud is a suite of cloud computing services from IBM that offers software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) models. The platform provides modern cloud platform capabilities, including artificial intelligence (AI) for analytics or automation, advanced security, compliance, data protection and scalability.
IBM Cloud is suitable for various enterprise cloud environments. It works for hybrid clouds, where customers combine on-premises cloud infrastructure with virtual cloud services, and multi-cloud approaches, which combine cloud services from different providers. IBM describes the platform as "open by design," meaning it can integrate with other vendors' products and services if needed.
Why is IBM Cloud used?
With IBM Cloud's IaaS functionality, organizations can deploy and access virtualized IT resources, such as compute power, storage and networking, over the internet. For compute, organizations can choose between bare-metal physical hardware or virtual servers.
IBM Cloud's PaaS functionality is based on open source cloud platform Cloud Foundry. It lets developers use IBM services to create, manage, run and deploy various types of applications for the public cloud, as well as for local or on-premises cloud environments. IBM Cloud supports several programming languages, including Java, Node.js, PHP and Python.
IBM Cloud offers security, risk management and compliance features that make it suitable for regulated industries, such as healthcare, finance and government. In healthcare, for example, care providers of any size can quickly store and manage large patient data volumes, while adhering to standards such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. For financial institutions, the platform adheres to IBM Cloud Framework for Financial Services to meet the industry's high regulatory standards.
IBM Cloud products and services
IBM Cloud supports a variety of tools and services, including IBM Cloud managed services, preconfigured software and consulting. It also supports access to IBM Watson, IBM Cloud Functions for serverless computing, IBM Databases, IBM Integration Bus and IBM WebSphere Application Server. In addition, IBM Cloud works with various products from third-party cloud providers.
IBM Cloud features
IBM Cloud services are grouped into 15 categories:
- AI and machine learning. The platform offers a collection of Watson-based offerings that are AI resources and tools for building generative AI models, such as IBM Watson Assistant or IBM Watson Discovery.
- Analytics. IBM Cloud offers IBM Analytics Engine to build analytics applications on Apache Spark and Hadoop, as well as analytics tools for streaming data.
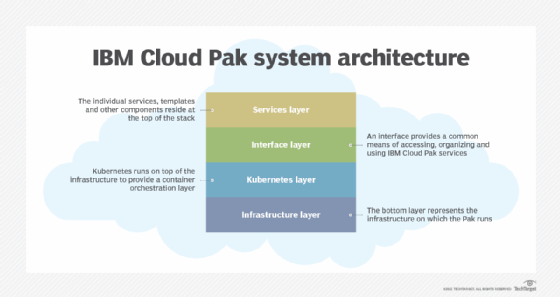
- Automation. Resources are available to automate business workflows and processes. These include Cloud Paks, which exist for business automation, data, integration, multi-cloud management, network automation, cloud security, Watson AIOps, and IBM Z and Cloud Modernization Stack.
- Blockchain. IBM Blockchain Platform is a SaaS offering to develop apps, enforce governance and monitor a blockchain network.
- Compute. IBM offers various compute resources, including bare-metal servers, virtual servers and IBM Cloud Functions for serverless computing, on which enterprises can host their workloads.
- Containers. IBM offers IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service, as well as access to its private container registry, Red Hat OpenShift and Istio, a service mesh for microservices.
- Cybersecurity. IBM Cloud includes services for activity tracking, identity and access management, and authentication.
- Databases. IBM provides a variety of Structured Query Language and NoSQL databases, as well as data querying, warehousing and migration tools.
- Developer tools. This includes a command-line interface, as well as tools for continuous delivery, continuous release and application pipelines.
- Integration. IBM Cloud services integrate cloud and on-premises systems and various applications, such as IBM API Connect, IBM App Connect and IBM Cloud Satellite.
- Internet of things. IBM Watson IoT Platform works with IBM Cloud to provide services that connect and manage IoT devices and analyze the data they produce.
- Logging and monitoring. IBM provides tools to log, manage and monitor cloud deployments, including IBM Cloud Monitoring and IBM Cloud Pak for Watson AIOps.
- Networking. The platform provides cloud networking services, such as a load balancer, a content delivery network, virtual private network (VPN) tunnels and firewalls.
- Quantum. IBM Cloud lets developers run workloads on quantum systems through the Qiskit software development kit.
- Storage. IBM's cloud storage offerings include block, file and object storage for cloud data.
IBM Cloud deployment models
IBM offers four deployment models for its cloud platform:
- Public. A public cloud provides access to virtual servers in a multi-tenant environment. An enterprise can choose to deploy its applications in one or multiple geographical regions.
- Dedicated. This is a single-tenant private cloud that IBM hosts in one of its data centers. An enterprise can connect to the environment using a direct network connection or VPN, and IBM manages the platform.
- Hybrid. This version is deployed as a combination of on-premises private cloud and public cloud infrastructure. IBM's hybrid cloud deployment supports public cloud offerings from third-party vendors, such as Google and Microsoft.
- Multi-cloud. This deployment model creates cloud infrastructures that mix and match cloud offerings from multiple vendors. This is the most flexible approach, enabling user organizations to avoid vendor lock-in.
IBM Cloud rebranding and competitors
In 2013, IBM acquired SoftLayer, a public cloud platform, to serve as the foundation for its IaaS offering. In 2016, IBM rolled the SoftLayer brand into its Bluemix brand of PaaS offerings, giving users access to both IaaS and PaaS resources from a single console. IBM then rebranded its entire cloud portfolio as IBM Cloud in 2017.
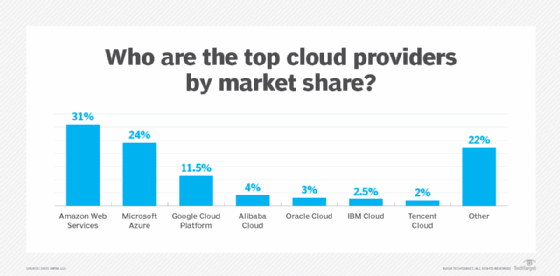
IBM's main competitors in the cloud market include Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure. AWS is considered the top vendor in this market with an extensive list of services. Azure is useful in enterprises using Microsoft 365 applications. Google Cloud is strong in AI and machine learning capabilities.
More on public cloud
Public vs. private vs. hybrid cloud: Key differences explained
On-premises-to-cloud migration: Top methods and tools to use
Breaking Down the Cost of Cloud Computing
IBM Cloud pricing
The cost of IBM Cloud services varies depending on resource use, deployment model, support and other factors. IBM offers a free tier, plus four pay-for-use pricing models.
The first of the four pricing options is IBM's basic pay-as-you-go account, where customers are billed monthly based on the resources they use. The Enterprise Savings Plan is also based on monthly resource consumption, where users commit to spending a certain amount on the platform to receive discounts.
The third option is IBM Cloud Reservations. In this model, the customer organization reserves cloud capacity in advance for one- or three-year terms and guarantees that capacity, which is billed monthly at discounted pricing.
The final account tier is a subscription account that's similar to the pay-as-you-go approach, where organizations commit to a certain spending amount. IBM offers discounted pricing for its services based on the monthly spending commitment, with larger commitments earning bigger discounts.
To better estimate costs, organizations have access to the IBM Cloud cost estimator.
IBM Cloud's list of services spanning AI, machine learning, cybersecurity and automation previews the future of cloud computing. Learn more about future cloud trends and predictions.







