What is data segregation and why is it important in the cloud?
Data segregation, also commonly referred to as data separation, involves the policies and practices for isolating data and workloads based on specific criteria.
Data segregation, also commonly referred to as data separation, involves the policies and practices for isolating data and workloads based on specific criteria.
Data can be separated based on several different traits, including access rights, sensitivity, type, purpose and functionality. It's separated either physically using different physical systems or logically by storing the data in logical partitions on a single system.
Data segregation is a key strategy in managing and protecting data. The goal is to improve data security and privacy by limiting access to it. Although data segregation is essential for many who work with data, the concept is a critical practice within cloud environments.
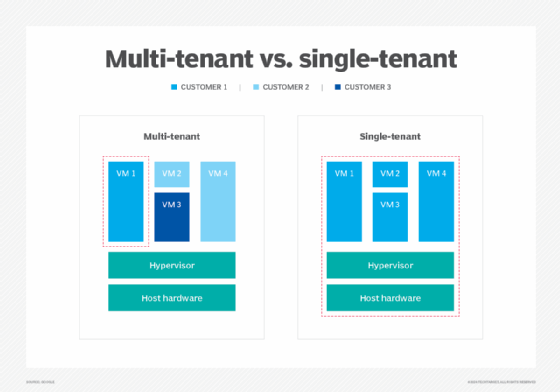
Cloud computing lets organizations run workloads and manage data anywhere, without significant computing resources residing in their data centers. Public cloud providers use multi-tenant infrastructures, which are efficient and cost-effective, but such multi-tenancy raises concerns about data management and control in the cloud.
Data segregation addresses the need to prevent one consumer of cloud services from disrupting or compromising the work or associated data of other consumers of cloud services. In effect, this acknowledges the potential risks of multi-tenant environments, where hypervisor flaws, malicious code running in the applications, excess workload demands and other factors can compromise workloads.
Thus, data segregation in cloud computing involves knowing exactly where workloads and data are running -- even though the very nature of a public cloud is intended to obscure such granular notions -- and then implementing decisions to relocate data so that security and performance are optimized.
Why is data segregation important?
Consider the noisy neighbor syndrome in which a virtual machine (VM) instance is running in a public cloud alongside a handful of VMs from myriad other users, all packed onto the same cloud server. Technically, this won't cause any issues until one of the neighboring VMs picks up traffic and takes excess network bandwidth or storage I/O, leaving other VMs struggling to maintain performance requirements.
Data segregation can rely on workload performance analytics to identify flagging performance and prompt cloud administrators to scale or migrate a stressed workload to another resource to alleviate contention and improve performance.
Beyond malicious code and performance sensitivity, today's legal and geopolitical landscape places serious boundaries on where a cloud customer's workloads and data can reside. A public cloud -- such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud or Microsoft Azure -- possesses a global presence comprised of data centers and other points of presence that operate in different countries around the world. In the early days of the public cloud, the physical location of servers and storage was largely opaque to users; the very idea of utility computing made such physical distinctions irrelevant.
However, as cloud use has expanded, governments, regulatory bodies and other organizations have become sensitive to the physical realities of global computing infrastructures. Some businesses and government agencies can be severely restricted by cloud region and tenancy. To address these data segregation challenges, cloud providers have given users more control over workload, data placement and reporting.
For example, a business located in the U.S. but with operations in the European Union might be obliged to isolate the data collected from EU customers and keep that separated data located on storage resources within an EU cloud region. This helps meet compliance and legislative demands for businesses operating in the cloud.
What are the benefits of data segregation?
Data segregation offers the following three principal benefits:
- Improves compliance. Users know exactly where data and workloads are running, such as specific regions or resource instances.
- Increases security. Data and workloads are separated to help prevent potential multi-tenancy issues.
- Enhances performance. Data and workloads can be migrated to varied service levels or tiers based on performance and access frequency needs.
What are the challenges of data segregation?
Data segregation also has a host of potential challenges as well, including the following:
- Complexity. It can be difficult for a business to organize and manage its data if it's spread across multiple servers or databases. This also increases the amount of required overhead concerning data policies, configurations and monitoring.
- Cost. Operational expenses can increase, considering an organization must maintain separate storage environments. Organizations dealing with cloud vendors don't have to deal with this consideration as much, as the vendor typically takes care of maintaining and updating its storage infrastructure.
- Integration. It's more difficult to bring together data that's spread across multiple databases or servers for analysis and reporting.
How to implement a data segregation strategy
For organizations, the key to optimizing data segregation is to exercise more control over the physical placement of workloads and data. However, the following three essential elements are needed to implement data segregation successfully:
1. Needs assessment
Data segregation can take many forms, so the first area of concern is a needs assessment to determine the desired goals or results from a data segregation strategy. What should data segregation look like for the business? This involves strong collaboration among business leaders, technology experts and legal teams.
2. Data insight
Organizations can host bewildering volumes of data across local, colocation and cloud resources. It's impossible to implement a comprehensive data segregation strategy unless the business has clear insight into the data available and its importance to the business. What data does the business have, where is it located now and why is it important to the business? Once that becomes clear, the business can start prioritizing the resources needed to improve availability, resilience and performance. This might involve relocating or tiering data, as well as implementing a storage and retention policy.
3. Data security
In terms of data security and better compliance posture, IT teams must understand that public clouds operate on the basis of a shared responsibility model. The cloud provider is responsible for securing the physical infrastructure, while the user is responsible for securing the workloads and data. Thus, a cloud user's responsibility starts with configuration.
Overlooked or incorrect configuration settings could expose a workload or data and potentially leave the business vulnerable to compliance violations. To avoid this issue, it's important to become familiar with the many different configuration options and best practices for the cloud provider's services. Proper configurations can be streamlined through cloud services -- such as AWS CloudFormation or HashiCorp Terraform Cloud -- that automatically provision and secure cloud resources across regions and accounts using templates or policies.
Another common practice to guard against the risks of multi-tenancy is the extensive use of strong encryption for any data housed within the public cloud. If the data is exposed through misconfiguration or malicious actions, the content remains secure. Ideally, encryption is applied to data both at rest and in transit.
The importance of geolocation
The question of geolocation -- knowing and ensuring the physical area of the world where applications and data reside -- is a more important consideration than ever before. Cloud architects must assemble a suitable infrastructure for a cloud workload that is provisioned in a suitable physical location with the necessary resources and services. Although simply selecting a specific region is not a tenancy discussion, location can affect workload performance, compliance and tenancy.
A region can be selected to improve workload performance, since the physical proximity to the workload's users can significantly reduce network latency. This placement of data can boost the workload's apparent performance and improve user satisfaction.
Services also vary by region, and not all cloud services might be available in all global regions. This could make it more difficult to deploy or secure workloads or application stacks in some regions. For example, if a needed service or resource isn't currently available in a particular cloud provider's region, the business might be unable to deploy the required environment and run its workload in that region. In that case, it would need to rearchitect the environment or select another suitable region.
Data segregation is a team effort
There's no single driver or implementation for data segregation, and businesses must approach data segregation based on their unique needs. Consequently, it's important to involve a team in any data segregation strategy. Business, IT and legal leaders should all have a place in any data segregation discussion to ensure that business goals, technical requirements for workload and data performance, and legal obligations for corporate governance and compliance are met for every jurisdiction in which the business operates.
Regulatory compliance
Data segregation also plays an important role in regulatory compliance. Many countries and industry standards have some form of data privacy regulations that require organizations to protect sensitive data.
For example, the General Data Protection Regulation in the EU requires businesses to better protect customer data. GDPR was created to focus on expanding the privacy rights of data subjects while also keeping businesses more transparent. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. is another example of a regulation that focuses on implementing stringent controls over how personally identifiable information is accessed and shared in the health field.
Keeping data separated in these instances helps comply with data privacy laws and regulations. Data segregation is meant to protect data privacy and ensure that only those who need to access specific data can do so.
Data segregation needs and strategies should be reviewed and updated regularly to evaluate changing workload demands and evolving legislative and regulatory landscapes. Special circumstances, such as new regulatory legislation or a data breach, should spark immediate reviews.
Data segregation also makes it easier to monitor and document data access and usage in multi-tenant cloud environments. This is useful for auditing and helps adhere to different compliance frameworks.
Cloud service tools and technologies for data segregation
Additional strategies to implement data segregation include the use of various enhanced cloud services intended to bolster security and control over cloud content. For example, users can employ a virtual private cloud, which provisions a logically isolated portion of the public cloud to create a user-defined infrastructure with full control over networking, subnets and other network characteristics. Although VPCs aren't physically isolated and are still multi-tenant environments, the level of security is much greater for the organization.
Tiering strategies can help enhance data quality and access needs. For example, products such as Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering automatically move data to a suitable cost-effective access tier as access patterns change. Data that's accessed less frequently over time can automatically be moved to less expensive -- and, as such, lower performing -- storage resources. This type of capability can handle vast quantities of data, including data lakes, data analytics repositories and customer content.
Cloud providers are also developing and expanding specialized cloud offerings for performance and security-sensitive users. For example, products such as AWS GovCloud and Microsoft Azure Government support numerous U.S. federal standards, including the Criminal Justice Information Services Security Policy, the International Traffic in Arms Regulations and the Export Administration Regulations. For additional security and oversight, AWS GovCloud is operated by U.S. citizens within the U.S. and is only accessible to U.S. organizations and prescreened account holders.
Similarly, both products support the architecting and implementation of storage and workloads for HIPAA-sensitive tasks. Many AWS component services support HIPAA compliance and can help cloud architects develop secure operational environments for medical usage and related tasks.
Several cloud providers, including AWS, Microsoft and IBM, offer an array of dedicated, single-tenant servers and cloud options to help improve workload performance and compliance. This can also be referred to as a bare metal cloud. Similarly, Amazon EC2 Dedicated Instances can be run in a VPC on hardware that's dedicated to a single customer.
Data segregation in the cloud is an important aspect of regulatory compliance. Learn more about GDPR compliance in the cloud.







