
robotic process automation (RPA)
What is robotic process automation?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a technology that mimics the way humans interact with software to perform high-volume, repeatable tasks. RPA technology creates software programs or bots that can log into applications, enter data, calculate and complete tasks, and copy data between applications or workflows as required.
RPA automates repetitive business processes in industries, including banking, IT, human resources and healthcare. These business processes, when performed by a bot, are faster and more efficient. RPA is growing in popularity because it can reduce costs, streamline processing and drive better customer experiences. Another attraction of RPA software is that business units can implement it without learning new tools, asking IT team members for support or changing an organization's underlying IT infrastructure.
The software bots RPA uses can understand what's on a display, navigate systems, input keystrokes, identify data, extract data as well as perform various other actions. These bots can understand and perform repetitive tasks by implementing scripts that emulate human actions while interacting with computers.
When combined with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, RPA can capture more context from the content it's working with by reading text or handwriting with optical character recognition (OCR), extracting entities like names, invoice terms or addresses using natural language processing (NLP), and capturing more context from images, such as automatically estimating accident damage in an insurance claim picture.
This article is part of
Ultimate guide to RPA (robotic process automation)
As RPA has grown in popularity, enterprises are seeing the need to integrate it in their IT systems. While RPA can dramatically speed up a business process previously handled by humans, bots can break when application interfaces or process workflows change.
Newer RPA tools use AI, machine vision and NLP to mitigate breakage problems. Modern RPA platforms also provide some integration with centralized IT governance and management capabilities, making it easier to scale the use of RPA across the enterprise.
How does RPA work?
RPA mirrors the way people are accustomed to interacting with and thinking about software applications. RPA's ability to copy the way humans perform a computer-based process has contributed to its popularity compared with automation tools such as application programming interfaces (APIs) or low-code development. Low-code development can also be used to build RPA automation scripts.
The simplest RPA bots are created by recording the clicks and keystrokes as a user interacts with an app. When problems emerge, a user can simply watch how the bot is connecting with the app and identify the steps that need to be fine-tuned.
In practice, these basic recordings often serve as a template for building more powerful bots that can adapt to changes in screen size, layout or workflows. More sophisticated RPA tools use machine vision to interpret the icons and layout on the screen and adjust accordingly.
Some RPA tools can also use these initial recordings to create hybrid RPA bots that start by simply recording an existing process or workflow and then dynamically generating a workflow automation on the back end. These kinds of hybrid bots take advantage of the simplicity of RPA development and the scalability of native workflow automation.
Legacy enterprise systems used with RPA might require front-end integrations if back-end systems aren't accessible. In other RPA implementations, process mining and task mining tools are used to automatically capture business process workflows that serve as starting templates for RPA automations. Process mining can analyze the logs of ERP and CRM applications to, for example, automatically generate a map of common enterprise processes. Task mining tools use a locally running app with machine vision to capture a user's interactions across multiple apps. All the major RPA vendors are starting to develop these kinds of process mining integrations.
RPA tools are also built to integrate with other systems, and include orchestration and administration tools to enable configuration, monitoring and security practices.
Tasks that RPA tools run can be done attended or unattended. Bots that are attended run in response to employee requests, while unattended bots run on a schedule.
RPA tools can also be connected to AI modules that have capabilities such OCR, machine vision, natural language understanding or decision engines, resulting in what is called intelligent process automation. These capabilities are sometimes packaged into cognitive automation modules designed to support best practices for a particular industry or business process.
Who is using RPA and its applications?
RPA is used in most industries, particularly those that include repetitive tasks such as insurance, banking, finance, healthcare and telecommunications.
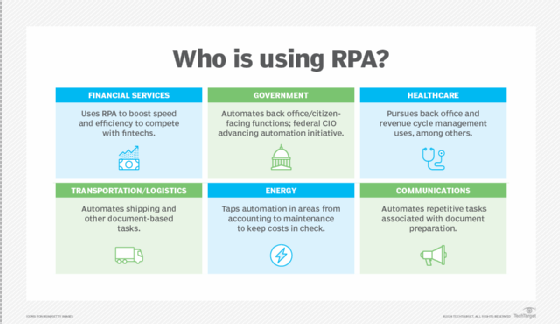
Some examples include the following:
- Finance. Financial services use RPA to automate governance, reconcile accounts, process invoices, exchange payments, automate account openings and closings, manage audit requests, and process insurance claims.
- Supply chain management. Organizations use RPA to automate data entry, procurement, predictive maintenance, automating order processing and payments for after-sales service support, tracking shipments, and monitoring inventory levels.
- Telecommunications. Telecommunications companies use RPA to configure new services and the associated billing systems for new accounts. They also use RPA to pull data from multiple systems when triaging equipment outages or predicting problems.
- Banking. Banks use RPA to help automate customer onboarding, close accounts and to provide customer service, credit card processing and fraud detection.
- IT. RPA is used in data collection, regulatory compliance, automated network management, data transformations and onboarding and offboarding.
- Human resources (HR). HR teams use RPA for recruiting, employee onboarding and offboarding, training, employee data management, expense management, employee information updating, and timesheet submission processes.
- Insurance. RPA is used to process the registering of claims, regulatory compliance, fraud detection, customer service, and policy administration and cancellations.
- Healthcare. In healthcare, RPA is used to automate appointment scheduling, account management, administer claims, billing, and regulatory compliance as well as manage electronic records and data.
- Customer service. RPA helps companies provide better customer service by automating contact center tasks, including verifying e-signatures, uploading scanned documents and verifying information for automatic approvals or rejections.
- Accounting. Organizations use RPA for general accounting, operational accounting, transactional reporting and budgeting.
What are the benefits of RPA?
Robotic process automation technology can help organizations on their digital transformation journeys by doing the following:
- Enabling better customer service.
- Ensuring business operations and processes comply with regulations and compliance standards.
- Dramatically speeding up processing time.
- Increasing efficiency by digitizing and auditing process data.
- Improving accuracy by enabling a bot to do repetitive tasks that are prone to human error.
- Reducing costs by decreasing manual and repetitive tasks.
- Improving employee productivity by focusing on more important or complicated tasks.
- Simplifying development by using low-code tools to make RPA scripts.
- Operating on the presentation layer of apps, which doesn't disturb inner systems.

What are the challenges of RPA?
There are also several challenges related to RPA that have limited its use:
- Scalability. Enterprises have struggled to scale RPA automation initiatives because although RPA's software bots are relatively easy to implement, they can be hard to govern and manage, therefore being hard to scale.
- Limited abilities. While its name includes the words "process automation," many critics have pointed out that RPA software tools automate tasks. More work is often required to stitch together multiple tasks into a process. At the Forrester Research New Tech and Innovation 2018 conference, analyst Craig Le Clair cautioned enterprises to observe the rule of five when building RPA applications. Yhey tend to break when a bot must make more than five decisions, manipulate more than five apps or make more than 500 clicks.
- Security. RPA bots sometimes need to access sensitive information to complete their tasks. If they're compromised, they pose an additional security risk for organizations.
- Limited resiliency. RPA failures can occur when applications change in ways that aren't anticipated by the software developers.
- New quality assurance (QA) issues. Bots require a variety of new QA practices to ensure they continue to work as intended.
- Privacy. Bots can work with personally identifiable information governed by privacy requirements. Teams need to ensure this data is processed in conformance with local data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). For example, if an RPA bot moved data outside of a given country without encryption that would be a GDPR violation. RPA vendors are starting to seek ISO 27701 certification from the International Organization of Standardization as a foundation for managing sensitive information.
- Efficiency. RPA bots manually plod through an application in the same way a human does. This might not be as efficient as automating applications through APIs or baking workflow automations into the application itself.
RPA vendors
The following are examples of RPA vendors:
- ABBYY. This vendor develops OCR tools to streamline back-office applications. The company recently expanded to help extend its automation capabilities across more use cases.
- Automation Anywhere. This vendor provides an enterprise digital workforce platform geared toward procure-to-pay, quote-to-cash, HR, claims processing and other back-office processes.
- Blue Prism. This vendor focuses on assisting organizations in regulated industries to automate processes by offering desktop-aligned and AI-powered bots that are defined and managed centrally.
- Nice. This vendor has traditionally focused on improving customer interactions with call centers and across multiple touchpoints. The company expanded its various automation capabilities to support RPA, with a strong focus on improving customer experience across multiple channels.
- Nintex. This vendor provides full cycle automation capabilities including process mining, governance and AI modules that can extend RPA capabilities.
- Pegasystems. This vendor has traditionally been a leader in business process management tools but expanded into RPA with the acquisition of OpenSpan in 2016, offering Pega Robotic Automation.
- UiPath. This vendor offers an open platform to help organizations efficiently automate business processes.
What to look for in RPA software
When enterprise leaders look for RPA technologies, they should consider the following features and functionality:
- Scalability. Enterprises are advised to select RPA platforms that can be centrally managed and scaled from a central control panel rather than deployed and scaled on each desktop.
- Speed. Enterprises should be able to design and test new robotic processes in a few hours or less as well as optimize the bots to work quickly.
- Reliability. As companies launch robots to automate hundreds or even thousands of manual tasks, they should look for tools with built-in monitoring and analytics that let them monitor the health of their systems.
- Simplicity. Organizations should look for products that are simple enough that their employees can build and use them to handle various kinds of work, including using low-code processes or collecting data and turning content into information that helps leaders make the best business decisions.
- Intelligence. The best RPA tools can support simple task-based activities, read and write to any data source, and take advantage of more advanced learning to further improve automation.
- Enterprise-class. Companies should look for tools that are built from the ground up for enterprise-grade scalability, reliability and manageability.
- Governance. Enterprises need to look at the various security and governance capabilities to help manage bot security credentials, assess any privacy issues and flag any other issues.
- Financial planning. Tools for logging bot usage can help teams assess the return on investment of existing bots and prioritize opportunities for new automation based on estimated value.
- Attended or unattended. Attended RPAs perform well when a business user requires them to perform a defined task at a specific time, while unattended RPAs are preferable when they're needed to perform in a continual workflow.
- Integrations. The RPA should be able to integrate well with an organization's application.
C-level decision-making around RPA
Though automation software will replace many jobs, others will be created for the people who maintain and improve RPA software.

When software robots do replace people in the enterprise, C-level executives need to be responsible for ensuring that business outcomes are achieved and new governance policies are met.
Robotic process automation technology also requires that the chief technology officer or chief information officer (CIO) take more of a leadership role and assume accountability for the business outcomes and the risks of deploying RPA tools.
Additionally, the chief operating officer (COO), CIO and chief HR officer, as well as the relevant C-level executive who owns the process being automated, should all work toward ensuring the availability of an enterprise-grade, secure platform for controlling and operating bots across systems.
- The chief executive officer should oversee making the digital transformation process a part of the company and should focus on enabling the coexistence between employees and bots.
- The chief financial officer is responsible for the cost-benefit analysis of deploying RPA and should assess and mitigate potential financial risks of RPA.
- The COO ensures the soundness of digitization strategies.
- The chief HR officer educates employees on the benefits of automation and provides information about the use of RPA and how it integrates with their workflows.
The evolution of RPA
The first developments of RPA began in the 1980s and 1990s. RPA is built on the success of macro technologies developed for automating manual tasks within applications such as Excel. In the 1980s, these capabilities were extended to many enterprise applications using highly customized data-scraping applications. In the 1990s, RPA developed further with the automation of user interface testing.
Several testing tool vendors beefed up their automation capabilities at the turn of the century to help automate user interaction testing and load testing. The actual term RPA was coined in 2012 by Phil Fersht, founder and lead analyst at HFS Research. The technology plodded along until about 2018, when it exploded in popularity as companies undertook digital transformation and RPA platform capabilities improved. Banks and insurance companies were some of the first industries to embrace RPA technology.
Today, RPA software is particularly useful for organizations that have many different and complicated systems that need to interact together fluidly. For instance, if an electronic form from an HR system is missing a zip code, traditional automation software would flag the form as having an exception and an employee would look up the correct zip code and enter it on the form. Once the form is complete, the employee might send it on to payroll so the information can be entered into the organization's payroll system. With RPA technology, however, software can adapt to interact with the payroll system without human assistance.
The future of the RPA market is driven by hyperautomation
Today, RPA continues to experience market growth. The increased adoption of RPA technologies by organizations to enhance their capabilities and performance and boost cost savings are prime reasons for the expected growth of RPA.
One of the leading factors of RPA's growth is the adoption and integration of AI and machine learning technologies into RPA products. AI-powered RPA bots can learn from data, thereby improving its performance over time. AI and machine learning also enable RPA bots to automate more complex tasks and be useful for a wider range of business processes.
Other trends increasing the potential future growth of RPA include the following:
- A shift to using cloud-based RPA.
- A shift to using RPA as a service.
- Development using no-code RPA.
- Process and task mining to help identify new automations.
In the past, Gartner predicted that over time, RPA's growth would also be accelerated using hyperautomation. Hyperautomation efforts combine RPA with other kinds of automation tooling, including low- and no-code development tools, BPM tools and decision engines. IPA and cognitive automation modules will make it easier to weave AI capabilities into these automations.
As hyperautomation takes hold, companies will need to develop a strategic approach to identifying and generating automation opportunities and then managing processes across the enterprise. Some organizations have established an automation center of excellence to coordinate and scale automation projects.
RPA and business process automation are complementary processes that drive digital transformation initiatives. Learn how RPA and BPA compare.







