process innovation
What is process innovation?
Process innovation is the application or introduction of a new technology or method for doing something that helps an organization remain competitive and meet customer demands. Innovations can be applied to a wide variety of processes in many companies and industries.
Different definitions of process innovation have emerged over the years.
For example, influential Austrian American management consultant and author Peter F. Drucker defined process innovation as "the systematic search for and implementation of better ways of doing things."
Henry Chesbrough, an American organizational theorist, proposes "the development of new ways of managing and organizing work that leads to improved performance."
Finally, author, consultant and Columbia Business School professor Rita Gunther McGrath states that process innovation is "the systematic enhancement of how work is carried out to increase value for clients or lower expenses."
These definitions notwithstanding, process innovation is simply the application of new technologies, strategies, techniques, people or skills to improve a process and generate tangible benefits for an organization. Often, organizations today bring in new information technology systems or find ways to use older systems in new ways to drive their process innovation efforts.
Why businesses need process innovations
A business process refers to a set of steps aimed at completing some kind of work or achieving some desired output. Sometimes an existing process doesn't produce the best outcomes.
Poorly designed or poorly performing processes can affect a company's productivity, competitiveness or profitability. Process innovation is meant to address these problems with the help of new technologies, techniques, strategies, people or skills.
Process innovation can generate value to internal customers, including employees or the organization itself, or it can create value to external customers, including business partners, end users or consumers.
Overall, an organization needs to see a significant increase in some of its KPIs to be a true process innovation.
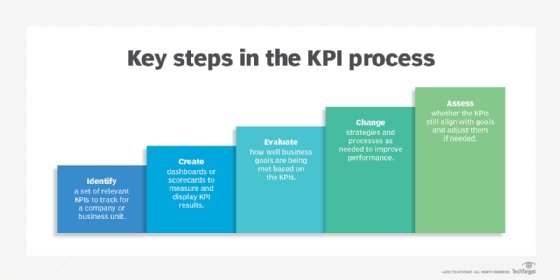
When and where does process innovation happen
Process innovation usually happens in one of two situations:
- When an organization needs to solve an existing problem.
- When it performs an existing business process in a radically different way that generates something highly beneficial to those who perform the process, those who rely on the process, those who benefit from the outcomes of the process or some combination of all three.
For example, the introduction of a completely new sequence to an existing production process in a manufacturing facility could be considered a process innovation, especially if the innovation can substantially speed up production saving the organization money and time.
Another example is harnessing robotic process automation (RPA) for a business process (e.g., data entry) that previously relied on human/manual inputs. Software robots (bots) can work every day and adapt to many kinds of process workflows.
Implementing bots instead of or alongside human workers can automate many repetitive manual tasks. Automation reduces task execution time and produces output with consistent quality. RPA bots also free up human workers to focus on higher-value tasks, which they can provide more benefits to the business with their capabilities.
A third example is a logistics company implementing truck platooning to improve vehicle-to-vehicle communication, improve fuel efficiency and reduce overall logistics costs.
What are the benefits of process innovation?
The key catalyst of any process innovation effort is the emergence of problems or gaps in an existing process. These problems can have a negative impact on the organization. For instance, the production costs of a company's manufacturing process may be too high due to underproduction, increased inventory costs or both.
By harnessing a new technology or method, the business might optimize its inventory levels or increase its production levels, thus decreasing unit costs and increasing overall profits.
In addition to lowering production costs, other possible goals of process innovation include the following:
- Improve product or service quality.
- Improve process efficiency and ROI.
- Produce new or improved products.
- Enhance customer experiences.
- Reduce the costs per product produced or service provided.
- Lower human resource costs.
- Reduce lead times or cycle times.
- Improve responsiveness to customer demands or emerging market forces.
- Strengthen the company's competitive advantage.
Examples of process innovations
Many companies have implemented radical innovations to improve processes and garner tangible benefits.
A well-known example is Ford. More than a century ago, Henry Ford implemented a conveyor belt system in the company's automobile manufacturing process. The new assembly line not only cut car production times and costs but also helped the firm improve its workers' shift times and wages.
Another automobile firm, Toyota, implemented process innovation in the form of the Toyota Production System. TPS focuses on lean manufacturing to improve production flows, cut waste and increase profits.
Walmart implemented inventory tracking systems and data analytics to improve its supply chain processes. These innovations helped the firm optimize its inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and meet customer demands for new or cheaper products.
Many other companies have implemented process innovations to improve their offerings and created a strong presence in their chosen market:
- Netflix.
- Starbucks.
- Amazon.
- Tesla.
- Airbnb.
Process innovation vs. incremental innovation
Incremental innovation is about making small changes to an existing process, product or service. These changes or improvements are usually low cost but have some tangible positive impact on the company in terms of product or process quality, cost savings, competitiveness or another factor.
Process innovation differs from incremental innovation in both scope and size. Whereas incremental or continuous improvements generate limited value, process innovation generates improvements that increase value by upward of 50%, 100% or even more.
Some describe process innovation as creating radical or game-changing shifts. In addition to the introduction of a radically new approach or technology, process innovation generally requires a longer planning time and support from executive management.
It is also riskier than incremental improvements and requires a higher level of culture and structural change. Process innovation typically impacts a broader portion of an organization or a larger number of stakeholders compared to incremental improvements or innovations.
Explore challenges for creating a culture of innovation. See the differences between value stream mapping vs. process mapping to drive process innovation.






