managerial grid model (The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid model)
What is the managerial grid model (The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid model)?
The managerial grid model (The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid model)is a self-assessment tool by which individuals and organizations can identify a manager's or leader's style. The grid was originally developed by Robert R. Blake and Jane S. Mouton in the 1960s and has evolved in subsequent decades.
Robert R. Blake was a pioneer in organizational dynamics and an American management theoretician. Jane S. Mouton was also a management theoretician. Both Blake and Mouton focused on the human side of business leadership in the 1950s and 1960s.
During their work to improve effective leadership at Exxon, they noted that management behavior worked on axes (i.e., concern for production and concern for people) and moved along a continuum. Based on this observation, they went on to create the Managerial Grid theory and model of leadership styles.
The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid model -- also known simply as the Blake Mouton Grid -- shows the degree to which a manager or leader focuses on production, people or both. Depending on where the person falls on the grid, their behavioral or managerial style can be determined.
The Blake Mouton Grid is created using a horizontal axis and a vertical axis that meet at a right angle and are rated on a nine-point scale:
- Horizontal axis -- concern for production. A one, or low concern for production, is placed to the far left of the horizontal axis, close to the right angle; a nine, or high concern for production, is located on the far right of the horizontal line. A high concern for production indicates that the leader prioritizes objectives, results and productivity when determining how a task should be accomplished.
- Vertical axis -- concern for people. A one, or low concern, falls at the bottom of the vertical line, close to the base near the right angle, while a nine, or high concern for people, is placed at the top of this vertical axis. A high concern for people indicates that the leader prioritizes the needs and interests of people when determining how a task should be accomplished.
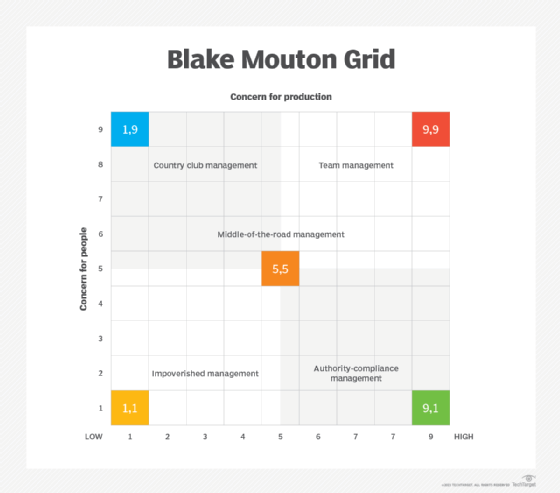
Leadership styles according to the Blake Mouton Grid
The Blake Mouton Grid shows whether an organization's leader is more people centric or production centric. On the basis of these focus areas, Blake and Mouton identified five leadership or management styles:
Impoverished management
This is represented by a manager who rates a 1/1 and falls on the grid's lower left quadrant. They have a low concern for both production and people. This is known as the impoverished management style, according to Blake and Mouton.
The impoverished management style is mostly ineffective both at meeting people's needs and at generating positive results for the organization. If anything, this style frequently leads to a disharmonious work environment and fails to resolve conflicts among team members.
Produce-or-perish management
A manager rated 9/1 will be positioned in the grid's lower right quadrant. This person has a high concern for production and results but low concern for people. They have a produce-or-perish management style.
Another term for a produce-or-perish manager is authoritarian or authority-compliance manager. This person can drive impressive results using strict rules and punitive measures. However, their unstinting focus on results over people adversely affects team morale and motivation, which then leads to an eventual decline in the quality and timeliness of desired results.
Middle-of-the-road management
A rating of 5/5 means that the leader falls in the center of the grid and is said to have a middle-of-the-road management style that suggests that the manager is equally concerned about both production and people. They try to balance both. However, the style can be ineffective because they are unable to prioritize either aspect.
Country club management
A manager with a 1/9 rating will be positioned in the top left quadrant. This person has a low concern for production but high concern for people and is said to have a country club management style.
Managers with a country club style of management try to make their people happy and satisfied at work. They believe that happy people will work hard and generate good results for the company. However, they trust people to manage themselves, so they may not provide adequate direction and coaching. As a result, they frequently find that productivity suffers and results are not what they expected or wanted.
Team management
A 9/9 rating would place the manager in the grid's upper right quadrant, indicating a team management leadership style. This person is highly committed to both production and people. These managers harness this commitment to creating a positive work environment where people feel respected, seen and heard.
This environment motivates and inspires people to give their best effort to the organization. In doing so, productivity goes up, and the leader can generate desirable results for the organization. By increasing employee satisfaction, they can also reduce absenteeism and turnover.
Additional management styles
In addition to those five leadership styles, Blake later identified two more styles:
- Paternalistic management. This leader is supportive of their people but also concerned with their own power and position, which they will guard zealously.
- Opportunistic management. An opportunistic manager puts their needs above the needs of their people or the organization. They are also willing to manipulate others to achieve their own goals.
Uses of the Blake Mouton Grid
The Blake Mouton Managerial Grid model is one of several assessment tools, such as the well-known Myers-Briggs Type Indicator personality inventory, that businesses can use to evaluate managers and leaders. Organizations use this tool to assess individual managers and identify their management styles with the aim of helping them build leadership excellence.
Individuals can also assess themselves using the grid by asking, for example, how strongly they value accomplishing a task as well as how much they enjoy the challenges of directing and coaching employees. The managerial grid, which is also known as the leadership grid, can also help managers understand their management strengths and shortcomings. This understanding can help them and their supervisors and HR partners to identify needed training and support to drive improvements in production processes and results, motivation levels and the overall work environment.
Creativity and innovation are the cornerstones of effective leadership. Learn the importance of innovative leadership in the workplace and the top qualities that innovative leaders possess.








