hard skills
What are hard skills?
Hard skills are specific abilities, capabilities and skill sets that an individual can possess and demonstrate in a measured way. Hard skills are learnable skills that enable individuals to perform job-specific tasks, or that may be required for a specific job.
While looking for new employees, employers will look at a candidate's hard skills listed in their resume. While job-specific hard skills are sought after, so can proficiency in more general hard skills -- such as fluency in a second language.
Hard skills typically focus on specific tasks needed to complete a job, like the use of specific software, tools or other equipment. They can be gained from experience or learned through training, schooling, apprenticeships, online courses and certification programs. Certifications, degrees and licenses can show a potential new hire has these skills.
As an example, a cloud engineer may want the hard skills shown in Figure 1.
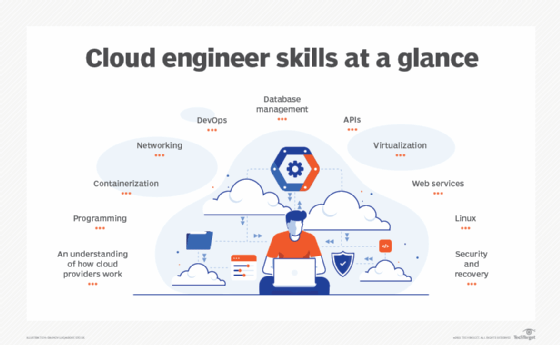
Types of hard skills
There are many types of hard skills, as they are skill sets that pair with any profession. Some examples of hard skills fall under specific categories, such as the following:
Analytical skills
- Data analysis.
- Data and metric interpreting.
- Data mining.
- Google Analytics or Google Search Console.
- Research.
Computer skills
- Computer software knowledge.
- Communication and collaboration tools.
- Microsoft Office Suite.
- Presentation software.
- Trello.
Communication skills
- Academic writing.
- Blog writing.
- Copywriting.
- Foreign language speaking.
- Proposal writing.
Marketing skills
- Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO).
- Email marketing.
- Pay per click (PPC) advertising.
- Search engine optimization (SEO).
- Social media.
Technical skills
- Computer-aided design (CAD).
- Machine learning (ML).
- Natural language processing (NLP).
- Programming languages.
- User interface design.
Additional skill examples
- Automotive services and design.
- Budgeting.
- Graphic design.
- Photo and video editing.
- Project management.
How to acquire hard skills
Although some individuals can have innate abilities that make it easier for them to learn a hard skill either through formal lessons or in informal ways, most people develop hard skills through some sort of educational process.
For example, some people have a natural sense of numbers that makes it easier for them to learn basic as well as complex math, yet they -- as well as others -- learn math through a series of lessons.
Individuals learn hard skills in various ways, including learning them in traditional schools, colleges and vocational education programs. Individuals can also learn hard skills through apprenticeships, mentoring, on-the-job training and hands-on training. Individuals can teach themselves hard skills, too, through books, online platforms and even through trial and error.
Certificates, diplomas, licenses and test scores are often used as proof that an individual has achieved a certain level of proficiency for a particular hard skill or set of hard skills.
A driver's license, for instance, demonstrates that an individual has demonstrated a minimum level of proficiency as determined by the government agency issuing the driver's license. A commercial driver's license shows that an individual has achieved another, higher level of proficiency.
Hard skills can also be considered technical skills.
Hard skills vs. soft skills
Soft skills, unlike hard skills, are characteristics or capabilities that are nearly impossible to quantify or measure in an objective way. So, judging one's soft skills is a subjective exercise.
Some soft skills are described as intangible; for example, being a good listener is a capacity that describes an individual's ability to hear a speaker's words and understand and empathize with the speaker. Although someone could measure the ability to correctly hear the speaker's words, the soft skill comes in the listener's capacity to understand and empathize -- a skill that's practically impossible to quantify, measure and compare against someone else using objective standards.
Soft skills are often called interpersonal or people skills.
Additionally, soft skills can describe an individual's own characteristics; examples of such soft skills include having a good work ethic or working well with others.
Individuals generally have a disposition that favors the expression of specific soft skills, but there is an element of nature vs. nurture as well. There aren't traditional degree programs or vocational programs focused on soft skills, but colleges, schools, organizations and even companies do indeed invest in developing soft skills in individuals.
Individuals can seek out learning opportunities and activities on their own to cultivate soft skills within themselves as well.
Why hard skills are important
Nearly all jobs today, including most professional positions, require hard skills.
Job descriptions frequently list a series of hard skills needed to be hired, and they also often list the preferred proof of those skills, such as degrees or certificates, that each job applicant needs in order to be considered for the position.
Possessing specific hard skills demonstrates one's ability to successfully perform the job and fulfill its duties.
For many professions in many companies, the possession of hard skills is important to ensure a company's financial success; however, in some instances, the worker's hard skills are critical to preventing catastrophic results. A surgeon, for example, must have very specific hard skills to ensure against unnecessary harm to a patient; a pipefitter must also be exacting in his or her application of hard skills to ensure against something like a gas leak.
Furthermore, many employers seek out soft skills, finding that interpersonal skills are needed -- sometimes in equal measure to their hard skills -- for individuals to successfully complete the jobs they're assigned to do.
Measuring hard skills
Hard skills are demonstrable and quantifiable; individuals who possess hard skills can be tested to prove their capacity in each hard skill they possess.
There are objective metrics that can be applied to the hard skill, not just subjective judgment.
Furthermore, an individual's proficiency in any particular hard skill can be measured against the proficiency of other individuals who possess that same hard skill.
Typing, for example, is a hard skill. Two individuals with the ability to type can be tested for speed and accuracy, with their scores determining which individual is more proficient in the skill.
Certifications, degrees and licenses can also show an individual has a certain aptitude for a hard skill. Hiring managers can measure an individual's hard skills by giving them a test during the interview process.
Hard skills to include on a resume and where to list them
Some of the most in-demand hard skills include the following:
- AI.
- Business and data analytics.
- Cloud and distributed computing.
- Data presentation.
- Digital marketing.
- Google Analytics.
- HTML/CSS/Javascript.
- Middleware and integration software.
- Project management.
- Machine learning.
- Mobile development.
- Network and information security.
- Software revision control systems.
- Structured Query Language (SQL).
- Statistical analysis and data mining.
- User interface design.
- Web architecture and development framework.
On a resume, a list of an individual's most relevant skills should be placed in a skills section.
First, determine what hard skills employers in the applying industry are looking for, then place the most relevant skills in the skills section of the resume. To help create a list of skills, job seekers should find the most relevant hard skills by researching the general job position and the specific job ad.
Hard skills in a job ad will include work experience needed, along with a list of skills required. These will include a mix of soft skills, like personality traits or communication skills, and required hard skills.
The skills section should be placed near the top of the resume so employers can quickly see the experience of the interviewee. Hard skills can also be referenced by providing examples in an accomplishments section -- this helps show employers that an individual is able to use their hard skills to be successful in a job.
The cover letter is another place to show an individual's hard skills. In a cover letter, hard skills can be mentioned as part of a story about work experience.
Learn more about valuable hard skills for cloud computing, must-have skills to succeed as an IT manager and IT skills required for e-commerce. Explore business intelligence skills to advance your career, technical skills required for human resources and 5 examples of VR's use in soft skills training.







