What is a decision support system (DSS)?
A decision support system (DSS) is a computer program used to improve a company's decision-making capabilities. It analyzes large amounts of data and presents an organization with the best possible options available.
DSSes bring together data and knowledge from different areas and sources to provide users with information beyond the usual reports and summaries. This is intended to help organizations make informed decisions.
A decision support application might gather and present the following typical information:
- Comparative sales figures between one week and the next.
- Projected revenue figures based on new product sales assumptions.
- The consequences of different decisions.
A DSS is an informational application as opposed to an operational application. Informational applications provide users with relevant information based on a variety of data sources to support better-informed decision-making. Operational applications, by contrast, record the details of business transactions, including the data required for the decision-support needs of a business.
A DSS is an information system commonly used by middle and upper management levels of an organization, typically in operations or planning teams.
What is the purpose of a DSS?
The purpose of a DSS is to gather, analyze and synthesize data to produce comprehensive information reports that an organization can use to assist in its decision-making process. Unlike tools that are limited to just data collection, DSSes also process that data to create detailed reports and projections.
DSSes are an adaptable tool meant to meet the specific needs of the organization using it. Finance, healthcare and supply chain management industries, for example, all use DSSes to help in their decision-making processes. A DSS report can provide insights on topics like sales trends, revenue, budgeting, project management, inventory management, supply chain optimization and healthcare management.
All of this is meant to provide decision-makers with comprehensive information that can be used to make quicker and more accurate decisions.
Decision support system components
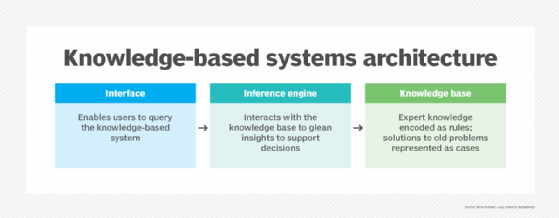
A typical DSS consists of three parts: a knowledge database, software and a user interface.
Knowledge base
A knowledge base is an integral part of a decision support system database, containing information from both internal and external sources. It's a library of information related to particular subjects and is the part of a DSS that stores information used by the system's reasoning engine to determine a course of action.
Software system
The software system is composed of model management systems. A model is a simulation of a real-world system with the goal of understanding how the system works and how it can be improved. Organizations use models to predict how outcomes will change with different adjustments to the system.
For example, models can be helpful for understanding systems that are too complicated, expensive or dangerous to fully explore in real life. That's the idea behind computer simulations used for scientific research, engineering tests, weather forecasting and many other applications.
Models can also be used to represent and explore systems that don't yet exist, like a proposed new technology, a planned factory or a business's supply chain. Businesses also use models to predict the outcomes of different changes to a system -- such as policies, risks and regulations -- to help make business decisions.
User interface
The user interface enables easy system navigation. The primary goal of the DSS's user interface is to make it easy for the user to manipulate the data that's stored on it. Businesses can use the interface to evaluate the effectiveness of DSS transactions for end users. DSS interfaces include simple windows, complex menu-driven interfaces and command-line interfaces.
What are the advantages of a DSS?
DSSes offer several advantages, including the following:
- Enable informed decision-making. By taking multiple different data sources into account, DSSes can facilitate better, up-to-date and informed decisions.
- Consider different outcomes. DSSes consider different business outcomes, as possible decisions are based on current and historical company data.
- Increase efficiency. DSSes automate the analysis of large data sets.
- Provide better collaboration. DSS tools might also include communication and collaboration features.
- Enable flexibility. DSSes can be used by many different industries.
- Handle complexity. DSSes can handle complex problems that have multiple interdependencies and variables.
What are the disadvantages of a DSS?
While DSSes offer several potential benefits, they also have notable downsides, including the following:
- Cost. Expenses for developing, implementing and maintaining DSSes can be high, which can limit their use by smaller organizations.
- Dependence. Developing an over-reliance on a DSS eventually takes away from the subjectivity involved in decision-making.
- Complexity. DSSes must consider all aspects of a given problem, which requires a lot of data. They can also be complex to design and implement.
- Security. Data that DSSes use might involve sensitive or critical data, meaning that an increased focus on security is required.
- Employee resistance. Some employees might be resistant to any workflow change based on the recommendations of a machine.
Intelligent decision support system
Users can also bake artificial intelligence (AI) into decision support systems. Called intelligent decision support systems (IDSSes), the AI mines and processes large amounts of data to get insights and make recommendations for better decision-making. It does this by analyzing multiple sources of data and identifying patterns, trends and associations to emulate human decision-making capabilities.
Designed to act like a human consultant, an IDSS gathers and analyzes data to support decision-makers by identifying and troubleshooting issues and providing and evaluating possible solutions. The AI component of the DSS emulates human capabilities as closely as possible, while more efficiently processing and analyzing information as a computer system.
IDSSes can include advanced capabilities and features such as the following:
- Advanced data analytics.
- A knowledge base.
- A user interface.
- Machine learning.
- Natural language processing.
- Adaptive learning.
- Automation of routine decisions.
- Personalization.
- Predictive analytics.
Examples of IDSS implementations include flexible or smart manufacturing systems, intelligent marketing decision support systems and medical diagnostic systems.
Types of decision support systems
DSSes can be broken down into the following categories, each based on their primary sources of information:
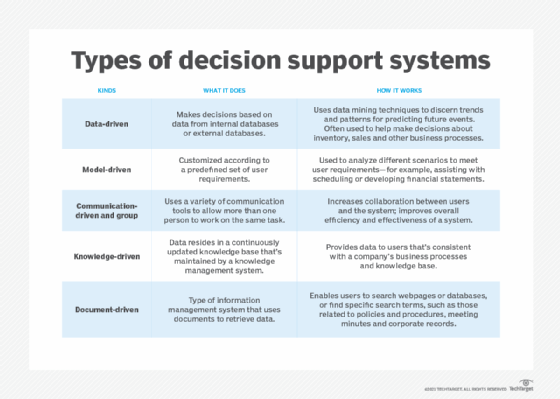
- Data-driven DSS. A data-driven DSS is a computer program that makes decisions based on data from internal or external databases. Typically, a data-driven DSS uses data mining techniques to discern trends and patterns, enabling it to predict future events. Businesses often use data-driven DSSes to help make decisions about inventory, sales and other business processes. DSSes are also used to help make decisions in the public sector, such as predicting the likelihood of future criminal behavior.
- Model-driven DSS. Built on an underlying decision model, model-driven decision support systems are customized according to a predefined set of user requirements to help analyze different scenarios that meet these requirements. For example, a model-driven DSS might assist with scheduling or developing financial statements.
- Communication-driven and group DSS. A communication-driven and group decision support system uses a variety of communication tools -- such as email, instant messaging or voice chat -- to enable more than one person to work on the same task. The goals behind this type of DSS are to increase collaboration between the users and the system and to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
- Knowledge-driven DSS. In this type of DSS, the data that drives the system resides in a knowledge base that's continuously updated and maintained by a knowledge management system. A knowledge-driven DSS provides information to users that's consistent with a company's business processes and knowledge.
- Document-driven DSS. A document-driven DSS is a type of information management system that uses documents to retrieve data. Document-driven DSSes enable users to search webpages and databases or find specific search terms. Examples of documents accessed by a document-driven DSS include policies and procedures, meeting minutes and corporate records.
Decision support system examples
Organizations use decision support systems in several different contexts, including the following:
- GPS routing. GPS route planning compares different routes, considering factors such as distance, driving time and cost. The GPS navigating system also enables users to choose alternative routes, displaying them on a map and providing step-by-step instructions.
- Enterprise resource planning dashboards. ERP dashboards can use a decision support system to visualize changes in production and business processes, monitor current business performance against set goals and identify areas for improvement. ERP dashboards let business owners see a snapshot of their company's most important numbers and metrics.
- Clinical decision support system. A CDSS is a software program that uses advanced decision-making algorithms to help physicians make the best medical decisions. Healthcare professionals often use CDSSes to interpret patient records and test results, and to calculate the best treatment plan. CDSSes in healthcare can help providers identify abnormalities during specific tests, as well as monitor patients after certain procedures to determine if they're having any adverse reactions. Some DSSes have been paired with neural networks to predict medication doses as well.
- Financial decision support. DSSes are commonly used in financial management to forecast financial trends, manage budgets, analyze investment options and assess risks. They enable organizations to make real-time data-driven, financial-based decisions.
- Marketing decision support. In marketing, DSSes assist in campaign planning, customer segmentation and market analysis. These tools provide insights into consumer behavior, marketing trends and past marketing efforts. They can also help businesses market to target audiences.
- Human resources support. HR departments use DSSes to help manage employee data, evaluate performance and make decisions regarding recruitment, retention and workforce planning. These systems can also help HR professionals analyze trends in employee satisfaction, productivity and turnover.
A decision support system can be integrated with AI to create an intelligent decision support system. Learn more about how AI can be integrated into business.







