Information and Content Exchange (ICE)
What is Information and Content Exchange (ICE)?
Information and Content Exchange (ICE) is an XML-based standard protocol for electronic business-to-business (B2B) asset management. Essentially, ICE makes it possible for companies to make content available to other websites and applications.
ICE version 1.1 was released in June 2000. Version 2.0 was released in 2004 and includes improved web service support. Version 2.0 is the most current release of the standard.
The ICE protocols define an architecture and a common language that can be used as a means of automating web content syndication -- information sharing and reuse between websites -- for publishing and e-commerce between syndicators and subscribers.
How does ICE work?
ICE enables the automation of functionality such as data supplying, exchanging, updating and controlling without requiring the supplier to manually package content or to maintain knowledge about the structure of recipient websites.
ICE specifies the creation of a trust relationship based on the Open Profiling System. The use of the ICE protocol enables data sharing between servers.
Digital assets sent over an ICE server can be in a range of formats including markup language like HTML, XML, as well as plain text, PDF, audio, video, graphics formats or streaming media.
For example, syndicated portions of a webpage can be automatically updated when the source is updated, or new content can be automatically entered and integrated with existing content on a webpage.
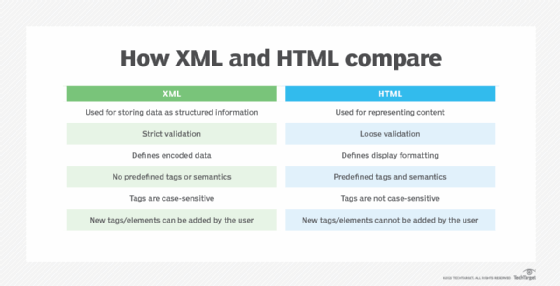
Each protocol message between servers consists of a valid -- conforming to namespace criteria -- XML document. XML tags are used to format data to be processed by the servers involved in the transaction.
What are the benefits of using ICE?
Because ICE makes it possible for almost every aspect of B2B asset exchange to be automated, it decreases the need to maintain a technical staff -- often a scarce resource -- for those purposes.
The use of the protocol allows information service providers to specify the content, customize it for specific recipients, schedule its delivery and implement content management to maintain it.
Nevertheless, the success of content syndication still relies on the development of a standard metadata vocabulary, considered to be another essential element.
The Publishing Requirements for Industry Standard Metadata ICE specification dictates a standard set of XML metadata vocabularies for content providers that aim to syndicate, aggregate and process multipurpose content.
ICE servers are also often used in conjunction with content management systems as an API where the XML metatags define the content format for data exchange between servers. This prevents the sender and receiver from having to manually format transmissions.
Notable Information and Content Exchange implementations
There have been two notable ICE implementations.
- ICEcubes is the original Java implementation of ICE 1.1. It has not been active since December 2000.
- TwICE and Rice are subsequent Java implementations of ICE 2.0.
However, ICE is not proprietary and may be developed by others.