ITIL V3
What is ITIL V3?
ITIL V3 is the third version of the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL), a globally recognized collection of best practices for managing IT and for implementing IT service management (ITSM) practices.
ITIL is one of the world's most popular frameworks for ITSM, an approach that is concerned with the design, strategy, operations, measurement, improvement and delivery of IT services. The original version of ITIL was a manual published in the 1980s to help government IT departments in the United Kingdom establish a framework for best practices.
Since its original publication, the ITIL framework has provided numerous best practices and recommendations that enable organizations to improve and optimize the way they use IT products and services. Leveraging ITIL for ITSM lets businesses capture more value from IT and facilitate desired outcomes by using IT.
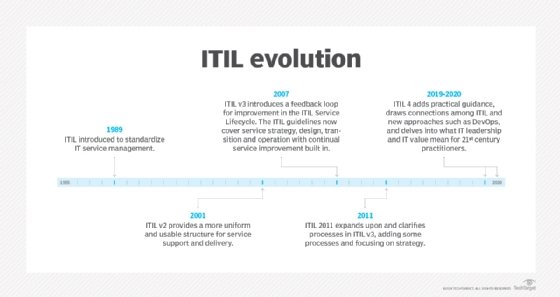
Like its predecessors, ITIL V3 provides a comprehensive set of best practices and processes that any organization can use to set up and optimize ITSM. Specifically, this version of ITIL consists of 20-plus processes and functions that revolve around the five stages, or "core books," of the ITIL service lifecycle. Each book in ITIL V3 covers one stage of the service lifecycle. A sixth book introduces ITSM and provides an overview of the five books within ITIL V3.
Phases in the ITIL V3 service lifecycle
The ITIL V3 framework describes five stages in the ITIL service lifecycle:
- ITIL service strategy. This specifies that each stage of the service lifecycle must stay focused on the business case, with defined business goals, requirements and service management principles.
- ITIL service design. This provides guidance for the production and maintenance of IT policies, architectures and documents.
- ITIL service transition. This focuses on change management and release practices, providing guidance and process activities for transitioning services into the business environment.
- ITIL service operation. This focuses on delivery and control process activities based on a selection of service support and service delivery control points.
- ITIL continual service improvement. This focuses on the process elements involved in identifying and introducing service management improvements as well as issues surrounding service retirement.
Together these stages form a closed loop process that helps organizations optimize ITSM and align it with evolving business requirements. Additionally, each stage is self-contained, and they help businesses gain a deeper understanding of ITSM and its key "how to" considerations. Those considerations include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Building a clear IT service strategy.
- Creating and delivering value with IT.
- Creating robust business cases to secure IT investments.
- Measuring service performance and improving service quality.
- Designing IT services that meet business requirements and delivering business desired outcomes.
- Managing service transitions and change.
Important processes in ITIL V3
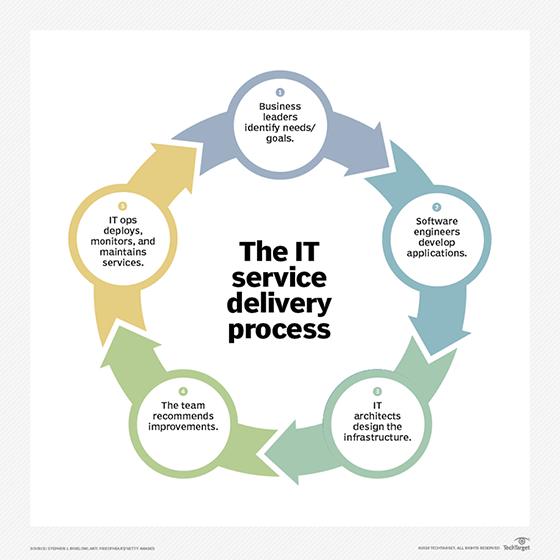
Each of the five phases of the ITIL V3 framework include several key processes that can help optimize ITSM. The first four phases include several important processes.
Phase 1: ITIL service strategy
The service strategy phase and publication in ITIL V3 helps organizations build a clear IT service strategy that clarifies what services are required (or should be offered), who will use these services, how the value of these services will be created and how service performance will be measured.
Process: Financial management
A systematic financial management process enables organizations to clarify and manage their IT budgeting, accounting and charging requirements. Apart from IT, other departments also use IT financial information to guide critical activities and decisions.
Process: Service portfolio management
The SPM process is an ongoing effort to create an IT portfolio, define IT inventory services, authorize services and resources, and communicate decisions to relevant stakeholders.
Process: Demand management
Demand management is an important process since it involves understanding the demand for IT services and the provisioning capacity required to meet these demands. If demand is not properly managed, it may result in under- or over-provisioning of capacity, both of which can negatively affect the organization.
Phase 2: ITIL service design
This phase of the ITIL service lifecycle phase is concerned with the design of IT services required by the business. It starts with a set of business requirements and ends with a service design package.
Process: Service catalog management
The SCM process helps create a consistent source of information about IT services. It also ensures that the services are available to those who are approved to access them.
Process: Service level management
SLM is concerned with documenting the business' IT service targets and ensuring that all operational services meet the business' needs. The SLM process generates information in the form of service level agreements, operational level agreements, and service improvement plan.
Process: Capacity management
The capacity management process provides a way to manage and mitigate capacity and performance-related issues and to ensure that available IT capacity matches business demands.
Process: IT service continuity management
The goal of ITSCM is to maintain the on-going recovery capability within IT services in order to match business needs and timescales.
Process: Information security management
ISM is crucial to maintain the confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA triad) of enterprise data. To secure and protect data, a detailed ISM policy as well as supporting controls with a Security Management Information System are all crucial.
Phase 3: ITIL service transition
In this phase, the IT services that were designed in Phase 2 are delivered to the business and put into operational use.
Process: Change management
A formal change management process is required to ensure only standardized methods are used to handle, implement and document all IT-related changes. Standardization helps the organization maintain control over changes and reduces business risk.
Process: Service asset and configuration management
The SACM process helps businesses to identify and control all service assets and configuration items and maintain their integrity across the service lifecycle. A configuration management system helps streamline SACM throughout the organization's infrastructure.
Process: Knowledge management
Knowledge management aims to ensure the right knowledge is available at the right time and to the right people to maintain a common understanding of available IT services and improve the efficiency and quality of those services.
Process: Release and deployment management
A strong release and deployment management process ensures all changes are delivered at the right speed, while minimizing risk and cost to the business. It also facilitates the effective use of new or changed services.
Phase 4: ITIL service operation
After the required IT services are designed and implemented, the service operation phase starts. The purpose of this phase is to deliver agreed-upon levels of service to users; to ensure that the services deliver value to the business; and to manage the various elements -- applications, technology, infrastructure -- that support service delivery.
Process: Event management
It's important to address events as soon as they are detected, especially if the event indicates that something is not functioning correctly. Event response may be automated or manual.
Process: Incident management
A well-planned, documented and tested incident management process helps restore normal service following an unplanned interruption. It also minimizes the adverse impact of an incident on business operations.
Process: Access management
Access management is a crucial process because it helps control access to enterprise systems and maintains the CIA of data.
Phase 5: ITIL continual service improvement
This last phase helps organizations to evaluate and improve IT service quality and ensure that IT continues to deliver value to the business. ITIL V3 suggests a 7-step improvement process:
- Define what should be measured.
- Define what can be measured.
- Gather data via monitoring tools and manual processes.
- Process the collected data to understand the performance of IT services.
- Analyze the data to understand trends and to determine if corrective actions are required.
- Present the information to decision-makers in their preferred format.
- Implement corrective action to optimize and improve IT services.
What is the difference between ITIL V2 and V3?
Businesses and business requirements continuously change. To keep up with these requirements, ITIL has also evolved. ITIL V3 follows ITIL V2, which was published in 2000.. V3 was made available in 2007 and is therefore also known as the ITIL 2007 Edition.
While ITIL V2 was process oriented and remained strongly focused on basic IT operations, ITIL V3 emphasizes the concept that IT is a service that supports business goals. At the same time, V3 builds on the best practices and processes of V2 as well as adds more useful recommendations to provide a more comprehensive ITSM framework that emphasizes the IT-as-a-service approach.
ITIL V3 certification
The ITIL V3 certification is highly sought after in the IT industry. IT professionals can achieve the certification after completing five levels: Foundation, Practitioner, Intermediate, Expert, and Master. The Foundation level covers the terminology and basic concepts of ITIL, while the higher levels go into greater depth for each of ITIL's major topics.
Explore ITIL and DevOps to see what path an enterprise should choose. See how to plan for a successful ITIL implementation.







