
What is a chief technology officer (CTO)?
A chief technology officer (CTO) is a high-level executive who is responsible for overseeing an organization's strategic use of IT. This job role typically requires successful candidates to hold a college degree and have a combination of technical expertise, business acumen and leadership skills.
What does a CTO do?
Job descriptions for CTOs can be quite fluid, and responsibilities can vary significantly depending on an organization's size, industry and business objectives.
In some companies, the CTO's responsibilities are primarily outward-facing and focus on how technology can be used to improve product offerings, enhance customer experience or drive innovation. In other organizations, the CTO role might be more inward-facing, and responsibilities might overlap with chief information officer (CIO) or chief security officer (CSO) roles.
In small organizations and startups, a single executive might act as CTO, CIO and CSO.
How to become a CTO
Chief technology officer is a multidisciplinary career path that typically pays quite well. Individuals who want to become a CTO should have an undergraduate degree in computer science or a related field of study. An advanced degree in business administration can also be helpful, especially when paired with relevant work experience. While there are no specific certifications required for CTOs, job candidates for this role are often encouraged to hold business project management certifications, cybersecurity certifications and cloud certifications.
This article is part of
The evolving CIO role: From IT operator to business strategist
Successful candidates for CTO jobs often have at least 10 years of experience working in IT. Many aspiring CTOs start their careers as IT specialists, network administrators or software engineers. This allows them to gain hands-on experience while preparing to move into a leadership role.
Strategies for becoming a CTO include the following:
- Pursuing advanced degrees in business and relevant areas of technology.
- Acquiring extensive experience in IT project management.
- Staying on top of emerging technologies and business trends.
- Building a strong professional network by engaging with industry professionals, attending tech conferences and joining professional organizations.
- Taking on responsibilities that involve overseeing product development, optimizing IT operations or leading a digital transformation initiative.
- Earning certifications in topics such as cybersecurity, infrastructure architecture, software engineering, AI and machine learning, cloud computing, project management, data science and analytics, information systems management, or blockchain.
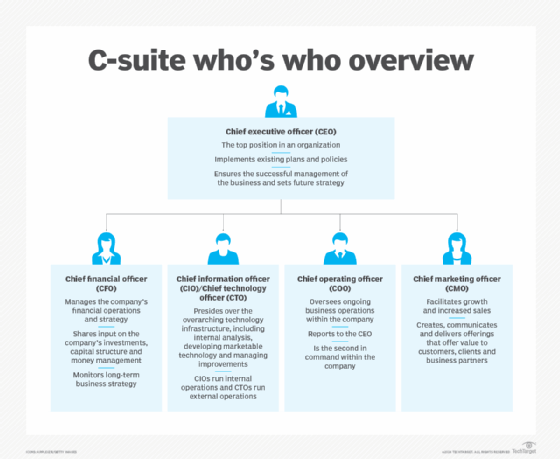
CIO vs. CTO
As an organization grows, its requirements for IT infrastructure can increase dramatically. To accommodate changing requirements faster and more effectively, many enterprise IT departments separate the chief technology officer role from the chief information officer role.
In some companies, the roles and responsibilities of the CIO and CTO are set up to complement each other. For example, the CIO might be tasked with managing internal IT operations, while the CTO handles customer-facing technologies designed to elevate customer experience.
In other organizations, however, the distinction between the two roles might be less defined, and a company might assign the title of CTO to a role traditionally held by a CIO, or vice versa.
Types of CTOs
To understand what type of CTO an organization is looking for, it can be helpful to examine the requirements for specific CTO job openings as they apply to the following four categories:
- Strategic planner. The CTO is responsible for aligning IT with organizational goals and helping to drive innovation through digital transformation.
- Customer-focused. The CTO works closely with product teams, marketing departments and customers to deliver user-centric technology that improves customer experience.
- Visionary and thinker. The CTO's job responsibilities involve researching emerging technology and educating executive leadership about how different types of technology can help the organization operate in a more cost-effective manner or gain a competitive edge.
- Infrastructure leader. The CTO is responsible for reducing technical debt and overseeing the acquisition, use and management of internal and cloud IT infrastructure.

CTO job responsibilities
If the CTO is responsible for technology strategy and innovation, job postings might mention the CTO's role in shaping the company's roadmap for digital transformation and ensuring that all technology decisions align with business goals. Specific responsibilities often include the following:
- Monitoring emerging technology trends in AI and machine learning and evaluating their potential impact on the organization.
- Identifying opportunities for technology-driven business transformation.
- Participating in corporate governance and strategic planning initiatives.
If the CTO is responsible for research and development, job postings might focus on how the organization uses technology to meet business goals. Specific responsibilities for this type of CTO often include the following:
- Overseeing technology infrastructure upgrades and software development projects.
- Managing AI, machine learning, cloud computing and blockchain adoption.
- Researching and approving information systems design and communication networks.
- Mitigating risk by supporting industry standards and enforcing regulatory compliance requirements.
If the CTO's responsibilities include business growth and market expansion, job postings might indicate that successful candidates will need to work closely with the organization's marketing, product development and operations teams. Key responsibilities typically include the following:
- Developing customer-facing technologies that enhance digital experience.
- Leading digital transformation initiatives.
- Identifying potential pilot opportunities to reduce the risks involved in deploying AI and other types of new technology.
- Collaborating or partnering with vendors, suppliers and industry leaders to drive innovation strategically.
If an organization's CTO is responsible for infrastructure, job postings might focus on tasks that will help make sure that in-house, cloud and hybrid infrastructures are scalable and secure. Specific responsibilities often involve the following:
- Managing cybersecurity threats and ensuring compliance with data privacy laws.
- Overseeing IT budgets.
- Researching the pros and cons of cloud computing and supporting hybrid IT environments.
- Researching technology spending forecasts and cost optimization strategies for cloud computing and AI projects.
In some cases, the CTO might also be responsible for working with human resources departments to recruit candidates who can fill the most in-demand IT jobs and to retain IT talent. In this case, job postings might include requirements that involve the following:
- Building a strong IT leadership team.
- Creating a succession plan for key roles in IT.
- Mentoring employees and fostering a culture of innovation.
- Supporting diversity, equity and inclusion initiatives within IT teams.
CTO skill requirements
Successful CTO candidates typically have the following skills:
- Business skills. It's important for CTOs to understand the fundamentals of their organization's industry. Successful candidates have in-depth knowledge of financial planning and risk management and are able to align technology investments with business goals effectively.
- Decision-making skills. CTOs must make different types of business decisions depending on the type of CTO their organization is hiring. An effective CTO can see the big picture and understand how technological decisions made today will affect the organization in the future.
- Leadership skills. CTOs need to have strong leadership skills. Engaging with industry peers, staying informed about technological advancements and having the ability to drive change within an organization can all contribute to career progression.
- Communication skills. CTOs need strong communication skills and should be able to explain technology to other executives in ways that accommodate varying levels of technical knowledge.
- Soft skills. Soft skills are personal attributes that enable individuals to work effectively with others. Important soft skills for CTOs include problem-solving, multitasking, time management and the desire to continuously learn new hard skills. Hard skills are technical proficiencies that can be acquired through education and on-the-job training.
CTO salary and job outlook
While not a hard-and-fast rule, it's increasingly common for CTO positions that have a strong focus on aligning technology with business goals to earn as much as CIOs, especially in industries where technology is a core business driver. Specific salaries can vary widely due to company size and location, but in general, the technology, finance and healthcare sectors offer the highest compensation.
According to Salary.com, the average CTO salary for April 2025 was $264,557 per year in the United States. According to a survey conducted in 2024 by STX Next, almost 20% of the more than 100 CTOs who responded to the survey indicated that they were "completely satisfied" with their salary.
The future of the CTO role
The CTO's role has been evolving over the years in response to digital transformation initiatives and an increasing reliance on technology. To make sure that IT remains a key enabler of growth and innovation, future CTOs will need to be more business-oriented and visionary than ever before.
It's likely that in the years ahead, the CTO role in large enterprises will become more specialized. Some companies might expand the CTO's leadership team by appointing chief AI officers or chief cloud officers, while other companies might appoint multiple CTOs who will focus on different technologies and business trends.
Technologies and business trends that are shaping the future of CTO responsibilities include the following:
- AI and automation. AI-powered systems are revolutionizing business intelligence, cybersecurity and customer engagement.
- Cloud computing and edge computing. Companies are adopting hybrid cloud infrastructure and edge computing to enhance scalability.
- Cybersecurity and data privacy. As cyberthreats increase, CTOs are playing crucial roles in data security and regulatory compliance.
- Sustainable and ethical technology use. Many organizations are focusing on eco-friendly technology and responsible AI development.
Learn more about the difference between CIO, CSO and CTO job titles and why the specific responsibilities of each role can vary depending on the company's product, business model and size.





