business services
What are business services?
Business services refer to all services that support a company. They do not create or deliver any physical products. Even so, they provide some benefits to the company, such as cost reductions, streamlined operations, increased employee productivity, etc.
Information technology (IT) is an important business service that supports many other business services, such as procurement, shipping and finance.
The services might be provided by one of a company's internal departments. Examples, besides IT, include accounting, marketing and business consulting. Companies that don't have the internal resources to provide needed services might turn to outsourcing. In doing so, they can not only access those services but also do so in what is typically a cost-effective manner.
Outsourcing also enables companies to get the professional services they need from experts or specialists who use the appropriate tools and technologies, but the only costs to the company are for the services being purchased. Furthermore, by outsourcing, a company can focus on its core competencies and leave noncore activities to the service provider.

What are the characteristics of business services?
The main characteristic of business services is that they are intangible, so the provision of these services doesn't result in the creation of a tangible or physical product. Also, since services have no physical component, they cannot be stored like inventory for later use. Furthermore, service production and consumption are inseparable, meaning services are consumed at the same time as they are produced.
It is difficult to ensure consistency in the performance and delivery of services. Services are usually performed by humans and inconsistency is a human trait. Also, the customer's demands or requirements might change and the service provider must make appropriate adjustments to service delivery to continue to meet customer expectations.
Finally, services are always provided in response to a customer's need. This also means that customer involvement is required to clarify requirements, convey expectations, set service-level agreements (SLAs) and verify quality of service (QoS).

Types of business services
Business services encompass many types of services. The five most popular and in-demand business services for organizations are:
Cybersecurity and information security. Certified cloud security service professionals (CSSPs) help organizations secure their IT networks and assets from cybercriminals. They might provide services related to information security, threat hunting, intrusion detection, incident response, data breach prevention, vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, etc. They might also provide security operation centers (SOCs) equipped with advanced security technologies and experts who monitor and protect the organization from threats and attacks.
Some CSSPs provide on-site security support while others provide only remote support. Either way, businesses that want to strengthen their security posture but do not have the funds to invest in cybersecurity tools and the appropriate personnel can benefit from the services of CSSPs.
Business consulting. Various types of companies hire business consulting service providers to provide insights, advice and recommendations for a variety of business processes. Some consultants help startups build a business strategy or roadmap. Others work with entrepreneurs to develop a business plan to attract investors.
Other consultants provide their expertise in company management, market research, risk management, compliance management, operations and many other fields. Regardless of their area of expertise, high-quality business consulting services help companies resolve problems and meet goals.
Training. Many companies need to train their employees in many disciplines, including health and safety, cybersecurity, soft skills, project management, ethical behaviors, compliance and more. Not all companies have extensive training departments or in-house trainers to design and deliver required training programs. Training providers help to fill the gap.
Most providers specialize in specific areas, which allows them to develop broad expertise in that area and provide high-quality training to their clients. Many training companies design their own courses, training sessions, workshops and presentations, tailor their offerings for specific clients, and then deliver them as required by clients.
IT. Many modern organizations have IT departments or ample resources dedicated to IT management. However, many companies still outsource IT activities to external service providers. These providers can help with software installations and patching, hardware configurations and installations, software development, cloud migration and systems integration.
Some IT providers also monitor and maintain an organization's IT infrastructure. Others provide IT help desk services for the organization's employees. Experienced providers also offer services to guide organizations with IT investments, streamlining IT service management (ITSM) and helping them to increase IT return on investment (ROI).
Marketing. Many companies hire firms that provide marketing and promotional services, especially if the services are more cost-effective to outsource than implementing an in-house marketing department. These providers help companies create marketing strategies, design new campaigns, advertise their products, increase return on ad spend, promote their brand and engage with customers on multiple channels.
Increasingly, organizations are also engaging with providers who provide the following services:
- Housekeeping.
- Creative services like graphic design, content writing and translations.
- Transportation.
- Waste management.
- Pest control.
- Event planning.
- Physical security.
- Accounting and bookkeeping.
- Public relations.
What is a service business?
A service business provides some kind of service to individuals or other businesses and typically engages in a detailed consultation with prospective clients before the actual work commences. A service business might also sign detailed contracts, identify SLAs, clarify the deliverables and associated metrics, and might sign non-disclosure agreements (NDAs).
Regardless of customer type, successful service businesses focus on customer satisfaction. They make an effort to build relationships with customers, ask for feedback and implement practices to improve their services and enhance customers' experiences.
Service level agreement and key performance indicators
A service level agreement clearly states a service provider's deliverables to a client and the consequences of not providing those deliverables. To be valid and legally enforceable, the SLA must be reviewed and signed by both parties.
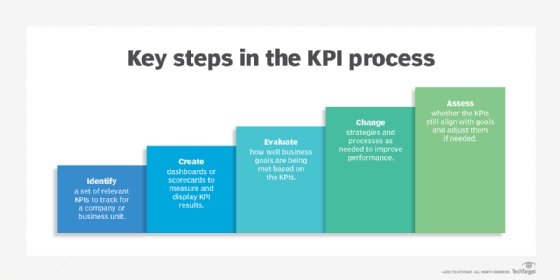
Most SLAs include details of the service being provided and the standards the provider is required to meet. Many SLAs also include the metrics that the client will use to measure the provider's performance and to confirm that it matches client expectations. These metrics are known as key performance indicators or KPIs. If KPIs are included in the SLA, the document might also include statements about how the KPIs will be measured and monitored, and the cost the provider will incur by not meeting them.
Business services and IT
A good business service aligns IT assets with the needs of a company's employees and customers and supports business goals, such as profitability. Documenting the value that an IT department provides to the business often involves an audit of IT processes, the creation or updating of an IT service catalog and/or the provisioning of an employee self-service portal to improve communication.
See how to adapt IT service management (ITSM) workflows for modern IT needs and explore the top five IT services trends for technology and service providers. Check out 16 top business process management tools and seven business process management challenges and how to fix them.








