
Seraphim Vector - Fotolia
Accelerate data migration with AWS DataSync
Dig into the details of AWS DataSync, such as deployment options and availability. Compare it to similar AWS services and see how it can fit into an organization's cloud strategy.
Cloud vendors try to balance the addition of new services with features that make it as convenient as possible to adopt.
The big three cloud vendors -- AWS, Microsoft and Google -- want to convince enterprises to move existing infrastructure and applications to their hosted infrastructure. Therefore, they need data migration services that reduce the friction of migrating applications and data to the cloud.
With that goal in mind, AWS rolled out DataSync to add to its existing set of data, database and server migration services. DataSync streamlines and accelerates network data transfers between on-premises systems and AWS. It copies data up to 10 times faster than open source tools used to replicate data over an AWS VPN tunnel or Direct Connect circuit, such as rsync and unison, according to AWS. Let's explore AWS DataSync's features, operating principles, advantages, usage and pricing.
AWS DataSync features and operating model
DataSync works through a VM agent that's mounted on a local server as a network file system (NFS) share. The agent establishes a secure Transport Layer Security (TLS) connection with the DataSync service, which can then access Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) file systems or S3 buckets.
AWS DataSync uses a proprietary data transfer protocol and accelerates data movement over the WAN with incremental transfers of changed files and inline compression with sparse file detection. It also enables transfer data validation and encryption.
Connections between the on-premises agent and AWS are multithreaded and horizontally scalable. Users can add agents to increase throughput and maximize utilization of up to 10 Gbps network links. Users can also configure bandwidth caps to avoid degraded network performance for other applications.
When copying to S3, each file is converted to an object, and file metadata is stored as S3 object metadata. When copying to EFS, DataSync mirrors the entire directory structure of the original NFS share and preserves file system metadata within EFS. For security, DataSync uses TLS encryption during transmission and writes encrypted data to either S3 or EFS. It integrates with AWS Key Management Service for user-managed keys but also supports Amazon-managed S3 encryption keys and EFS encryption.
DataSync works with the full complement of AWS infrastructure services, and users can monitor, log and audit usage with CloudWatch and CloudTrail.
Deploy AWS DataSync in three steps
Use of AWS DataSync involves a few simple steps:
- In AWS Console, set up the DataSync agent for either on-premises transfer to AWS or vice versa.
- Download the agent software in the form of an open virtualization archive image from AWS Console. The image runs on VMware ESXi -- version 6.0 or greater) -- in your data center and requires a VM with four virtual CPUs, 80 GB free space and at least 32 GB of memory. Once installed, mount the agent via NFS on systems with data -- or access to arrays with data -- you wish to transfer to AWS.
- In AWS Console, create a data transfer task that specifies the data source, destination and any required options, such as copying file metadata.
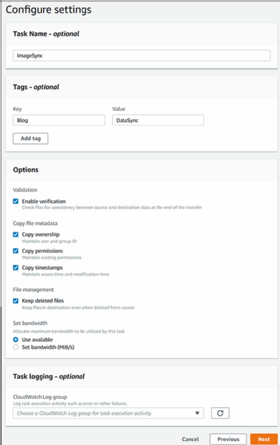
The result is a DataSync task that you can run via AWS Console or a command-line interface. After DataSync makes its initial copy for each run, it scans the source and destination for changes and copies the differences. As displayed in the configuration screen, you can keep previously copied files that have subsequently been deleted on the target in the destination; otherwise, they are purged.
Uses and comparison with other Amazon services
AWS DataSync can migrate active application data to S3 objects or EFS files, but it is useful for other scenarios as well. It can:
- copy data from on-premises sources for cloud processing by AWS machine learning, AI or analytics services or custom high-performance computing applications run on AWS;
- replicate data for long-term archival or disaster recovery; and
- use S3 as an auxiliary storage location with data accessed by on-premises applications via AWS Storage Gateway or even a third-party hybrid storage appliance, such as Avere.
Amazon has several services for bulk data transfers:
- Snowball Edge is more appropriate for massive, one-time data copies for users with limited bandwidth. In comparison, DataSync is better for data set synchronization between environments that regularly change.
- Storage Gateway is a hybrid storage service that complements Data Sync and provides a real-time, low-latency connection between environments. DataSync can seed data set into AWS, and Storage Gateway can provide transparent access for on-premises users and applications.
- S3 Transfer Acceleration provides similar capabilities to DataSync but is designed for applications using the S3 API. S3 Transfer Acceleration loads large quantities of data from remote clients into an S3 bucket. It is particularly appropriate for applications with global reach since it integrates with CloudFront to optimize the network path between remote clients and AWS infrastructure.
Pricing and availability
AWS DataSync has a straightforward pricing model with a flat rate of $0.04 per GB of data transferred. DataSync also relies on several other Amazon services that carry their own separate charges, such as S3, EFS, Site-to-Site VPN, VPN CloudHub or Direct Connect network connections, and CloudWatch.
As of publication, DataSync is available in 10 regions -- four in the U.S., two in Europe and four in Asia-Pacific.





