Fotolia
Craft an application integration strategy and pick the best tool
Application integration is easier said than done. Learn how to navigate this challenging process -- particularly, if you're integrating legacy applications with new applications.
Forming a proper application integration strategy is an essential part of enabling applications to work with one another. While it can be a difficult process, the benefits are worth it.
Application integration enables apps to exchange data with one another by invoking services that are exposed by those applications -- it helps create interoperability between disparate systems. It also helps enterprises transition to new technologies quickly and easily, which increases productivity.
Application integration is especially important in these scenarios when enterprises need to:
- Integrate a large number of applications
- Integrate several APIs in the near future
- Publish services or APIs for external consumption
- Have a seamlessly scalable platform
- Expand the number of communication protocols you can support
This process should not be confused with data integration. While the purpose of data integration is to link, transform and translate application data, application integration consolidates data from several sources into a single repository. This helps simplify and automate business processes, keep applications updated and reduce data redundancy.
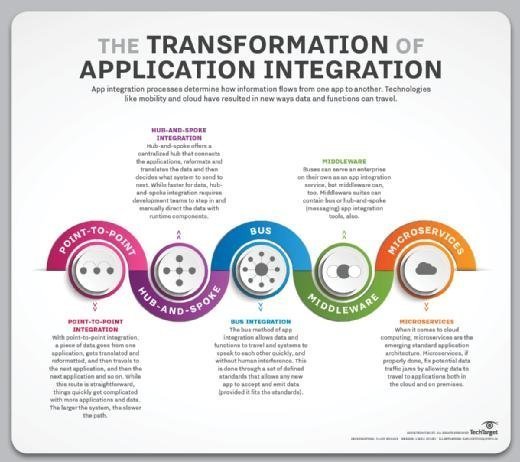
Application integration strategy benefits
A well-defined application integration strategy helps an organization in numerous areas. Here are few of the top reasons to adopt an application integration strategy for your organization:
- Costs. Once you have a defined strategy in place, costs decrease because developers don't need to reinvent the wheel each time there is a need for application integration.
- Scalability. A scalable integration platform that supports all types of apps helps the business to grow.
- Control. Application integration improves the control of the information flow. It provides improved data visibility, which enables organizations to observe, measure and embrace data all through the workflow.
Top application integration tools
With a wide variety of application integration tools available, selecting the right tool for your organization might be difficult. Try to focus on three particular factors:
- Flexibility
- Integration beyond the cloud
- Connection to several endpoints
Here are a few popular application integration tools:
IBM MQSeries is an enterprise application tool that works with multiple computing platforms, application types, web service frameworks and communications protocols. You can use this tool to link disparate applications residing in diverse environments and to integrate the back end with external systems in a consistent manner.
Microsoft BizTalk Server helps organizations optimize business processes through adapters that are built for multilanguage communication. BizTalk contains tools that help develop, design, deploy and manage business processes across large organizations.
Oracle Fusion represents one of the most complete and unified application integration tools. Fusion aims to maintain optimized portability as teams develop, monitor and improve processes over time. One of the striking features of this tool is modularity, which allows you to install, configure and use only the services the organization needs.
Tibco Software's integration tools possess some of the most advanced business process management features available in application integration services. These tools are widely used to integrate enterprise applications residing in heterogeneous business systems.
Talend offers various tools, such as Talend Data Fabric and Talend Cloud Data Integration. These open source integration tools can help organizations achieve better operational agility. One standout feature in its portfolio of offerings is a simple GUI that allows developers to quickly build, test and publish application services.
Specific use cases for application integration
Application integration has a significant, tangible impact on organizational processes. Here are some industry-specific examples of where it affects the business:
- Banking. Banks need to integrate customer profiles, credit card accounts and other back-end services with easy-to-use mobile apps.
- Manufacturing. Manufacturing plants need to monitor production processes across various systems, such as scheduling systems.
- Healthcare. Healthcare organizations must integrate patient records with electronic health record systems and allow doctors to easily access medical histories, treatment details and other related information.
- Business mergers. Many times, enterprises have multiple independent systems that contain the same data due to mergers and acquisitions. This requires the integration of multiple data repositories.
- Sales. Marketing and sales personnel need dashboards that provide customer information and insights on ROI. This means they must integrate data from multiple sources, particularly point-of-sale applications.