
Getty Images
How to add and enroll devices to Microsoft Intune
The Intune enrollment process can follow several paths, but one of the most common and efficient approaches involves Windows Autopilot. IT can set this up within Intune.
All aspects of Microsoft Intune devices management begin with the same step: device enrollment.
The enrollment process requires Intune to install a mobile device management (MDM) certificate on the device that allows Intune to communicate with it directly. Via this communication with Intune, IT administrators can deploy policies, control updates and perform general management tasks on devices such as Windows desktops.
What are the options for enrolling Windows devices?
There are multiple options that IT can choose to enroll Windows devices with Intune, and the differentiator for these enrollment scenarios often comes down to the ownership of the device. There are different enrollment scenarios available for personally owned devices and corporate-owned devices with the goal of keeping personally owned devices personal and keeping corporate-owned devices corporate.
- Windows Autopilot. For corporate-owned devices, Windows Autopilot is the most common option. Windows Autopilot is a service with a collection of technologies that aims to simplify the initial setup and deployment of new devices. During that process, the device is automatically joined to Microsoft Entra ID and automatically enrolled into Microsoft Intune. After that process is completed, the device is ready for management and use.
- Microsoft Entra join with automatic enrollment. When using Windows Autopilot is not an option, IT administrators can set corporate-owned devices to automatically enroll into Microsoft Intune. They can do this by choosing to join the device to Microsoft Entra ID and providing a work or school account during the out-of-box experience (OOBE). During that process, the same end result of enrollment will happen as with the Windows Autopilot method. However, this approach offers a lot less control over the full lifecycle of the device and a less user-friendly experience.
- Bulk enrollment with provisioning package. When there are a lot of corporate-owned devices that IT needs to enroll, bulk enrollment with a provisioning package can be an efficient alternative to Autopilot. Admins can apply a provisioning package during the OOBE that ensures the device is automatically joined to Microsoft Entra ID and automatically enrolled into Microsoft Intune.
- Intune Company Portal app. For personally owned devices, the Intune Company Portal app is the most common option. The user can download and install the Intune Company Portal app from the Microsoft Store and walk through the process within the app to enroll the device into Microsoft Intune. Once this process is complete, the device is enrolled as a personal device with only a few management options and insights for IT to work with.
- Connecting a work or school account. Another option for personally owned devices is to use the available process within the Settings app to add a work or school account. The result will be similar to the Intune Company Portal app but with fewer insights about the status of the device and no direct overview of the available apps.
What is the most common scenario for corporate-owned Windows devices?
The enrollment of corporate-owned devices via Windows Autopilot is the most commonly used scenario for enrolling Windows devices into Microsoft Intune. Within this scenario it is important that those devices are registered with the Windows Autopilot service. The easiest way to achieve this is by arranging that during the purchase process of those devices.
Most vendors and OEMs support enrollment at the time of purchase for new devices. Often this means the vendor gets access to the tenant to automatically upload the required information to those devices. When the vendor only provides a CSV file with the device information, the IT administrator must upload that information to the Windows Autopilot service.
What are the requirements for using Windows Autopilot?
There are not many requirements that need to be in place before an IT administrator can use Windows Autopilot. Admins must make sure the following licenses and configurations are in place:
- At least Microsoft Entra ID P1 license for automatic enrollment and at least Microsoft Intune P1 for Intune management. IT must have both assigned to the users.
- Basic Intune tenant setup with the MDM authority set to Microsoft Intune.
- Devices running at least a supported version of Windows 10 or 11 Pro, Windows 10 or 11 Enterprise, or Windows 10 or 11 Education.
- An administrator account with at least the Global Administrator or the Intune Service Administrator Microsoft Entra role assigned.
How to set up automatic enrollment for Windows Autopilot via Intune
When admins use Windows Autopilot for automatic enrollment of devices to Microsoft Intune, there are a few activities they must perform.
Configure automatic enrollment
The first task is to configure automatic enrollment. Automatic enrollment will ensure the device is automatically enrolled into Microsoft Intune -- after joining Microsoft Entra ID.
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Devices > Windows > Windows enrollment > General > Automatic enrollment.
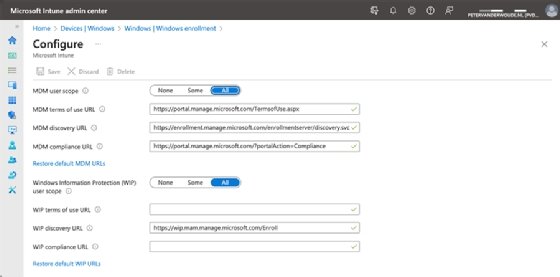
- On the Configure page, configure the MDM user scope by choosing one of the following options (Figure 1).
- None. MDM automatic enrollment is disabled.
- Some. MDM automatic enrollment is enabled only for the selected group.
- All. MDM automatic enrollment is enabled for all users.
- Leave MDM terms of use URL, MDM discovery URL, and MDM compliance URL to their default configuration and click Save to store the changes.
Register the devices with Windows Autopilot
The second task is to register devices with Windows Autopilot -- this is only necessary if the devices are not already registered by the vendor. This will use information accessible via a CSV file.
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Devices > Windows > Windows enrollment > Windows Autopilot Deployment Program > Devices.
- On the Windows Autopilot devices page, as shown in Figure 2, click Import. Select the CSV file and click Import again.
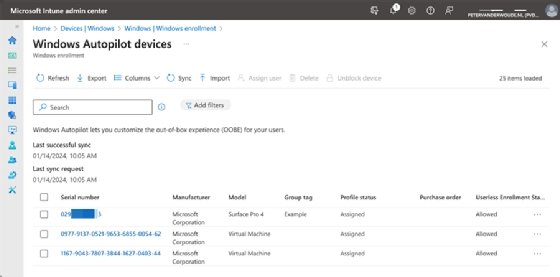
The Windows Autopilot devices overview also provides insights with important details that IT admins can use to filter and group devices. The most important of these is the Group tag, which IT can easily adjust. To create an Entra device group based on that tag use the following example code:
device.devicePhysicalIds -any (_ -eq "[OrderID]:Example"))Create a Windows Autopilot deployment profile
The third task is to create a Windows Autopilot deployment profile, configure the deployment mode of the devices and customize the user's OOBE. The following steps will walk through the creation of that profile:
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Devices > Windows > Windows enrollment > Windows Autopilot Deployment Program > Deployment Profiles.
- On the Windows Autopilot deployment profiles page, click Create profile and then select Windows PC.
- On the Basics page, specify a name for the profile and click Next.
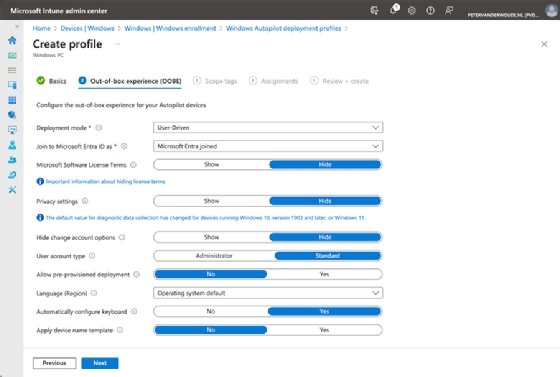
- On the Out-of-box experience (OOBE) page, configure at least the first two settings and click Next (Figure 3).
- Deployment mode. Select User-Driven for a standard Windows Autopilot deployment, in which users provide their credentials during the enrollment and the device is assigned to that user.
- Join to Microsoft Entra ID as. Select Microsoft Entra joined for the Microsoft recommended location to join new devices.
- For the remaining settings, choose what's applicable based on internal policies. Determine which pages should be shown, choose the account type, configure the language and determine the name standard.
- On the Scope tags page, click Next.
- On the Assignments page, configure the appropriate assignment of the profile based on an Entra device group. Consider using a group based on a Group tag.
- On the Review + create page, review the configuration and click Create.
After these configurations are complete and in place, IT admins can use Windows Autopilot to deploy corporate-owned devices. Admins should also configure an Enrollment Status Page to block the device until all the required configurations have been applied and the required apps are installed. Remember to update the configuration profiles that will be applied and configure the apps that need to be deployed.
Peter van der Woude works as a mobility consultant and knows the ins and outs of the ConfigMgr and Microsoft Intune tools. He is a Microsoft MVP and a Windows expert as well.






