LTO-5
LTO-5 is a tape format released in 2010 by the Linear Tape-Open Consortium. LTO-5 has since been supplanted by LTO-6, LTO-7 and LTO-8, with planned LTO-9, LTO-10, LTO-11 and LTO-12 versions as-yet unreleased. The standard form-factor of the LTO data cartridge developed and released by the LTO Consortium is called Ultrium, and it is often used for data backup and archiving.
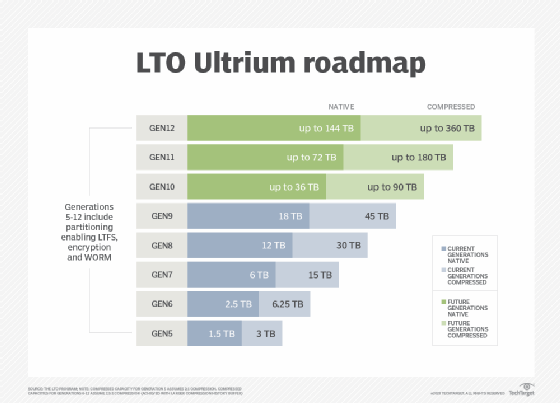
Capacity for the LTO-5 tape drive is in the area of 3 TB, with data transfer rates of up to 280 megabytes per second (MBps). In both cases, LTO-5 tape capacity assumes a 2:1 compression ratio; uncompressed capacity/throughput is 1.5 TB per 140 MBps.
What LTO-5 is used for
While tape storage has been replaced by disk and other modern data storage methods in some instances, the technology still has its benefits. Tape is well-suited to long-term storage and archiving thanks to its lower cost, high capacity and portability.
Ultrium tape storage, like the storage available in LTO-5, is commonly used for data backup, archiving and offline storage. LTO can also be used for high-capacity transfers, in some cases physically moving terabytes of data faster than an upload to the cloud or a remote data center. Nearline storage -- storing data that is neither immediately needed nor fit to be archived -- is also well-suited to LTO storage.
Organizations worried about compliance and security may find LTO storage to be a good fit. From LTO-3 onward, all LTO generations are write-once, read-many (WORM) capable. WORM technology preserves data in a format that is unalterable, non-rewritable and non-erasable. With WORM capability, LTO-5 can provide a cost-effective way to meet compliance needs.
From version 4 onward, LTO storage is also capable of encryption. Encryption on LTO drives is performed at the drive level, enabling compression prior to encryption and maximizing tape capacity.
History of LTO-5 tape and the LTO Consortium
LTO is a magnetic tape data storage technology developed in the late 1990s as an open standard alternative to the formats available at the time. The LTO-4 tape format was released in 2007, and it can hold 1.6 TB -- 800 gigabytes uncompressed. LTO-4 was the first iteration of LTO tape to include 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard-Galois/Counter Mode drive-level encryption.
The LTO Consortium was formed in 1998 by three companies: Hewlett Packard -- now Hewlett Packard Enterprise -- IBM and Seagate, which eventually sold its tape business to Quantum.
In the 1980s, tape was enclosed in a cartridge in a single reel, and there was no compatibility between different products. IBM, Quantum and Sony made up the original vendors of this closed tape format, with Quantum and Sony leading with their high-capacity tape storage.
Noting that the incompatibility of Sony's tape products enabled the market to be tightly controlled by these vendors, HP, IBM and Quantum developed open format tape technology that offered users multiple sources of media and products. In developing this technology, the three vendors formed the LTO Consortium, which typically releases a new generation of Ultrium LTO tape every two to three years.

LTO-5 was the first Ultrium version released by the LTO Consortium with more than a terabyte of native capacity. Prior to the release of LTO-5, previous versions only went up to 800 GB.
LTO-5 is also the first version to enable partitioning, which reserves a portion of the tape for indexing to tell the drive where a particular file in the tape is stored. This addition enabled the integration of the Linear Tape File System (LTFS). LTO-5 has a maximum of two partitions, with later versions allowing up to four.
LTO-5 vs. other specifications
LTO-5 has been surpassed by LTO-6, LTO-7 and LTO-8, with LTO-9 and LTO-10 set to arrive in the next couple of years. As noted above, LTO-5 marked a number of milestones for the format, but its capacity is far lower than the newer iterations.
LTO-6 was released in December 2012. According to the Consortium, LTO-6's capacity is 6.25 TB, with data transfer rates up to 400 MBps, assuming a larger 2.5:1 compression ratio, with uncompressed capacity/throughput of 2.5 TB per 160 MBps.
LTO-7 was released in 2015 and has a 15 TB tape capacity. LTO-7 has data transfer rates up to 788 MBps and uncompressed capacity/throughput of 6 TB per 315 MBps.
The latest version, LTO-8, was released in 2017. With 30 TB of tape capacity, data transfer rates of up to 1,180 MBps and uncompressed capacity/throughput of 12 TB per 472 MBps, it is the most advanced version of the technology.
LTO tape drives can read tapes from two prior generations, so users with LTO-6 and LTO-7 drives can still read LTO-5 tapes. LTO drives can write to tapes from the previous generation, so LTO-6 can write to LTO-5 tapes.
As with previous and future Ultrium generations, LTO-5 is open format, enabling interoperability among different vendors.
Storing and cleaning tape cartridges
Because tape is particularly sensitive to storage conditions, the estimated tape life expectancy of 30 years is based on specific conditions: a constant temperature of 70 degrees Fahrenheit with 40% relative humidity. Humidity, light levels and higher temperatures -- even a five-degree temperature increase -- can all contribute to the deterioration of the media.
LTO tape cartridges do require cleaning. A tape drive will visually indicate when it requires cleaning, at which point an LTO cleaning cartridge should be inserted into the tape drive to perform an automatic cleaning cycle. Cleaning tape drives reduces buildup and stains deposited during use.
Major vendors
LTO Consortium founders IBM, HPE and Quantum currently sell LTO-8, though previous generations can also be purchased.
Other major LTO Consortium vendors include Fujifilm, GlassBridge Enterprises, Maxell, Sony and Spectra Logic.
Future LTO specifications
The Consortium has announced the LTO-9, LTO-10, LTO-11 and LTO-12 tape formats, but they are not yet available as of April 2018. Data transfer rates for LTO-11 and LTO-12 are still unavailable. Here are the projected specifications:
- LTO-9: 60 TB tape capacity, data transfer rates of up to 1,770 MBps and uncompressed capacity/throughput of 24 TB per 708 MBps.
- LTO-10: 120 TB tape capacity, data transfer rates of up to 2,750 MBps and uncompressed capacity/throughput of 48 TB per 1,100 MBps.
- LTO-11: 240 TB tape compressed capacity, 96 TB uncompressed.
- LTO-12: 480 TB tape compressed capacity, 192 TB uncompressed.





