Getty Images/iStockphoto
CDC Report Links People Seeking Substance Misuse Treatment to Psychiatric Issues
A 2019 CDC study links people seeking treatment for substance misuse to moderate-to-severe psychiatric issues across multiple biopsychosocial domains.
An alarming pre-pandemic CDC study reveals that substance misuse is linked to mental health issues. The study investigated how many people pursuing treatment for substance misuse also reported moderate-to-severe psychiatric problems across multiple biopsychosocial domains.
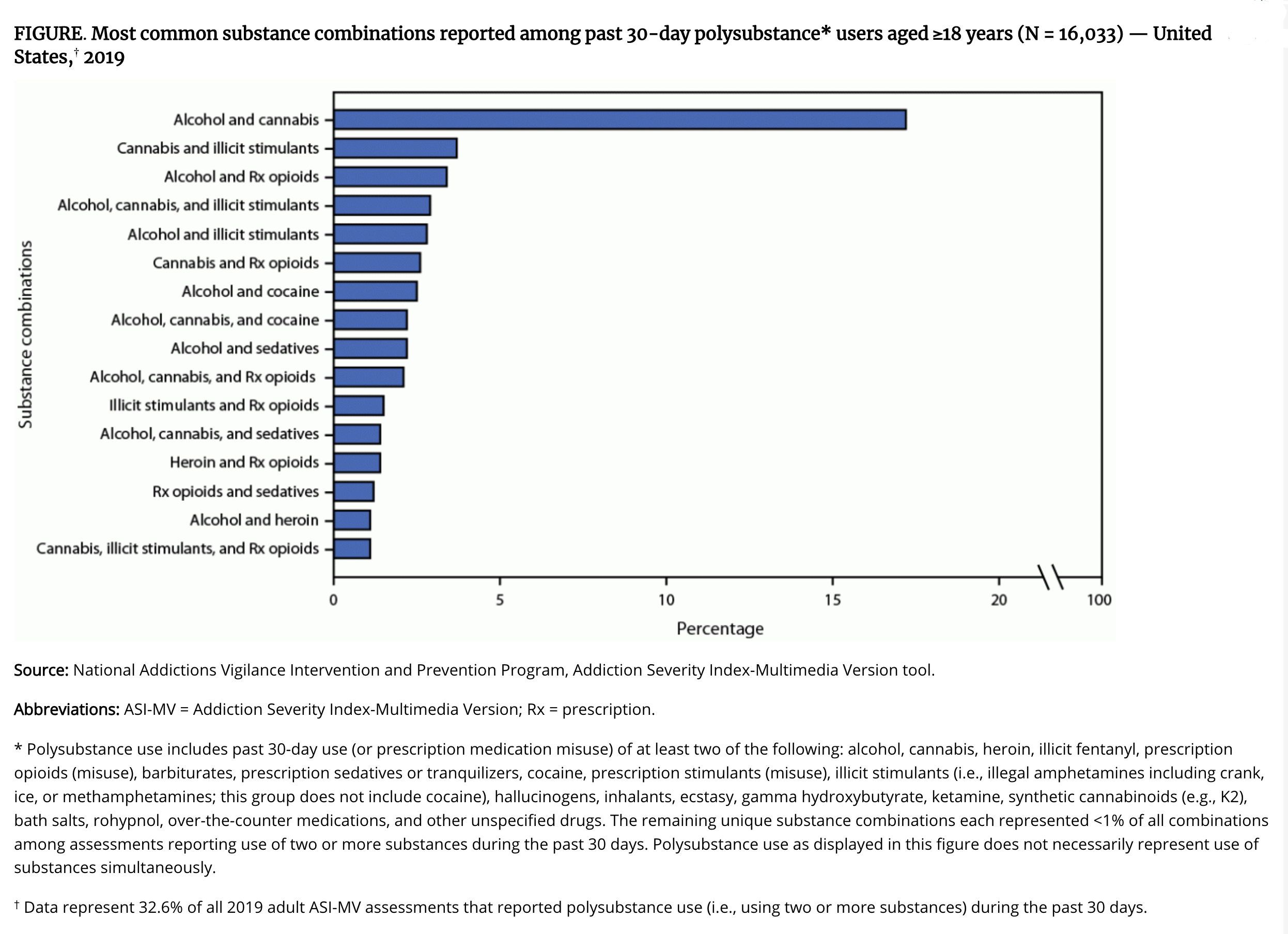
The researchers discovered that alcohol (35.8%) was the most commonly used substance among more than 49,000 adults at 499 treatment centers, followed by polysubstance use (32.6%), defined as any combination of alcohol, opioids, cannabis, stimulants, sedatives, or cocaine.
Over a third of participants seeking help with substance misuse also claimed they had psychiatric or biopsychosocial issues — including family, medical, work, and legal issues.
“Actions to enhance comprehensive substance use programs that incorporate polysubstance use and co-occurring mental health problems into strategies for prevention, treatment, and response are needed, as is expanded linkage to services,” says the authors of this study.
In 2019, 65.8 million adults in the United States reported binge drinking, and 35.8 million reported illicit drug use or prescription pain reliever misuse in the past 30 days. People with substance use disorders are at high risk for overdose and vulnerabilities.
“The CDC provides data and resources to equip and inform states, territories, and local jurisdictions to help improve opioid prescribing practices, improve linkage to care for the treatment of opioid use disorder, and prevent and reverse overdoses,” the authors explain.