
ipopba - stock.adobe.com
Exploring the Benefits of a Collaborative Global Pharmaceutical Industry
As healthcare professionals call for collaboration, exploring the historical and projected benefits of a collaborative global pharmaceutical industry is necessary to incentivize industry leaders to contribute.
The COVID-19 pandemic displayed the potential of a collaborative pharmaceutical industry. The worldwide cooperation between researchers, healthcare professionals, pharmaceutical companies, and industry leaders contributed to the now available vaccinations and treatments against this otherwise deadly virus, SARS-CoV-2. While not without its challenges, exploring the historical and projected benefits of a collaborative pharmaceutical industry may incentivize trailblazers in the industry to adopt and implement a collective global pharmaceutical industry.
The benefits of this industry include improved healthcare outcomes, better preventative care, cost savings, and economic growth.
Basic Economic Benefits
It is becoming increasingly apparent that the pharmaceutical industry has contributed significantly to economic growth. In 2017 alone, the global pharmaceutical sector contributed $532 billion to the world’s GDP, equivalent to the GDP of the Netherlands. It also created 5.5 million jobs that year. According to a research report titled The Global Economic Impact of the Pharmaceutical Industry, the 2017 global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,135 billion.
This research report states that the industry has two significant economic impacts. First, the production of pharmaceutical products contributes to GDP and makes jobs available. Additionally, the economic activity associated with the global pharmaceutical industry has a critical impact.
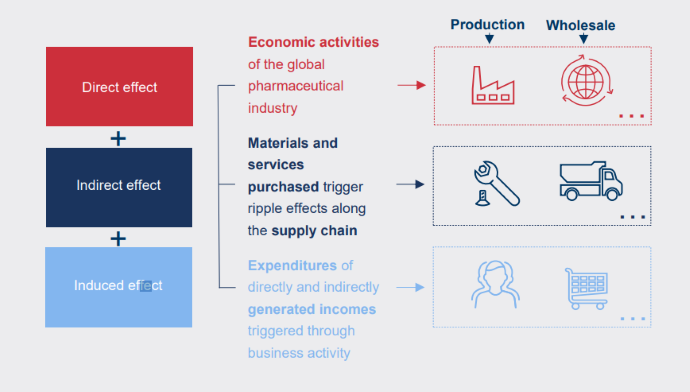
The report divides the effect of the global pharmaceutical industry into four sections: direct, indirect, induced, and total economic impact.
The direct effects are the outcomes that are directly generated by the industry. Researchers in the report added, “indirect effects are effects arising due to the input the industry demands from other economic sectors.” Additional effects are induced effects that result from direct and indirect incomes. The total economic effect combines all three. Below is a graphic that describes the different effects of the global pharmaceutical industry.
Understanding Research and Development
Despite the economic benefits of a global pharmaceutical industry, it would be daft to consider the revenue without acknowledging the costs. According to a report by the International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Associations (IFPMA), only one of every 5,000–10,000 compounds researched is promising.
Below is a graphic from the IFPMA outlining the research and development process for biopharmaceuticals. While regulatory and approval procedures may vary from country to country, the basics of approval are the same.
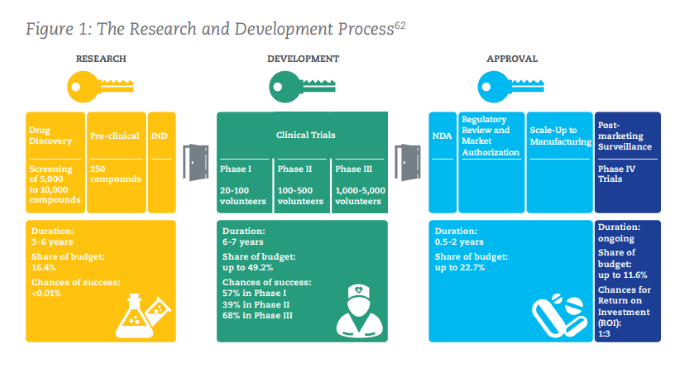
Investing in research and development is the first step taken by the global biopharmaceutical industry to address public health challenges. On average, the research and development process takes 10–15 years for one medicine or vaccine. In addition to discovering the benefit of a medication or other agent, researchers must also conduct clinical trials to test the safety and measure the cost–benefit of each biopharmaceutical product.
The IFPMA states, “the research-based biopharmaceutical industry plays a vital role in developing new medicines and vaccines to prevent and treat diseases, improving the lives of patients worldwide."
Research and Development Spending
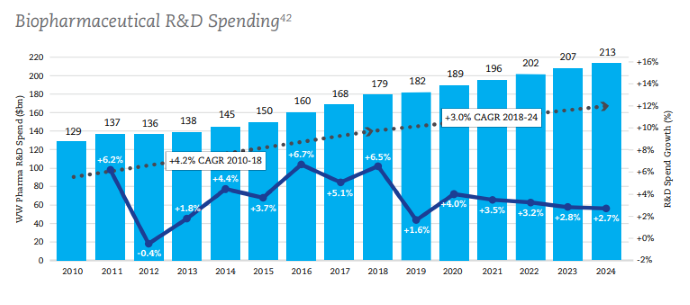
The organization also notes that the global biopharmaceutical industry is the sector that spends the most on research and development, with annual research and development spending approximately 7.3 times larger than that of the aerospace and defense industry. Additionally, it is nearly 1.5 times greater than the software and computer services industry. The average cost of researching and developing a successful medicine is around $2.6 billion.
Below is a graphic from the IFMPA mapping and projecting the growth of research and development spending between 2010 and 2024.
Healthcare Contributions
Aside from the financial contributions associated with the global biopharmaceutical industry, there have also been significant benefits from a healthcare standpoint.
In 2018, 59 new medications were launched worldwide. An additional 8,000 compounds were in various stages of development. In 2020, 2,740 cancer drugs were in development, and additional development included 1,535 immunology, 1,498 neurology, and 1,213 infectious disease drugs.
Cancer Care
Global pharmaceutical efforts have contributed to DNA and genome mapping, leading to significant cancer diagnosis and treatment progress. The growth of immunotherapy — driven partly by the global pharmaceutical industry — has also played a critical role in the treatment.
Between 1996 and 2000, the average survival rate for all cancers was 52%. However, due to the progression in the pharmaceutical space, between 2011 and 2015, the survival rate rose to 64%. It is thought that today, the survival rate is even greater.
HIV/AIDs Treatment and Life Expectancy
Another space attracting pharmaceutical innovation has been HIV and AIDS treatment. According to the IFPMA, approximately 222 anti-retroviral drugs for HIV and AIDs have been developed.
Universally, drug development, vaccinations, and other innovations by the global pharmaceutical industry have lengthened life expectancy. According to the IFPMA, “over the last 50 years, globally, life expectancy has increased by around 20 years. As the world continues to confront medical challenges, there are biopharmaceutical advancements and breakthroughs that are set to improve the lives of millions of people.”
Covid-19 and Vaccinations
The IFPMA states that the biopharmaceutical industry has significantly contributed to COVID-19 care. The sector is contributing to vaccine production, among other things, including treatment and diagnostic tools.
“Since the development of the first modern vaccine in the late 1700s, vaccines have earned their reputation of being one of the safest, most effective, and cost-effective medical technologies ever developed. It is estimated that immunization currently prevents 2–3 million deaths each year in all age groups,” states the IFPMA.
Antimicrobial Stewardship
In addition to the benefits of preventing disease, the development of vaccines by the global pharmaceutical industry has partially helped control the growing issue of antimicrobial resistance. The availability and uptake of vaccines reduce the infection rate, thus, reducing the opportunities for the use and misuse of antibiotics.
The discovery of new antibiotics is an incredibly challenging task for this industry. In lieu of new antibiotics that can treat resistant bacteria, the next best option is to minimize the risk of perpetuating the issue.
HPV Vaccinations
As previously mentioned, vaccination is a fundamental tool utilized by the healthcare industry. Beyond its ability to prevent infection, improve patient outcomes, and facilitate better antimicrobial stewardship, vaccination can also lead to significant savings.
According to the IFPMA, in Germany, every euro invested into HPV vaccination leads to 3.3 euros saved for a net savings of 2.3 euros.
In addition, the Gavi program, which has facilitated HPV vaccination, has calculated that throughout the countries it assists a $1 investment yields a $54 return.
Looking Ahead
The number of medications made available through the efforts of the global pharmaceutical industry has led to reduced hospital stays and long-term care. While the up-front buy-in for developing a drug may seem daunting, the cost-savings down the line can be unparalleled. That said, global pharmaceutical collaboration will be essential for the progression of healthcare. Industry leaders are encouraged to educate themselves on the benefits and advocate for worldwide collaboration.






