
gmast3r/istock via Getty Images
Exploring FDA-approved birth control injections
Injectable contraceptives, like Depo-Provera and Depo-SubQ Provera 104, are name-brand FDA-approved hormonal birth control methods that prevent pregnancy.
Birth control injections are FDA-approved hormonal contraceptives that effectively prevent pregnancy. Among the various birth control methods available, injections have gained popularity due to their convenience, high efficacy, and ease of use. Currently, there are two name-brand FDA-approved birth control injections available in the United States market: Depo-Provera and Depo-SubQ Provera 104, made by Pfizer.
Birth Control Injections
Birth control injections are a form of hormonal contraception administered via an intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. These injections typically contain progestin, a synthetic form of the hormone progesterone. The primary mechanism of action includes the inhibition of ovulation, thickening of cervical mucus to block sperm penetration, and alteration of the uterine lining to prevent implantation.
Potential side effects include menstrual changes, weight gain, decreased bone mineral density, mood changes, headaches, nervousness, abdominal pain, breast tenderness, nausea, and delayed return to fertility after discontinued use. Birth control injections are not suitable for women with certain health conditions, such as a history of thromboembolic disorders or certain cancers.
According to the 2015–2019 National Survey of Family Growth, injectable contraceptives accounted for 24.5% of all contraceptive use during the surveyed periods, with Black women being more likely to use injectables compared to other racial groups.
FDA-Approved Birth Control Injections
There are currently two name-brand FDA-approved birth control injections available in the US market, both owned by Pfizer (Table 1):
- Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension)
- Depo-SubQ Provera 104 (medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension)
Table 1. Name-Brand FDA-Approved Birth Control Injections
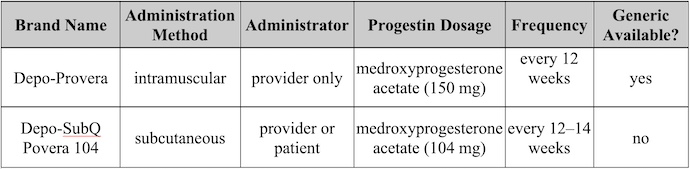
Depo-Provera
Depo-Provera is a widely recognized birth control injection. It is administered as an intramuscular injection of 150 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate every three months (12 weeks). It should be administered during the first five days of the menstrual cycle or immediately postpartum for non-breastfeeding women.
- Benefits: offers a long-acting, convenient form of contraception with no daily administration required and may reduce menstrual cramps and anemia
- Cost: $58–67 per injection
- Dosage: 150 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Efficacy: over 99% effective when used correctly
- FDA Approval Date: October 29, 1992
- Manufacturer: Pfizer
Depo-SubQ Provera 104
Depo-SubQ Provera 104 contains a lower dose of medroxyprogesterone acetate (104 mg) compared to Depo-Provera. This version can be administered as a subcutaneous injection by a healthcare professional or self-administered at home every 12–14 weeks.
- Benefits: offers a lower dose with similar efficacy, providing a convenient at-home option; may reduce menstrual cramps and anemia
- Cost: $56–66 per injection
- Dosage: 104 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Efficacy: over 99% effective when used correctly
- FDA Approval Date: December 17, 2004
- Manufacturer: Pfizer
Mechanism of Action
The primary mechanism of birth control injections is the suppression of ovulation. The hormone released by the injection inhibits the release of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland, preventing the maturation and release of eggs from the ovaries. The thickened cervical mucus also acts as a barrier to sperm, and the altered endometrium reduces the likelihood of implantation.
Advantages
Birth control injections offer several advantages over other contraceptive methods. They require less frequent administration compared to daily oral contraceptives, significantly reducing the likelihood of user error. The continuous release of hormones ensures stable blood hormone levels, minimizing the risk of hormonal fluctuations and associated side effects. Additionally, injections are discreet and do not interfere with sexual activity, providing a convenient option for users. Many women also experience more predictable and lighter menstrual periods, along with reduced dysmenorrhea, making injections an appealing choice for effective cycle control.
The development and FDA approval of birth control injections such as Depo-Provera and Depo-SubQ Provera 104 represent significant advancements in contraceptive technology, providing healthcare providers with reliable and patient-friendly birth control options. For businesses in the healthcare technology sector, these products illustrate the potential of innovative delivery systems to enhance patient adherence and satisfaction. By offering a convenient, effective, and low-maintenance solution, birth control injections can reduce the burden on healthcare systems and improve outcomes for a diverse patient population. Investing in and supporting such technologies can drive market growth and contribute to the broader goal of advancing reproductive health and autonomy.






