
Mohammed Haneefa Nizamudeen/isto
Assessing the impacts of noncontinuous digital diabetes solutions
Peterson Health Tech Institute's report assesses noncontinuous digital diabetes management solutions and their clinical and economic impacts.
In a recent health technology assessment conducted by the Peterson Health Technology Institute (PHTI), the clinical and economic impact of noncontinuous digital diabetes management solutions for adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) has been rigorously examined. Using evidence-based research, the assessment sheds light on the effectiveness of these innovative healthcare technologies, their implications for health equity and access, and their potential for cost savings.
The Need for Effective Diabetes Management
Diabetes, affecting 11% of the United States population, is one of the nation's most expensive chronic conditions. For instance, in 2022, the total estimated expenditure for diagnosed diabetes in the US amounted to $412.9 billion. This encompasses $306.6 billion in direct medical expenses and $106.3 billion in indirect costs associated with diabetes.
Diabetes also disproportionately impacts people of color and lower-income populations.
Diabetes care necessitates significant self-management to monitor and control blood glucose levels, as measured by hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). Recognizing these challenges, digital tools have emerged as potential aids in empowering patients to manage their diabetes better.
The Evaluation Focus
PHTI's assessment concentrated on noncontinuous digitally enabled diabetes management solutions for adults with T2D, including remote patient monitoring, behavior, and lifestyle modification support, and connected noncontinuous glucose monitors for HbA1c measurement. The evaluation aimed to determine their clinical benefits, economic impact, and effects on health equity and access.
This comprehensive evaluation scrutinized the clinical benefits and economic implications of these solutions and examined their potential to address healthcare disparities within diabetes management. By assessing the inclusivity and accessibility of these digital solutions, PHTI's evaluation offers valuable insights into leveraging technology to bridge gaps in diabetes care and ensure equal opportunities for all individuals, irrespective of their background or socioeconomic status, to manage their conditions and enhance health outcomes effectively.
Recognizing the existence of healthcare disparities within diabetes management, PHTI's assessment delved into whether these solutions were specifically designed to cater to the needs of diverse populations and mitigate inequities. The evaluation aimed to identify how these technologies could reduce disparities and enhance access to care. Through its examination of the inclusivity and accessibility aspects, PHTI's evaluation serves as a resource for understanding the potential of technology in addressing health disparities and promoting equitable access to diabetes management resources.
Clinical and Economic Impact Findings
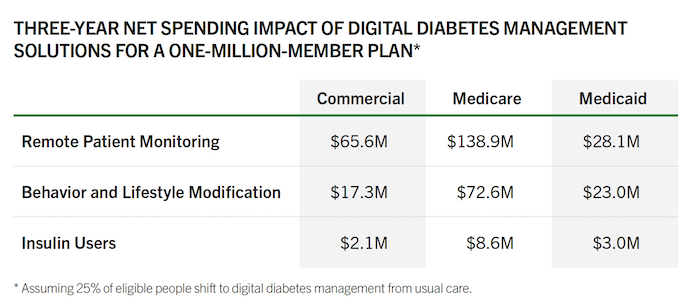
The evaluation's findings indicate that the digital diabetes management technologies examined do not deliver clinically meaningful benefits compared to usual care for adult patients with T2D. The evidence reveals that these solutions' glycemic control improvements were minimal and short-term. The assessment also highlights that the average price of these solutions outweighs the savings achieved from marginal clinical benefits, leading to increased net spending over three years in commercial insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid (Figure 1).
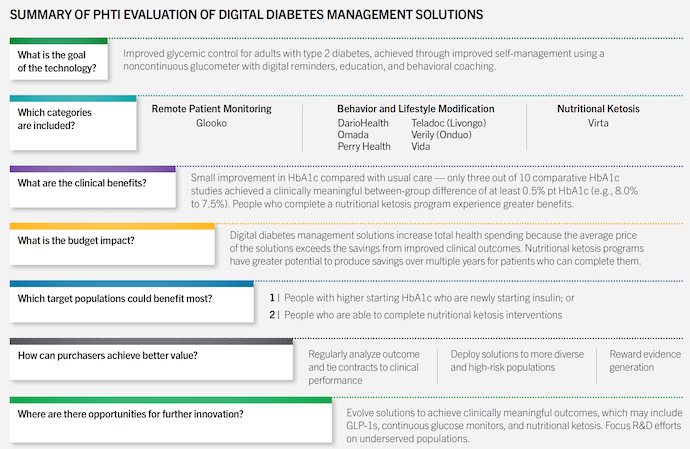
The evaluation (Figure 2) found that the digital diabetes management solutions currently available do not demonstrate significant clinical benefits for adults with T2D. Healthcare stakeholders must carefully consider the evidence before implementing these technologies on a large scale.
Exceptions and Potential Savings
While the general findings suggest limited clinical benefits, exceptions exist. The evaluation highlights that people with higher starting HbA1c who are newly starting insulin, as well as individuals seeking diabetes remission through nutritional ketosis, may experience clinically meaningful results. Nutritional ketosis programs show potential for producing long-term savings for patients who can complete them.
The assessment also highlights that certain subgroups, such as younger adults and individuals with higher engagement in self-management, may benefit from noncontinuous digital diabetes management solutions.
These subgroups may experience improved adherence to treatment plans, enhanced self-monitoring of blood glucose levels, and increased motivation for behavior change, leading to better overall diabetes management outcomes. Further research and tailored interventions for these populations could unlock additional potential for clinical benefits and cost savings.
Promoting Health Equity and Access
Ensuring health equity and access is a pressing concern in diabetes management. The evidence reviewed by PHTI indicates that the evaluated solutions do not preferentially address health disparities. Moreover, the solutions have been primarily tested in less complex patient populations, lacking representation from individuals at the highest risk of diabetes-related complications. To bridge this gap, policymakers and healthcare stakeholders must review published results carefully and analyze the evidence before generalizing across populations.
Promoting health equity and access in diabetes management requires addressing the barriers and disparities across different populations. The PHTI assessment emphasizes the need for inclusive research and testing of digital diabetes management solutions that specifically target underserved communities, including racial and ethnic minorities, individuals with lower socioeconomic status, and those facing geographic or cultural barriers to healthcare access.
By actively involving diverse populations in clinical trials and incorporating their perspectives and needs in the design and implementation of digital solutions, healthcare stakeholders can work toward reducing disparities, improving health outcomes, and ensuring that the benefits of these technologies are accessible to all individuals affected by diabetes.
Policy Implications and Strategies
Based on the assessment's findings, the evidence suggests that the broad deployment of the evaluated solutions results in little clinical benefit and increased costs. However, solutions focused on nutritional ketosis show promise for both clinical improvements and potential cost savings. To achieve better value, purchasers are advised to regularly analyze outcomes, tie contracts to clinical performance, deploy solutions to more diverse and high-risk populations, and reward evidence generation.
Policymakers and payers, including Medicare and Medicaid, can target the use of digital diabetes management tools and solutions more effectively. By aligning contracting models and reimbursement policies with evidence about clinical benefits, we can optimize the value and impact of these technologies.
Opportunities for Further Innovation
The assessment identifies opportunities for further innovation in diabetes management solutions. These include evolving solutions to achieve clinically meaningful outcomes through utilizing GLP-1s, continuous glucose monitors, and nutritional ketosis. Additionally, research and development efforts should focus on underserved populations to address existing disparities.
The PHTI health technology assessment provides valuable insights into the clinical and economic impact of digital diabetes management solutions for adults with T2D. While the findings indicate limited clinical benefits and increased costs, exceptions exist for specific patient populations. By carefully analyzing the evidence, policymakers, payers, and healthcare stakeholders can make informed decisions to optimize the value and impact of digital diabetes management technologies, ensuring better health outcomes and improved cost-effectiveness in diabetes care.
As the healthcare field continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts are crucial to drive innovation and address the complex challenges of diabetes management. By leveraging emerging technologies and focusing on underserved populations, the healthcare tech industry can contribute to a future where effective diabetes management is accessible.






