
Getty Images/iStockphoto
5 Life Sciences Market Entry Strategies in the United States
LifeSciencesIntelligence expands on previous articles focused on the steps to market entry by highlighting five potential market entry strategies.
Entering the highly competitive life sciences market in the United States can be difficult, but effective strategies can ease entrants into the market. In this article, LifeSciencesIntelligence explores five life sciences market entry strategies.
A Look into the Global Life Sciences Market
According to Deloitte’s 2023 Global Life Sciences Outlook, the life sciences sector encompasses biotechnology (biotech), medical technology (medtech), and pharmaceutical companies.
Below is a figure from the Journal of Marketing that outlines the role of the life sciences market in the healthcare system:
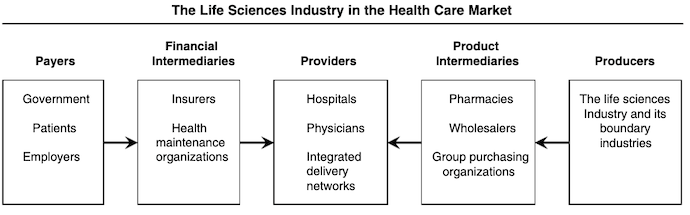
Licensing and Partnerships
One potential market entry strategy that can help ease new life sciences companies into the market is partnering with local companies for licensing agreements to help with product distribution or development.
Licensing agreements may include technology and product licensing. Technology licensing agreements allow partners to access proprietary technology and local development, production, and distribution strategies. This business model will enable organizations to access cutting-edge, proprietary technology to improve local healthcare systems while bringing in capital for the life sciences company through royalties and licensing fees.
Product licensing agreements allow manufacturers or distributors to sell the product on the company’s behalf while making some profit. The benefit for life sciences companies is that they can access the market more readily if they license a company established in the market. Additionally, local companies may have more insight into the best regulatory and distribution practices.
In addition to partnering with local companies, research collaborations can effectively facilitate additional healthcare research. Research partnerships may include joint research initiatives, clinical trial partnerships, or training and capacity building.
Joint research initiatives can be a collaboration between a life sciences company and research institutions, universities, or healthcare organizations. Researchers can gain more insight and establish local relationships by engaging with the local scientific community.
Alternatively, clinical trial partnerships can help life sciences or biopharma companies connect with local research centers, understand market needs, and gain insight into patient demographics.
Finally, training and capacity building can allow biopharmaceutical or life sciences companies to collaborate with local research institutions or healthcare facilities for knowledge exchanges and collaboration.
Licensing and partnerships can be lucrative for new companies or those looking to enter a new market. Some of the benefits include the following:
- Risk mitigation
- Cost efficiency
- Accelerated market entry
- Access to established networks
- Cultural adaptation
- Shared risk and rewards
- Access to local resources
- Strategic alliances
- Adaptability
- Faster market entry
- Relationship building
Licensing and partnerships can be challenging because companies have to consider intellectual property protection, regulatory alignments, and building a relationship with other stakeholders.
Strategic Alliances with American Companies
Alliances with American companies can help start-ups or foreign life sciences organizations enter the US market more readily. Companies may form alliances through research collaborations, distribution partnerships, joint marketing efforts, strategic planning and goal alignment, technology or knowledge transfer, and regulatory compliance.
Research collaborations can alleviate some financial burdens on newer or foreign life sciences companies. Established US companies can provide expertise and name recognition. Collaborating with an established company for R&D can widen a company's resource availability.
Distribution partnerships, similar to research collaborations, provide companies with additional resources. Companies that do not have their own distribution guidelines may choose to identify reputable distributors in the US that can provide rapid market entry.
Across research collaborations and distribution partnerships, companies can develop strategic plans for the alliances between the companies to establish mutual goals, share technology, exchange knowledge, share decision-making, and create a robust supply chain.
Beyond collaborations with other companies, life sciences organizations may establish alliances with regulatory bodies to ensure a comprehensive understanding of regulatory approval and a smooth transition from research and development to commercial strategy.
“Prior to the pandemic, developing, testing, and releasing a new vaccine, therapy, or medical device in less than 10 years was almost unheard of. Today, companies, shareholders, and consumers all want faster cycles, but they can’t do it alone. Long drug and device development times can add significant human, health, and economic costs to R&D efforts. By working to reduce those times through international interagency collaboration, regulators could help mitigate those costs,” noted the Deloitte 2023 outlook paper.
Direct Marketing and Sales
In lieu of strategic alliances, companies may choose direct marketing and sales, essentially going at market entry alone. A white paper published by Quintiles notes that working alone allows a company high strategic control and intense product focus. In addition, companies yield the entirety of the economic benefit. However, the trade-off is that they also bear the financial risk.
“In the long run, going it alone is the most financially beneficial route to take because it represents the best chance that the product will get the right marketing attention and product messaging and that its value to the company will remain fully intact. It can also be an important step in a company’s strategic plans if it is seeking to expand its global presence and to gain a permanent foothold in that burgeoning new market,” noted the report.
Acquisitions or Mergers
Mergers and acquisitions are another great way to enter the market with lower costs. For example, a life sciences company looking to enter a new market may consider acquiring local companies to establish an immediate presence. It involves purchasing a controlling stake or the entirety of an existing company already operating in the life sciences sector in the desired market.
According to a Deloitte paper, in 2022, 198 mergers and acquisitions across the life sciences market contributed to over $130 billion in revenue.
The advantage of acquiring a local company is having a previously established presence with an existing patient demographic. Local insights can also provide easier and faster market entry, as the companies acquired have already done the market research and understand the community.
A merger with a local life sciences company to create a new joint entity can benefit market entry because it allows the companies to share resources and reach new markets and customers, share the risk between the two entities, and complement each other to develop a more comprehensive product.
Acquisitions and mergers are potent strategies for life sciences companies looking to expand into new markets or enhance their capabilities. Success in these strategies depends on thorough due diligence, effective integration planning, and a strategic alignment of goals between the acquiring and acquired entities.
Clinical Trials and Regulatory Approval
Clinical trials and regulatory product approval are essential parts of life sciences market entry. With adequate evidence that a product fills an unmet need or is superior to existing products, companies are likely to secure regulatory approval and market shares.
The standard of proof for many organizations, including the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in America, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, the National Medical Product Administration in China, and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization in India, is clinical trial data with a comprehensive analysis of the product and its efficacy in comparison to no intervention or the current standard intervention.
Clinical trials continue to be one of the costliest components of the research and development (R&D) process. A 2022 report revealed that the cost of bringing a pharmaceutical asset to market has reached approximately $2 billion. Even once drugs reach the launch stage, over one-third of the launches fail to meet expectations.
“R&D innovation is one of the top actions that 91% of life sciences organizations plan to invest in more heavily during 2023, according to a Deloitte survey of 60 senior life sciences executives from biopharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers with revenue of more than US $500 million,” noted Deloitte analysts in the 2023 outlook report.
However, few clinical trials actually result in regulatory approval. In the US, it is estimated that only one-tenth of drug candidates that enter clinical trial phases obtain regulatory approval and reach product launch stages.
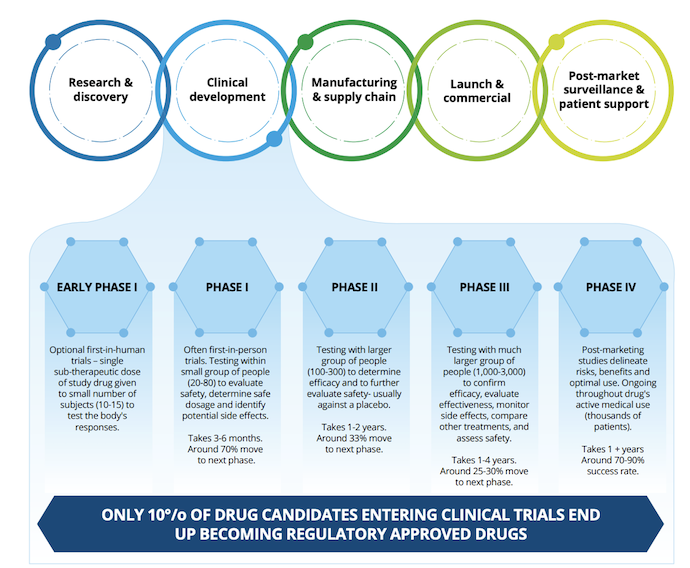
Many companies are turning to alternative forms of clinical trials to minimize the financial strain that clinical trials place on life sciences organizations. For example, Deloitte notes that the pandemic prompted the accelerated use of digital trials, trial simulations, decentralized clinical trials, and real-world evidence alongside artificial intelligence (AI) to design more effective clinical trials and minimize human error.
Understanding domestic regulatory protocols of life sciences companies entering the US market is vital as violations of regulations can result in legal repercussions and, eventually, a decline in profits.






