What is user experience and UX design? Why should you care?
User experience design, or UX design, is the process of building a product that's user-friendly and provides enhanced user experiences through elements like the user interface (UI), visuals and navigation features. The main objective of UX design is to focus on the end user's needs and accordingly design (or redesign) a product that effectively meets those needs. Such products tend to resonate more with users, which then enables organizations to drive customer satisfaction and garner their loyalty.
What is user experience design?
The goal of UX design is to design and implement a product that will provide positive and relevant interactions with users. UX design, sometimes called user-centric or user-centered design, involves all aspects of product development and design, such as the following:
- Packaging and branding.
- Installation and setup.
- Operation, usability and performance.
In short, UX design helps designers create products that are both practical and usable. UX design addresses six major areas:
- Usefulness. The product must fill a practical need for the user.
- Desirability. The product should use attractive and consistent aesthetics, such as visual design.
- Usability. The product must be simple to use and provide a familiar suite of features and functions.
- Accessibility. The product must be usable by everyone, including users with disabilities.
- Supportability. The product must be well-supported so that users can resolve problems quickly and easily.
- Credibility. The product must be trustworthy, such as from a reputable company or implementing effective security.
While UX design is often associated with software design or digital services design, the term is also readily applied to any physical product or construct.
Furthermore, the scope of UX design is not limited to external users or customers. UX teams can also implement UX design best practices to enhance UX for internal and/or business users rather than individual consumers.
For example, UX in enterprise IT involves designing software and applications for businesses and their employees. For such projects, UX teams perform UX research to understand business requirements so they can focus on meeting business needs for specific user groups and improving complex or unique business workflows.
Why is UX design important?
The user experience is a critical consideration in attracting and retaining users or customers.
Consider any physical or digital product. If users don't need the product, don't enjoy using the product or can't reasonably use the product without undue difficulty, they will simply stop using the product and possibly adopt a competitor's product instead.
Conversely, an effective and reliable product that meets a clear need and offers good performance and support can drive business revenue, boost business reputation and enhance user loyalty to the business and its brand.
Because users provide the business revenue derived from products or services, a good user experience is critical for the businesses that provide those products and services. Ignoring or taking shortcuts around UX processes, such as usability testing or user acceptance testing, can be a risky decision for project managers and product stakeholders.
Finally, UX design should be treated as a dynamic part of any product design. UX design decisions aren't permanent, so user experience strategies can be regularly updated and modified as market demands, competitive forces, user expectations and enabling technologies evolve. User research and user experience testing are often employed to periodically reassess UX design choices.
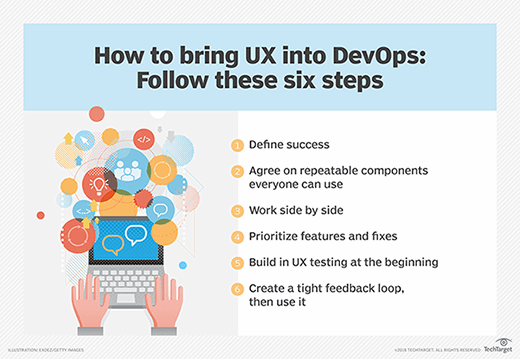
UX design principles and best practices
UX design should not be a haphazard or unstructured effort which could result in poor quality products that negatively affect UX. UX design should be a systematic, structured and repeatable process that helps in the development of products that are usable, accessible and intuitive. Such products deliver digital user experiences that are frictionless, enjoyable and foster customer engagement and loyalty.
A structured UX process is made possible by applying several UX design best practices and principles that enhance the business value of UX, including the following:
- Focus on the end user. UX design should always consider user needs and pain points at every step of the design and implementation process. A user-centric design process never loses sight of the end goal: to create a product that enables target users to solve their problems and reach their goals in an easy, quick and enjoyable way.
- Prioritize product simplicity and usability. A simple product tends to be easy to use, allowing users to effortlessly find what they need and accomplish what they set out to do. One way to determine what users are looking for is usability testing. Usability testing enables designers to understand how users want to navigate within the product, and whether they are facing any issues impeding navigation that should be addressed. It also provides useful insights that can pinpoint design problems and highlight gaps that should be closed to improve the product's UX.
- Ensure a visually consistent design. A visually consistent design goes a long way toward improving UX. Consistency in the layout, format, elements, visuals and other interface elements makes the product more intuitive and helps to eliminate confusion for users during product navigation.
- Balance simplicity with function. Simplicity should not come at the cost of functionality. A simple design can also deliver great functionality when UX designers aim to balance both. Functional testing will help ensure that the end product functions as intended without inconveniencing the user.
- Focus on hierarchical design. A well-thought-out visual hierarchy enables users to intuitively understand the various product elements and navigate to them easily. It focuses on key aspects like scale, color and contrast to create a user-friendly and engaging product. Within such products, users can easily understand the content and find what they are looking for without losing their way or getting frustrated.
- Simplify accessibility and navigability. UX-focused products are intuitive and easy to use by all kinds of users, even users with vision, hearing or other limitations. To design accessible products, UX designers can refer to reliable sources, such as the W3C consortium's Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). These recommendations are meant to help product designers and developers to "make web content more accessible to people with disabilities." The term web content means the information provided in both web pages and web applications.
UX vs. UI vs. CX: What's the difference?
The terms UI and UX are often used interchangeably. This is a common mistake because the UI is the primary mechanism for user interaction with a product and is central to the overall user experience.
In practice, UI design is a subset of UX design. User experience design involves all aspects of a product and its behavior, while user interface design focuses on the look, shape and other user interactions with the overall product.
Consider a software product with a menu-based UI. Even though the software product might fill a practical need and operate flawlessly as part of the overall UX, a software UI with cumbersome, inconsistent, poorly defined, multilayered menus or visually confusing button placement can have a negative effect on the user experience.

Similarly, the terms customer experience (CX) and UX are also used synonymously. The two concepts both aim to improve user interactions with a brand and ultimately enhance their experiences during interactions. However, the scope and focus of a customer experience strategy is much broader than that of UX.
Where UX focuses on enhancing user interactions with a specific product or service, CX aims to enhance the entire user journey with a brand. Customer brand journeys typically include multiple interactions over multiple touchpoints. These touchpoints in the customer journey map might be offline or online, direct or indirect.
For example, User A might see an ad for a product on social media, prompting them to think about purchasing it. They might then research the product through a Google search and then go to the company's website to purchase it. A few days later, they might interact with the company's contact center via a phone call or an automated chatbot to get clarification about a specific feature or functionality. A couple of months later, they might fill out a survey form to provide product feedback or they might join the brand's online community to share their experiences using the product. They might also purchase other products from the same company after receiving email newsletters.
All of these are various touchpoints and CX aims to improve user-brand interactions on all of them. Thus, where UX focuses on ensuring that users can easily achieve their objectives with a particular product, CX is about enhancing user perceptions and experiences across all stages of their relationship with the brand.
Benefits of a strong user experience
By designing products that enhance user experiences, companies can enjoy the following benefits:
- Enhanced customer satisfaction. User-centric products enable users to easily find what they need, solve their problems and reach their goals. Users don't encounter issues that might otherwise cause resistance, so they enjoy their interactions with the product.
- Increased customer loyalty and retention. Customers are more likely to be loyal to user-friendly, intuitive, consistent products with enhanced UXs, which can result in higher customer retention.
- Stronger revenues and profitability. When users enjoy seamless product experiences, they are more open to interacting with the product, engaging with its content and taking actions such as purchasing more products (cross-sell) or higher-value products (upsell).
- Elevated brand reputation. Products that consistently deliver an improved UX enhance the brand's reputation. Brands that are considered customer-focused, trustworthy and reliable can boost the company's market standing and competitive posture.
- Lower customer acquisition costs. Products that have a reputation for offering a superior UX stand out from competitor products. This can be an important unique selling point (USP) in crowded markets saturated with similar products. By prioritizing UX, businesses can attract more potential customers while reducing the cost of acquiring those customers.
- Lower support costs. User-friendly products allow users to easily work with the product the way it's intended to be used, so they are less likely to contact customer support with enquiries or complaints.
How to measure and evaluate the user experience
UX is a measurable concept that informs how businesses approach and optimize product design. It's important to evaluate and measure the impact of UX to ensure that the product is enhancing user lives in some way and empowering them to meet their goals.
Some effective ways to measure UX include:
- Conduct usability testing and gather user feedback. A usability test involves a small group of actual users who interact with a product to assess its usefulness, features, intuitiveness and accessibility. The product's designers and developers observe the behaviors of these users and ask them for detailed feedback via forms or surveys to identify issues and pinpoint improvement areas. They then implement these findings to improve the product design and, ultimately, deliver a more intuitive, user-centric product.
- Run a split test (A/B test). In an A/B test, different groups of users are shown different versions of the same product to determine which version performs better against a certain goal, such as more newsletter sign-ups, more button clicks, more in-app purchases and so on. The two versions might differ in terms of layout, theme, color scheme, navigation elements, headlines, etc. The tester tracks user behaviors with each version and measures the outcomes of each group to identify the winning product version to implement real-world deployment.
- Collect UX metrics for executives and business decision-makers. Executives and decision-makers can use many metrics to measure UX and gauge whether the product meets user expectations and needs. These metrics include the following:
- Page load time. How long a page takes to load -- a lower load time is desirable.
- Bounce rate. The percentage of users who leave the product after viewing only a single page -- a lower bounce rate is desirable.
- Time on task. The amount of time a user takes to complete a specific activity -- the lower this time, the easier the product is to use and navigate.
- Error rate. The number of bugs or crashes that negatively impact UX -- fewer errors means that users encountered fewer problems while interacting with the product.
- Session length. The amount of time users spend per visit -- a longer session along with a higher interaction rate suggests that users like the product and are willing to spend more time using it.
- Click-through rate (CTR). The percentage of users who click on a button or call-to-action link -- a higher CTR indicates greater user satisfaction and a willingness to keep engaging with the product.
In addition to gathering the above metrics, UX teams can implement end-user experience monitoring (EUEM) to monitor the product performance from a user's perspective. EUEM helps highlight performance issues that need to be resolved to improve UX.
- Use customer service metrics (NPS/CSAT/CES). Quantitative metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and customer satisfaction (CSAT) are typically used to measure CX. However, they can also be used to measure and optimize UX. For example, NPS can highlight how pleased a user is with the product and how likely they are to recommend it to others. The company can then determine what they need to do to improve UX and NPS to try to enhance the user's product (and brand) loyalty. Similarly, a CSAT score shows how satisfied a user is with their product experience. A low score indicates that there is room for improvement. Brands can also use customer effort score (CES) to measure how easily a customer is able to use the product. They can then determine what changes are required to improve the product's usability, accessibility or navigability.
- Determine actions from measured data points. It's important to analyze all the gathered data points. Deep analyses enable teams to identify improvement areas and take appropriate actions to resolve issues and enhance UX.
What does a UX designer do?
In general terms, a UX designer plays a central role in product design and is typically responsible for the user's overall product or service satisfaction. A UX designer can often approach the role as a customer advocate by looking for new and innovative ways to improve the customer's experience through the product or service using the following why, what and how considerations:
- Why. Addresses user motivations in selecting and using a product.
- What. Addresses the features and functionalities of the product.
- How. Addresses the accessibility and aesthetics of the product.
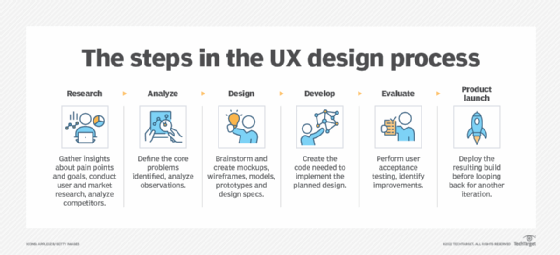
In more specific terms, UX designers perform a variety of design-related tasks, including the following:
- Understand the business, the brand and the user base, as well as the problem the product is intended to solve.
- Research users to identify behaviors, needs, goals and challenges through tools such as surveys, interviews, focus groups and user acceptance testing.
- Use that understanding and research to visualize how user workflows should operate; for example, what does a clear and concise software menu or interface look like?
- Design the product using mockups, wireframes, models or other prototypes to give other stakeholders and designers a clear picture of the product, including the UI.
- Test the product to validate user interactions and acceptance; make changes to the design as needed to optimize the design for user experience.
UX designers employ a wide range of technical and interpersonal skills to accomplish their tasks successfully. Technical skills can involve strong research, data organization and prototyping skills, as well as basic visual design and coding skills for software development environments. Interpersonal skills include strong communication, collaboration and critical thinking.
How to become a UX designer
There are no formal requirements to become a UX designer. Most engineers and developers start with a basic technical degree and gain experience in UX concepts through their day-to-day projects.
Professionals who seek a dedicated UX design role can:
- Take advantage of educational opportunities to study UX concepts and tools.
- Become involved with projects that use UX design skills and perhaps volunteer as a member of a product design/UX team.
- Develop a portfolio of successful UX designs.
- Apply for related UX design jobs inside or outside of the company.
UX roles can go by many names, including product designer, service designer, user interaction designer and UX designer. Smaller organizations typically provide a broader scope of UX roles and responsibilities, while larger organizations might expect greater levels of specialization from UX designers, such as research, analysis or engineering. Senior UX designers can often move into management roles, such as project manager or UX director.
How to align enterprise goals with UX strategy
Aligning UX strategy with broader enterprise goals enables organizations to enhance customer engagement and retention. Satisfied customers are more loyal and play a big role in boosting enterprise revenues, profits and growth. Alignment between UX and business goals also reduces support costs, which again, contributes to higher profits.
Some strategies to achieve alignment between UX strategy and enterprise goals include the following:
- Define measurable UX goals. Vague goals like "we want to increase our customer base" or "we want to increase revenues from Product X" are hard to understand and even harder to achieve. Instead, organizations should define clear UX goals like "decrease bounce rates by 10%" or "reduce page load time from 7 seconds to 3 seconds." It's also helpful to tie UX goals with business KPIs like NPS, CSAT or customer acquisition cost (CAC). Such alignment ensures that the UX team never loses sight of the company's broader goals and consistently works toward achieving them during the UX design process.
- Break down larger goals into smaller more specific tasks. A broad goal can be overwhelming for some teams because it often states the "what" but does not clarify the "how." One way to remedy this situation is to break down the goal into smaller action items. For example, goal of "reduce page load time from 7 seconds to 3 seconds" can be split into the following smaller goals:
- Resize images to reduce their file size.
- Implement lazy loading for images to improve initial load size.
- Reduce the size of HTML, CSS and JavaScript files.
- Reduce page size.
- Distribute content across multiple servers with a content delivery network (CDN).
- Minimize redirects.
- Limit third-party scripts.
- Change or upgrade hosting to boost server response time.
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration. Successful organizations don't just build customer-centric products, they are customer-centric. In a customer-centric organization, all departments collaborate closely to define UX goals and the various tactics that are most likely to achieve those goals. This means removing communication siloes between product, design, engineering, sales, marketing, support and any other department that is directly or indirectly involved in UX or CX design and optimization. Breaking down siloes ensures that everyone is always on the same page and working together to solve user problems and deliver useful, user-centric products.
- Build a feedback loop into the design process. User feedback can help firms to continually improve their products and ensure that those products align with their business goals. Real-world inputs received via surveys, interviews, usability testing, A/B testing and so forth, reflect the behavior of real users. Design teams can then analyze the information to bridge the gap between what users want and what the product actually delivers.
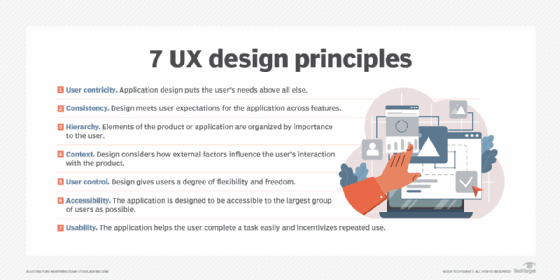
Common UX design mistakes
Some common UX design mistakes that limit digital product usability and might diminish UX include:
- Not putting the user at the center of all product decisions. Teams that don't put the user first might end up with products that fail to satisfy user needs. Conducting user surveys and gathering user feedback can help them to design products where the user is front and center.
- Not defining clear UX goals. Every part of the product design should be aimed at enhancing UX. This requires defining clear goals and metrics that inform design strategies and decisions and also enable UX teams to measure whether they are progressing appropriately.
- Making too many changes. Too many or too frequent design changes in an ad hoc manner can confuse users and diminish UX. When making changes, it's vital to consider the user's perspective and the expected benefits of the changes. It's also important to make a clear business case for the changes. If the benefits and business case are not clear, it's better to pause or abandon the redesign effort or to reduce the redesign scope.
- Not gathering user feedback. Many teams fail to gather user feedback prior to product launch, usually due to time constraints and tight schedules.
- Not testing the product regularly. Regular testing can reveal bugs and usability issues early during development. It's easier and less expensive to fix issues early in the design and development cycle. Testing pre-launch product iterations also ensures that the end product actually meets user needs and improves UX.
- Complicating the design. A simple, user-friendly design is usually better than a design that offers too many options and features. If a feature (button, link, text, etc.) is not absolutely necessary, it shouldn't be included.
- Not coordinating with other customer-facing teams. UX and CX are closely related, so the UX and design teams must collaborate with other customer-facing teams, such as marketing and support. Regular check-ins and clear communication among all teams will help ensure that they can coordinate their efforts to improve UX and build a customer-centric organization.
History of UX
User experience is basically the notion of how well people and machines interact. Thus, UX as a discipline can trace its roots back to the 19th-century industrial era when factories proliferated and required people to operate the factory production machines. The ways that production equipment and factory workflows brought efficiency to manufacturing are often considered the precursor to UX.
Eventually, traditional factory environments and workflows evolved to improve working conditions for people, bringing concepts of human factors, safety and ergonomics into the design of equipment and devices -- designing systems and workflows that better fit human capabilities and behaviors.
As computer technology emerged and evolved, the ideas of UX translated into early computer designs. These early innovations included the graphical user interface (GUI) and the mouse, physical and virtual mechanisms still standard today. The actual term user experience is thought to have originated in the 1990s when cognitive psychologist Donald Norman joined Apple with the title user experience architect. Norman's book, The Design of Everyday Things, is still standard reading for UX studies.
By the 1990s, the field of human-computer interaction emerged, blending fields of GUIs, cognitive sciences and human-centric design concepts to refine and expand what UX entails. As technology introduced devices such as PCs, tablets and smartphones, the role and importance of UX in technology continued to expand.
The future of UX and UX design
Enhancing UX and focusing on UX design continue to be high priorities for customer-centric organizations. In the coming years, it's likely that these businesses will continue to maintain this focus, but they will also explore newer ways to design and deliver memorable UX to their users and customers.
To do this consistently and cost-effectively, they will leverage advanced technologies like AI and machine learning (ML) to inform their UX design strategies. These technologies will enable UX teams to design hyper-personalized UX. AI will allow them to deliver tailored content to match the needs and expectations of individual users. AI tools will help them to seamlessly adapt product interfaces in response to user actions, thus ensuring natural and intuitive real-time user-product interactions.
AI features and AI agents are already being integrated into popular UX tools like Figma and Dovetail. As AI technology develops further, more tools will include AI capabilities that will help to streamline many time-consuming UX-related tasks, such as user research. This will enable UX designers and developers to save time and focus on more strategic tasks where their human skills can provide more value than AI, such as conducting qualitative research, building user maps and personas, and analyzing user feedback to inform design decisions.
Also, small and domain-specific LLMs will improve in the near future. These models will power AI-enabled UX products for specific domains and environments. For example, organizations in regulated industries like healthcare and finance will be able to use these products to enhance UX for their user base, while also maintaining compliance with applicable user privacy laws and regulations.
Recent research by the User Experience Professionals Association (UXPA) International, an organization that champions the advancement of UX through education, community, shared knowledge and collective action, suggests that many UX professionals are already using AI in their roles. According to the research report, in 2024, 47% of them said that they "found some value" by applying AI to their work. Many more (53%) expect to use AI in the coming years as they gain a better understanding of not only the appropriate uses of AI for enhancing UX, but also the potential pitfalls and weaknesses of AI that might lead to UX deterioration.
Apart from AI and ML, UX specialists will also embrace technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and the internet of things (IoT) to reshape how users interact with products and to enhance the experiences delivered by those products. They will also leverage the human-centered design thinking approach to develop innovative solutions that effectively address human problems and needs.
To effectively use these technologies, UX professionals should invest in continuous learning. They should also keep themselves updated on emerging developments in areas like human-centered ethics, data privacy, CX and even cognitive psychology. An understanding of the key concepts within these areas will enable UX specialists to create products that resonate with users and deliver memorable UX.






