Enterprise 5G: Guide to planning, architecture and benefits
An enterprise 5G deployment requires extensive planning. This guide helps you understand 5G use cases and deployment options as well as the latest advances in wireless technology.
5G, the latest generation of cellular technology, delivers faster speeds, lower latency, higher reliability and greater capacity for multiple devices than its 4G predecessor.
In the coming years, 5G will become a cornerstone of enterprise communications. To that end, it's essential that organizations thoroughly understand 5G's benefits and challenges now and begin evaluating how the technology will affect the way they do business.
This enterprise 5G guide explains how the cellular technology works, its architecture options, emerging use cases, how it compares to 4G and Wi-Fi 6, and more. Click on the links for details about key topics.
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of cellular communications technology. Initially released in 2017 by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) after years of development, the standard greatly increases the capacity and versatility of wireless connectivity.
5G's potential speed of 20 Gbps is a significant draw, but its low latency -- ultimately two milliseconds or less -- is even more attractive for enterprise applications, such as augmented reality, IoT, location awareness and branch connectivity. 5G is engineered to be more secure than its cellular predecessors, thanks to more comprehensive transport security algorithms and other safeguards.
How does 5G work?
5G uses a vast network of small cell base stations located on light poles and building roofs, among other locations, to transmit signals via the millimeter wave (30 GHz to 300 GHz) spectrum. Due to its shorter wavelength, millimeter wave (mmWave) can only travel short distances and is susceptible to weather and obstacles, such as buildings, walls, coated windows and foliage. It works best in densely populated areas or open venues, such as in factories or stadiums, which can be blanketed with low-power small cell stations to avoid line-of-sight limitations.
In addition to small cells, 5G networks can be connected and distributed via macrocells and femtocells. Macrocells transmit low-frequency radio signals for miles by using large towers and antennas, while femtocells are book-size, private and designed to improve coverage in buildings with furnishings and walls that could obstruct transmission of high-frequency mmWave signals.
Enterprises in areas that aren't served by mmWave can gain access to 5G services through the low-frequency bands (low-band and midband). The tradeoff is support for fewer devices at potentially lower speeds and greater latency. For now, many organizations concentrate their enterprise 5G efforts in dense areas or open venues to take optimal advantage of 5G's capabilities.
Two other 5G options are 5G standalone and non-standalone 5G. Both are valid ways to build 5G networks and provide roadmaps that enterprises can follow when migrating to the 5G standard.
The 3GPP continuously reviews 5G standards to improve the technology, so enterprises need to pay close attention to its work. This new generation of cellular technology has its own lingo, so make sure to brush up on the 5G terms you need to know.
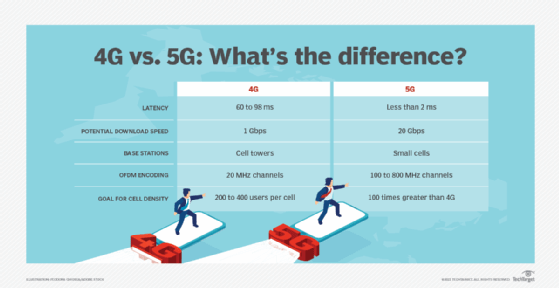
The differences between 5G and 4G
5G ushers in dozens of new features and capabilities. 4G cellular service has been instrumental in powering the mobile workforce, but 5G will be better known for improving enterprise operations and making possible the delivery of a new constellation of applications and services.
4G LTE is limited by its spectrum, which only reaches as high as 6 GHz. 5G's millimeter wave operates between 30 GHz and 300 GHz, which means the wider channels can transmit more data. 4G's use of lower-frequency bands impedes latency, speed and capacity, even though its signals can travel farther between radios or tall cell towers. Compared to 4G networks, some 5G networks might be able to support from 10 to 100 times more users and devices per square kilometer.
Another key advancement is 5G New Radio (5G NR), which will eventually replace the long-term evolution (LTE) standard that anchored 4G and previous cellular generations. 5G NR adds beamforming and other techniques that boost 5G's capacity, throughput and range.
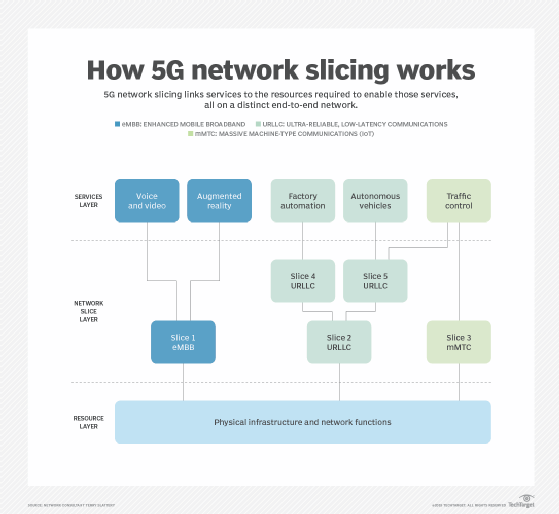
5G also supports network slicing. The technique -- unavailable in 4G -- lets enterprises create multiple virtual networks on top of the existing physical network, allowing users to safely and cost-effectively share 5G connectivity.
These new capabilities don't come without cost: 5G requires organizations to invest in new core infrastructure that includes base stations and antennas, as well as onboard radios for devices and sensors. 5G's shorter travel distances also demand more infrastructure -- typically, more small cell stations, about the size of a pizza box -- to get signals from one point to another without interference.
Business benefits of enterprise 5G
5G offers organizations a flexible and secure connectivity option. To that end, the standard is expected to benefit businesses in several key ways, including the following:
- Automation. Increased speed and lower latency make cellular technology a viable option to bring automation to factories, offices and other facilities.
- Flexible alternatives to dedicated links. 5G services provide less costly and more flexible alternatives to MPLS and other dedicated lines now used for latency-sensitive applications.
- More users and devices. Thanks to its increased capacity, 5G supports more users and devices connected in the same physical area without affecting availability.
- Power savings. 5G can cut the power consumed by devices by up to 90%, giving some IoT devices battery lives that can reach 10 years and making IoT a compelling 5G use case.
- Augmented security. Additional security features, including key management services, make 5G a more trusted option than 4G for IoT, branch and other enterprise traffic.
Providers, manufacturers and the U.S. government are working to make 5G a secure technology. Newer security tactics, such as zero trust, take advantage of 5G's programmability to ensure only validated users get access. What's more, 5G uses 256-bit encryption, doubling the 128-bit standard used in 4G.

5G architecture and features
5G architecture supports machine-to-machine communication and other advanced applications better than its predecessors because it can transmit large data streams with low latency and supports a much greater number of connected devices.
Three 5G service categories -- eMBB, URLLC and mMTC -- provide many of these advantages. Enhanced mobile broadband enables peak data rates of 10 Gbps to 20 Gbps and is designed to keep data rates steady for large numbers of users as they move through different environments. High-definition video streaming and virtual reality are common uses of eMBB. Ultra-reliable, low-latency communications support autonomous vehicles and other applications that demand immediate response and high network availability. Massive machine-type communications can connect up to 1 million low-power devices -- among them IoT sensors.
5G's programmability makes it easier to connect with more data sources, including resources stored in the cloud. Finally, 5G is backward compatible with other wireless technologies, including 3G, 4G and Wi-Fi, enabling enterprises to aggregate the standard with other communications systems.
Private 5G network architecture
5G networks can be either public or private. To better secure their operations, many large enterprises build private 5G networks as an alternative to procuring network capacity from 5G providers. While private networks can be more costly, they enable enterprises to customize their 5G buildouts to meet application requirements, more finely manage infrastructure and better secure data on premises.
When enterprises consider building private 5G networks, they should ask themselves some key questions:
- Do we need ubiquitous coverage for devices or a new type of wireless backhaul?
- Despite 5G's ability to support higher speeds, are we willing to trade larger cells and lower frequencies for speeds that might not meet expectations?
- Will most of our traffic stay on our enterprise network or head out to the internet?
- What device types, capabilities and density will be involved?
Typically, a private 5G network design includes small cell hardware and upstream connectivity to the LAN. Private 5G networks are not one-size-fits-all, however.
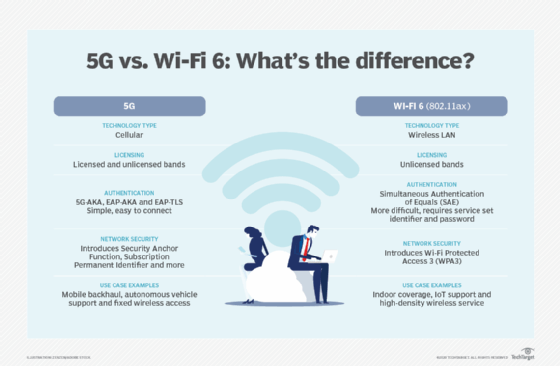
5G and Wi-Fi 6
The intersection of 5G and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) presents some intriguing options for enterprises. For instance, Wi-Fi 6 might be better suited for congested spaces that have obstacles and little line of sight, while 5G works well in open spaces that require high speeds and low latency. Seamless handoffs between Wi-Fi and 5G networks mean the two technologies can be used together to support a growing mobile workforce.
5G and Wi-Fi 6 both have powerful signal modulation, authentication and security features. In addition, each can help companies reduce their power consumption, either by design or through power-saving functions that can reduce the load on access points.
Typically, one main difference between cellular and Wi-Fi technology is their respective operation in licensed versus unlicensed frequency bands. 4G primarily operated only in licensed bands, but 5G operates in both. As a result, using 5G in an unlicensed band could create interference with Wi-Fi. Businesses should carefully map out their coverage.
Also, Wi-Fi alone can't transfer sessions between access points. This limitation comes into play if a company wants to use Wi-Fi to track the movement of products. By contrast, 5G can handle those transfers with ease.
5G, IoT and edge computing
IoT and edge computing have distinct demands for high speed and low latency. In many cases, sensors are sending mission-critical information to edge or cloud-based devices to be aggregated, analyzed and acted upon. Examples are self-driving vehicles, assembly line equipment and city surveillance cameras that constantly send and receive data.
5G's low-power requirements extend battery life, making it a perfect match for IoT networks. This capability enables enterprises to be innovative in their architecture designs because devices won't have to be tied to a power source.
One option is multi-access edge computing (MEC), a type of edge computing that reduces reliance on centralized cloud servers by enabling local data processing on mobile and cellular base stations or other edge nodes. 5G and MEC are closely intertwined. For example, MEC enhances 5G's network slicing capabilities and can make radio access networks (RANs) more responsive, while 5G's low latency and high bandwidth make MEC more effective in real-time applications.
Experts recommend enterprises use an application's requirements to select the best wireless connectivity option -- understanding that 5G might be overkill in some cases.
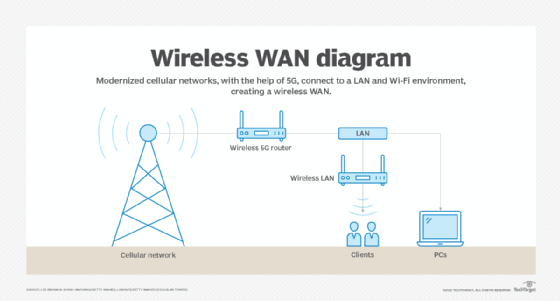
5G and SD-WAN
Organizations can pair 5G and SD-WAN to manage wired and wireless connections to remote offices as well as home offices. The combination redefines WAN deployment strategies and offers significant benefits when organizations determine how best to connect distributed workforces.
SD-WAN could also be useful in helping sites toggle between 4G and 5G connections, automatically selecting the appropriate link for the demands of the application and traffic conditions. Some industries, including retail, could employ SD-WAN to provision 5G as a primary option for pop-up locations, with secondary links via MPLS and broadband.
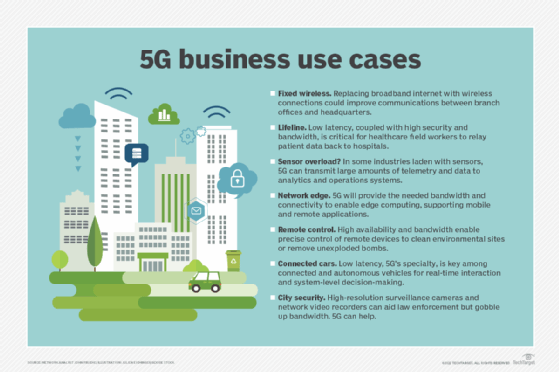
Enterprise 5G use cases
Use cases for enterprise 5G are expanding rapidly as businesses evaluate where the cellular technology could improve their operations. Here are six of the most common ones:
- Retail. 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) can replace broadband connections, enabling faster connectivity and more flexible management. By combining it with SD-WAN, companies could provision and manage hundreds of locations.
- Healthcare. The healthcare sector is using technology to make greater use of limited resources, including surgical staff. Initial 5G deployments have been mostly geared to improving connectivity for existing mobile devices and patient engagement tools, such as portals, heart monitors and other wearables. However, 5G's low latency could soon enable surgeons to operate remotely via robotic applications. Hospitals also plan to use 5G to transmit critical diagnostic data and images that can be shared among emergency departments, ambulances and field teams to provide faster and more comprehensive care.
- Sports venues. Sports organizations -- among them the National Football League, National Hockey League, National Basketball Association, Major League Baseball and NASCAR -- have deployed 5G to enrich the fan experience through real-time access to video highlights, such as instant replay and more immersive applications.
- Manufacturing. Companies have started to use 5G to speed connectivity from IoT sensors on machines to the cloud for more complex real-time analytics. 5G's speed and low latency mean information extracted from the analytics can be put to use for real-time decision-making that could improve operations on the factory floor.
- Smart cities and autonomous vehicles. Again, the low latency, capacity and throughput of 5G make it a prime candidate for innovation in city management and transportation. Streetlights, signals and other public safety applications can benefit from 5G to change patterns based on real-time events or AI models. Autonomous vehicles, which use AI, machine learning and analytics to process information in real time, can communicate over 5G to automatically adjust speeds in response to road conditions or increased traffic.
- Utilities. Electricity and water companies are among utilities increasingly turning to private 5G to manage and secure their vulnerable infrastructures and improve worker safety. Private 5G lets utilities extend their networks to regions with poor connectivity and enables automated metering, monitoring and remote control, even as it helps improve communication and coordination of field crews.
5G enterprise challenges
For all of 5G's benefits, enterprises should be mindful of its challenges as they consider the future of their wireless and wired infrastructure.
Network security concerns
5G can simultaneously support more connected users and devices than previous cellular technology, but that also means companies have to assess and monitor many more vectors of exposure. 5G also requires far more extensive infrastructure that must be protected from threats. Experts warn that hackers could use a 5G network to exploit existing vulnerabilities or develop new modes of attack. Finally, the 5G standard itself does not support application-level end-to-end encryption, and that gap early in the connection process can leave enterprises open to attack.
Staffing and training
As with any evolving technology, finding qualified IT staff to integrate 5G will be an ongoing challenge. IT staff need specific skills to oversee a network that seamlessly shifts between wired and wireless connectivity. They must also be able to troubleshoot myriad technical issues as well as manage 5G-enabled network components that range from simple IoT sensors to complicated machinery.
Cost
5G requires a hefty investment to reap its full reward. Legacy network components must be swapped out with 5G-compatible ones. Companies also have to buy new wireless gear to ensure adequate coverage.
Signal interference
Perhaps more than any other wireless technology, 5G requires network teams to pay close attention to site surveys. The easiest use cases are venues with open spaces all under one roof. A site survey can reveal the extent of signal penetration challenges -- specially coated windows, walls, etc. -- and radio dead spots, as well as how much effort would be needed to mitigate them either with a facility redesign or additional equipment, such as antennas.
Although enterprises might face some indoor coverage challenges with 5G, small cell technology can help.
Availability of 5G
Companies that want to take full advantage of 5G enterprise-wide must first determine whether the technology is fully available at all their locations.
Service providers have largely succeeded in making 5G available in densely populated areas. Their focus is now shifting to deploying 5G capabilities to more rural and remote areas, and they are increasingly using FWA to extend broadband internet to those areas. However, service levels -- among them speed and latency -- might not match what enterprise users get in larger cities. That's because carriers targeting rural areas might rely on lower-capacity options that range from employing lower-frequency bands to layering 5G on top of existing LTE backbones to extend 5G services. Building the infrastructure necessary to support high-speed mmWave transmission in rural areas still poses a financial and logistical challenge.
How AI is changing 5G
AI has touched nearly every technology sector, and 5G is no exception. AI and 5G impacts go both ways. Users -- both consumers and enterprises -- expect top performance from their AI apps and platforms. At the same time, carriers and enterprises employ AI to make their 5G networks more intelligent and flexible.
For example, private 5G underpins AI applications that use edge-to-cloud video analytics to spot manufacturing defects, or provide predictive maintenance and coordination of robots in warehouses. Providers are building AI models that can analyze network traffic to identify trouble spots.
They're also starting to use AI to design more energy-efficient and reliable RANs. These new AI-RANs enable AI to run directly on RAN infrastructure and, in some cases, combine the two functions in a software-defined approach that runs in the cloud. The result, proponents say, is RANs that are more secure, reliable and efficient in their use of network resources, and well suited to edge computing.
AI-RANs are an example of Open RAN (ORAN), a mobile architecture designed to standardize proprietary RANs from different vendors so their components are more open and interoperable, which could drive down costs. Major wireless carriers have begun adopting ORAN. The process of standardizing the interfaces between components is overseen by the O-RAN Alliance.
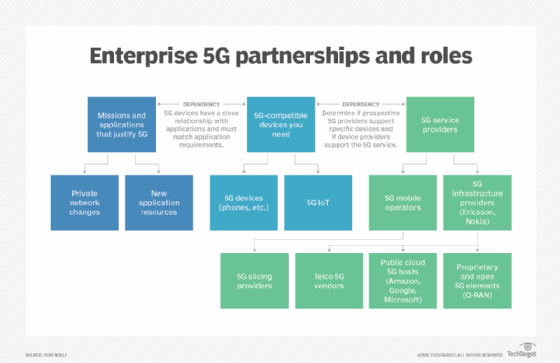
How to find partners and buy 5G
5G service is only as good as the devices and applications using it, so organizations should chart a roadmap for when enterprise equipment and applications will be available to support 5G. From that, they can create a timeline for procuring 5G services, then carefully examine 5G infrastructure companies to find one that fits their needs, especially if they're planning a private 5G network.
Businesses have to decide whether to buy, lease or build a 5G network. With those three options, enterprises could buy public 5G services from a mobile operator, lease a 5G network slice or build a private 5G network.
Enterprises that want to build their own private 5G network should partner with an integrator, vendor or service provider to help with some of the more nuanced aspects of 5G. For example, 5G can significantly increase network traffic, so organizations must assess if other parts of the network -- such as the VPN -- can handle the load.
Enterprises that choose to build their own 5G networks should consider the following four factors:
- Spectrum for the radio network.
- 5G infrastructure to provide the required features and interfaces.
- Small cells or microcells to transmit and receive.
- Interconnected facilities to link the private 5G network to the public mobile network if required.
The future of enterprise 5G
Enterprise 5G is all about innovation and applications. What comes next depends on how effectively enterprises take advantage of 5G's speed, low latency and capacity to push AI, machine learning, real-time analytics and other advancements deeper into their operations.
New iterations of 5G are arriving on the scene. The first 5G-Advanced standard (3GPP Release 18) came out in June 2024, with initial deployments soon following. Broad rollout of networks and devices is ramping up now and should continue through 2026.
Among other benefits, this release was designed to make 5G networks more intelligent, adaptable and energy-efficient, largely through the deep integration of AI and machine learning. It also added features for the precise timing needed for time-sensitive networking, which transforms Ethernet -- both wired and wireless -- into a deterministic, real-time network. This gives 5G the guaranteed low latency and reliability required for advanced applications, such as industrial automation and autonomous vehicles. 5G-Advanced also supports extended reality communications, which build on existing augmented and virtual reality applications.
A second 5G-Advanced release, 19, was expected to be solidified late in 2025 and build on its predecessor with additional support for network intelligence, low latency and time-sensitive applications. Read more about what might happen with 5G in the coming years.
Meanwhile, the 3GPP is working on 6G technology, expected to launch commercially in 2030 and potentially support data rates of up to 1 Tbps. 6G will build on 5G's capabilities for applications, such as imaging, presence technology and location awareness. 6G technology will be able to selectively use different frequencies to measure electromagnetic absorption rates and adjust frequencies accordingly.
Chuck Moozakis is editor at large of the Infrastructure group at TechTarget.
David Essex is an industry editor who creates in-depth content on enterprise applications, emerging technology and market trends for several Informa TechTarget websites.







