remote sensing
Remote sensing is the use of various technologies to make observations and measurements at a target that is usually at a distance or scale beyond those observable to the naked eye. Remote sensing is used in fields such as land surveying, geography, and other earth sciences as well as in the internet of things (IoT). Remote sensing is useful for collecting data in dangerous or inhospitable areas such as measuring the changes in the size of glaciers in the Arctic.
Remote sensing technologies include LiDAR, RADAR, infrared radiation (IR), thermal, seismic, sonar, electric field sensing and GPS. Depending on what is being detected, these various sensors might be mounted to a satellite, airplane, boat, submarine, UAV drone or from another convenient observation point such as a building top.
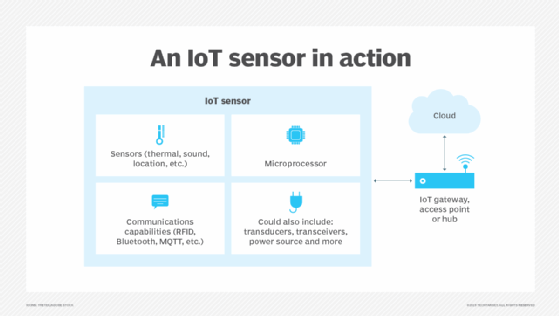
Remote sensing is one of the basic enabling technologies for IoT, in which almost any imaginable entity can be equipped with unique identifiers and the ability to transfer data over a network autonomously. Some applications of remote sensing may require continuous or frequent observation, such as when the target requires the measurement of small changes over time. IoT is commonly used in these instances, where IoT sensors deliver data.
Examples of remote sensing
The data gathered by remote sensing is used for a large and growing number of applications including geology, oceanography, hydrology, ecology or meteorology.
IoT sensors, for example, can be used to detect valve pressure changes in a pipe. External sensors can be set outside of the pipe to provide additional data. IoT remote sensing can also be used areas such as studying trends pertaining to waterfowl and rainfall.
Pertaining to earth sciences, remote sensing can be used in instances such as:
- Cartography.
- Resource exploration.
- Atmospheric chemical measurements.
- Healthcare monitoring.
- Surveillance.
- GPS tracking.
- Mapping the ocean floor via sonar.
- Tracking the movement of natural disasters.
- Monitoring land use/development.
Types of remote sensing
Remote sensing can be conducted through passive or active sensing. In passive sensor technologies, an existing observable phenomenon is measured. For example, sunlight can be captured by a sensor such as a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera mounted on a satellite. In active sensing, an internal sensor emits a signal to collect data. The sensor device will typically include a transmitter that sends out a signal, for example, a particular light wavelength or electrons to be bounced off the target. The sensor will then gather data upon their reflection. Raider and LiDAR are examples of this.
Once data is received, in either use of remote sensing, the data is processed to find the most pertinent information. Data will go through being reconstructed and unprocessed to being cut to focus on smaller and more relevant datasets. Three levels normally separate data. The first is when the data is unstructured, featuring artifacts, and sometimes duplicate information. The second level of data is usable for an organization and is generally cut down, and more focused on a specific target. The third level of data is cut down on more and requires less overhead in terms of additional data. This level is generally applied more frequently.






