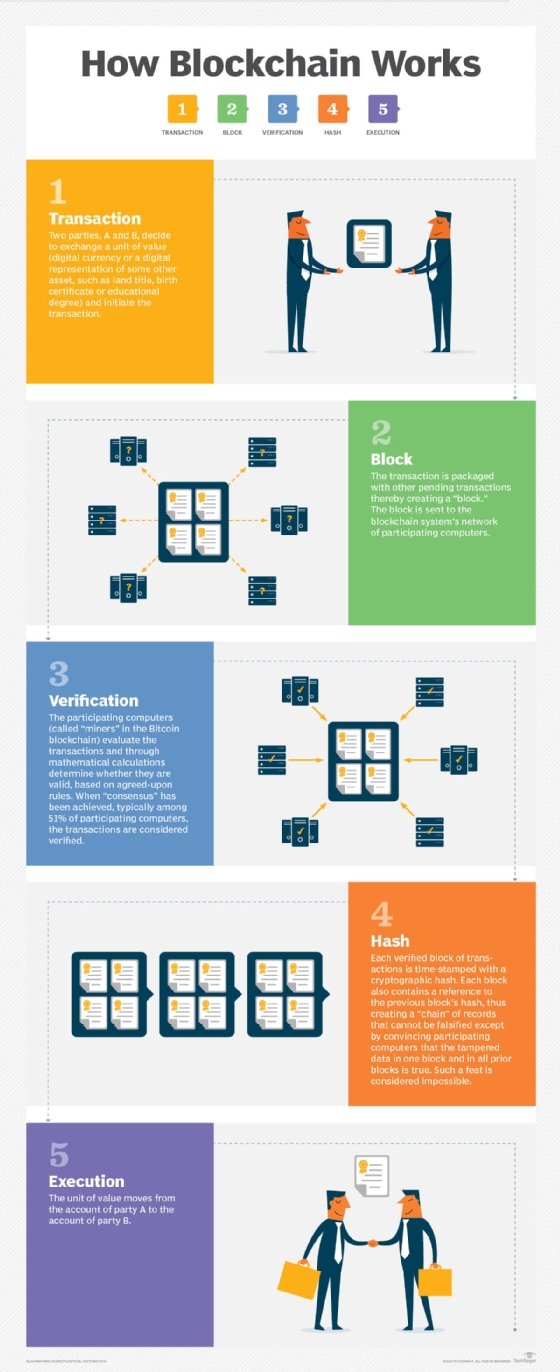
decentralized application (DApp)
What is a DApp?
A decentralized application (DApp) is a type of distributed, open source software application that runs on a peer-to-peer (P2P) blockchain network rather than on a single computer. DApps are similar to other software applications that are supported on a website or mobile device, but they're P2P supported. DApps are considered part of Web3, the present evolution of the World Wide Web.
The decentralized nature of DApps means that, once a developer has released a DApp's codebase, others can build on top of it. The app is not controlled by a single authority. DApp development creates a variety of applications, including those for decentralized finance, web browsing, gaming and social media.
DApps are built on a decentralized network supported by a blockchain distributed ledger. The use of blockchain means a DApp can process data through distributed networks and execute transactions. DApps are often built using the Ethereum platform.
Distributed ledger technologies, such as the Ethereum blockchain, have helped popularize DApps. The major advantages of DApps are that they're always accessible and have no single point of failure.
How DApps work
Decentralized apps have the following three key attributes:
- Open source. This requires the codebase to be available to all users for evaluation, and changes require a consensus of the majority of users.
- Decentralized storage. Data is stored on decentralized blocks.
- Cryptographic support. The decentralized blocks of data are validated and proven true.
DApps are stored and executed on a blockchain system, commonly using the Ethereum network. Apps are validated with cryptographic tokens, which are needed for application access.
DApps are similar to conventional apps in the front-end code they use to render a webpage. But their back-end code is different; it runs on a decentralized peer network. This removes DApps from the control of a single authority.
While centralized servers and databases support a traditional application, a smart contract stored on a blockchain supports a DApp. Ethereum is the most popular blockchain for running smart contracts, which enforce rules defined in the code and mediate transactions. A smart contract consists of the back end only and is often just a small part of the whole DApp. Therefore, creating a decentralized app on a smart contract system requires combining several smart contracts and using third-party systems for the front end.
The blockchain that a smart contract runs on is a ledger of data records stored in blocks as opposed to a central location. The blocks of data remain dispersed across distributed locations; all the data blocks are linked and ruled by cryptographic validation in the ecosystem.
Not all DApps work on standard web browsers; some may work only on websites with customized code to open that specific application.
Benefits of decentralized applications
Decentralized applications provide several benefits, including the following:
- Fault tolerance. If a single network is working, a decentralized platform can remain available, though performance may be severely hampered. Unable to target a centralized network, a hacker would struggle to attack enough nodes to take down a DApp.
- Data integrity. Data stored on a blockchain is immutable and secure because blockchain consensus algorithms ensure data stored in the blockchain is resistant to change.
- Flexible platform. The flexibility of Ethereum blockchain accommodates quick development of DApps for different industries.
- User privacy. Users need not submit personal information to DApps to use app-specific functionality.
Drawbacks of decentralized applications
Decentralized applications also have the following weaknesses:
- Maintenance. Fixes require the use of a consensus mechanism to ensure agreement among all peers in the blockchain-based network, which complicates DApp maintenance, debugging and updates.
- Scale. Decentralized networks are harder to scale than centralized ones.
- Network congestion. If a DApp uses too many resources, it can bog down the whole network.
- User experience. Developers can have difficulty creating a user-friendly experience for DApp end users. With a DApp, users need a public and private key to log in versus a username and password for a traditional app.
DApp scams
The decentralized nature of DApps makes it difficult to track scams and hold perpetrators accountable. Users must exercise caution to avoid dApp scams such as the following:
- Ponzi schemes and fake initial coin offerings, which are the cryptocurrency equivalent of an initial public offering.
- Phishing attacks that trick users into revealing sensitive financial information.
- Malware and data theft.
- Exit scams where DApps build trust with a community and solicit fundraising before abandoning a project with users' investments and data.
- Pump and dump schemes in which traders create excitement and hype around a DApp to drive the price to an unsustainable price before selling their shares and crashing the stock.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities that can enable attackers to drain funds from a contract.
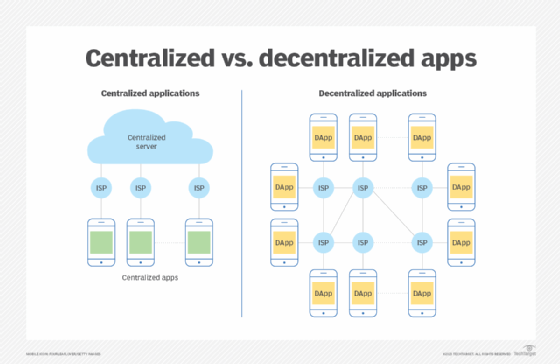
Comparing centralized vs. decentralized apps
Centralized apps operate on servers controlled by a single entity, meaning the application software is owned and controlled by its owner or company. In contrast, DApps use blockchain and P2P networks that work without a central authority.
With centralized apps, users have separate versions of the app and communicate with one another through a company's server. With DApps, users communicate directly with one another. This communication includes financial transactions executed without intermediaries and cross-chain bridge communication.
Examples and use cases of DApps
Thousands of DApps have been developed and are in use. The following are three examples:
- Chainlink is middleware that provides tamper-proof inputs, outputs and computations for Oracle networks. Google uses it for its BigQuery platform-as-a-service data warehouse.
- TraceDonate is a service that connects charities and donors to beneficiaries with the goal of building trust that donations reach those in need. Funds are kept in a digital wallet and let the donor track how the donation is spent.
- Minds is a DApp-based social media platform that runs on open source code and encrypts all personal data that users send.
Here are some common ways DApps is used:
- Financial services. DApps facilitate crypto and other P2P financial transactions, enabling secure, efficient cross-border payments and decentralized lending.
- Gaming. Blockchain-based games let players trade in-game assets as non-fungible tokens, which are secured on the blockchain, providing verifiable ownership and scarcity.
- Social networks. Decentralized social media platforms empower users by giving them control over their data and eliminating the risk of censorship. DApp platforms, like Hooked, let users interact and share content without any central authority.
- Supply chain management. DApps can improve supply chain management by providing transparency and traceability. Blockchain-based approaches enable real-time tracking of goods, preventing fraud and ensuring the authenticity of products.
- Music. DApp services, such as Audius. rewards users with social tokens for uploading original music, interacting with other musicians and sharing songs online. Users can buy songs with their social tokens, which also double as governance tokens that let them vote on proposed changes to Audius.
- Identity verification. Blockchain-based DApps securely store and verify identity information, eliminating the need for centralized databases. They support voter registration, passport applications and other identity-dependent processes.
- Healthcare. DApps also securely store and share patient records, facilitating interoperability among healthcare providers and enabling secure collaboration.
DApps are one of the most common ways blockchain technology is being used. Learn about the top nine blockchain platforms.







