
Getty Images/Tetra images RF
What are Top HIPAA Compliance Concerns, Obstacles?
Maintaining HIPAA compliance and the exposure of patient data following a breach and are among the top challenges for HealthITSecurity.com readers.
Maintaining HIPAA compliance should always be a key area for leaders in the healthcare industry, but as technology continues to evolve, there are numerous factors coming into play that could affect how organizations keep patient data secure.
With the next round of OCR HIPAA audits set to take place later this year, covered entities are already working to ensure that they are staying aligned with all federal regulations, as well as any state and local ones.
But what type of obstacles are standing in provider's’ way? Are there certain difficulties when it comes to HIPAA compliance?
We’ve previously discussed the legal perspective on HIPAA regulations, and various experts in the field have claimed that “it’s not a matter of if, but a matter of when” a data breach will take place. Recent OCR HIPAA settlements not only show that size is not a factor when it comes to enforcement, but that organizations need to be mindful of everything from physical safeguards to conducting regular risk assessments.
Technical advancements have also proven to be potentially beneficial to covered entities. Whether an organization is looking to implement secure messaging options or potentially invest in cloud storage, privacy and security issues cannot be overlooked.
To better understand how healthcare organizations approach data security and HIPAA regulations, HealthITSecurity.com quizzed our readers about their current approach to HIPAA compliance, using mobile technology and secure messaging, and their top pain points.
A comprehensive approach to HIPAA compliance
External data security threats, employee training, and evolving technology were all top concerns cited by respondents when it comes difficulties in HIPAA compliance. Thirty-two percent of those surveyed said that external threats to data security was the top issue, while 28 percent listed employee training and evolving technology.
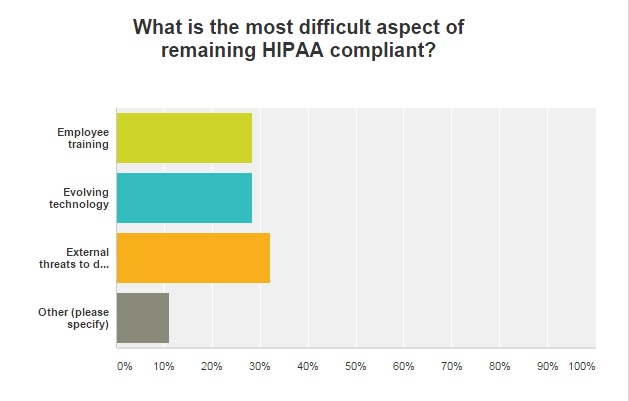
Employee negligence, the evolving regulatory environment, and the evolving threat landscape were also listed as top concerns when it comes to HIPAA compliance.
When it comes to the OCR HIPAA audits, 43 percent of respondents said that technical safeguards were the most difficult aspect. Administrative safeguards were a close second, cited by 39 percent of those surveyed.
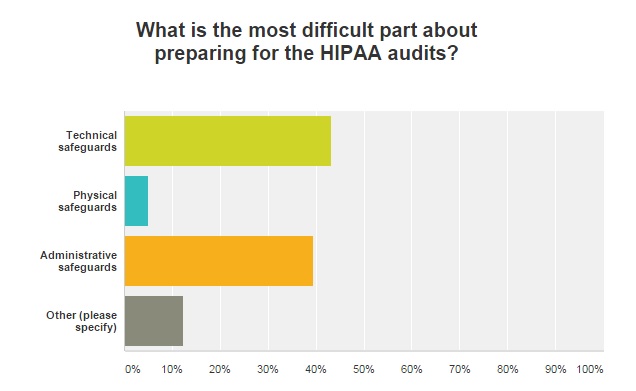
Just 5 percent of respondents said that physical safeguards were the most difficult part of preparing for HIPAA audits.
Additionally, several respondents maintained that keeping the necessary documentation prepared for potential HIPAA audits was a top issue. Having a clear understanding of the business associate or vendor’s responsibility in case of a breach was also cited in the survey as a difficulty.
Majority push for data encryption, mobile device management
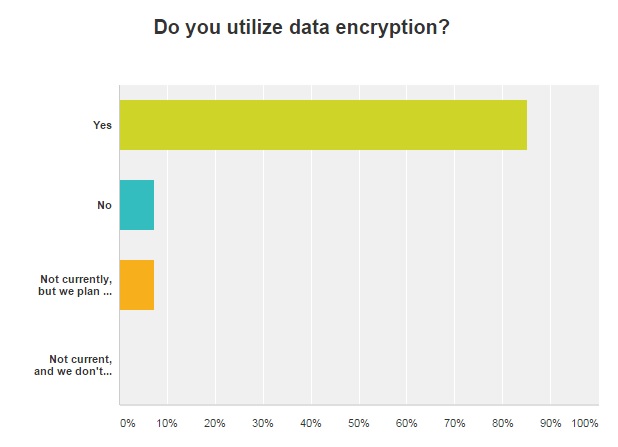
With the previously mentioned technological push in the healthcare IT environment, it should come as no surprise that the majority of survey respondents said they utilize data encryption.
Eighty-five percent stated that they use data encryption, while just 7 percent said they do not. Additionally, 7 percent of respondents said that while they do not currently utilize data encryption options, they plan to do so soon.
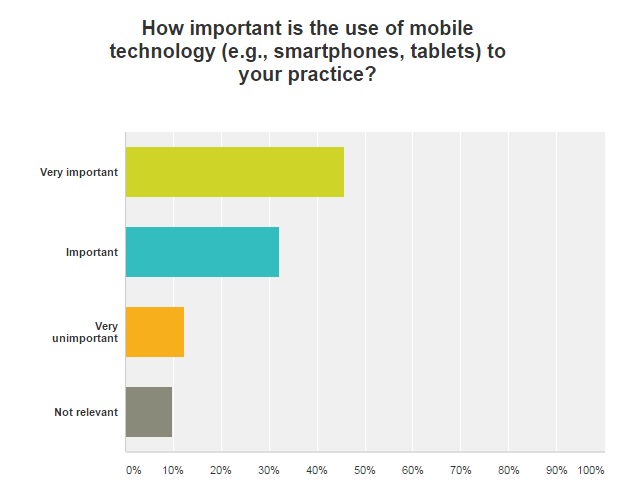
Mobile technology is also becoming a more prominent feature for healthcare organizations. For example, 45 percent of those surveyed said that it was “very important” to their practice. Approximately one-third of respondents said that mobile device usage was “important,” while 12 percent called it “very unimportant.”
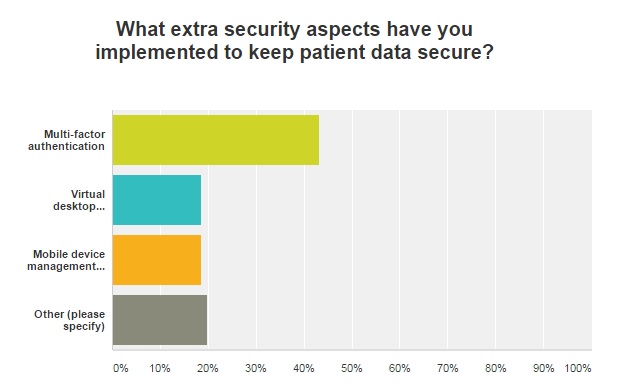
In terms of mobile options, mobile device management was also listed by some respondents as an extra security measure implemented to ensure patient data security.
Specifically, 18 percent said MDM was an extra security aspect, while 43 percent listed multi-factor authentication as additional measures to secure patient data. Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), anti-virus softare, and high-end firewall with DLP technology were also cited as extra security measures
Learning from large scale healthcare data breaches
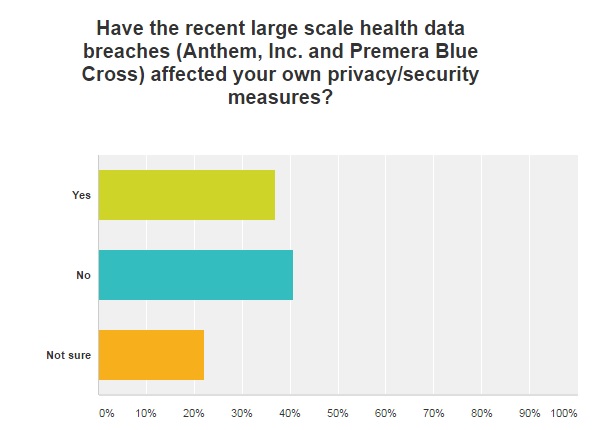
Last year was filled with large healthcare data breaches, such as Anthem, Premera, and Excellus. With the top three healthcare data breaches alone combining to potentially affect nearly 100 million individuals, covered entities cannot afford to ignore these incidents.
However, 40 percent of survey respondents said that the recent large scale health data breaches did not affect their own privacy or security measures. Thirty-seven percent of those surveyed said the data breaches did affect their own approach, and 22 percent said that they were not sure.
In terms of data breaches in general though, the exposure of patient data was a top concern for nearly all survey respondents - 69 percent. Potential federal fines and reassuring patients that changes were being made were also listed as key concerns.
Outside hackers, the loss of patient trust, and being able to immediately notify patients of a potential incident were also top issues cited by respondents.
Finding the right balance between innovation and security
Overall, healthcare organizations need to ensure that even as they implement new technologies - such as secure messaging and cloud storage - that they keep privacy and security issues a top priority.
HIPAA regulations are not going to disappear anytime soon, and neither will outsider threats to patient data. Instead, the threats will only likely continue to evolve and become more sophisticated. Whether it comes in the form of a phishing scam or just a third-party hacking into a system, covered entities must deploy comprehensive security plans.
Regular risk assessments and employee training will also be beneficial. Neither small nor large facilities are exempt from federal regulation, and as such, need to implement safeguards that apply to their daily operations.
The healthcare industry is seemingly on the right track in prioritizing privacy and security, even as technical options become more intricate and the healthcare ecosystem more data-centric.




